Table of Contents
Introduction to Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure that involves the extraction and analysis of amniotic fluid from the womb, has revolutionised prenatal diagnostics and genetic testing. This intricate process allows healthcare professionals to gain valuable insights into the health and genetic makeup of the developing feotus, aiding in the early detection of various genetic disorders and developmental anomalies. While offering a window into the foetal world, amniocentesis also raises ethical and societal questions, as demonstrated by its banning for sex determination in India due to the alarming rise of female foeticide.
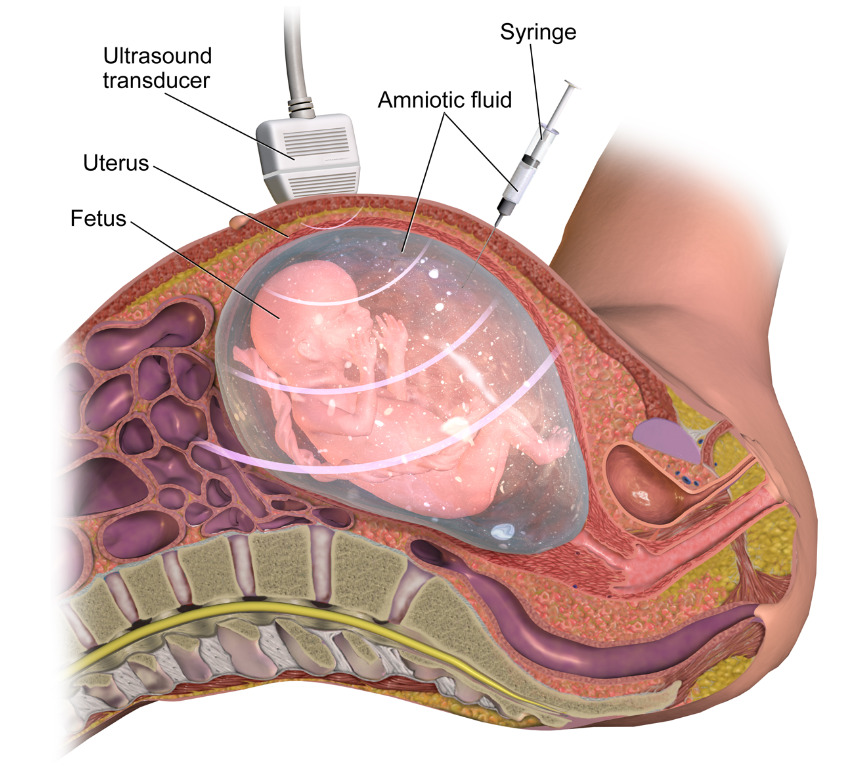
Procedure
Amniocentesis, derived from the Latin words “amnion” (referring to the protective membrane surrounding the fetus) and “centesis” (meaning puncture to remove fluid), is a delicate procedure performed during the second trimester of pregnancy, usually between the 14th and 18th weeks of gestation. It involves the skilled extraction of amniotic fluid, the nourishing liquid that envelops the developing foetus, through a thin needle inserted into the mother’s abdominal wall and into the amniotic cavity within the uterus. The procedure is guided by ultrasound imaging to ensure accurate placement of the needle, reducing the risk of harm to the fetus.
Genetic information
The amniotic fluid collected during amniocentesis holds a treasure of genetic information. Foetal cells suspended within the fluid, along with dissolved substances, provide crucial insights into the health of the foetus. One of the primary applications of amniocentesis is the detection of genetic disorders such as Down syndrome (DS), hemophilia, Tay-Sachs disease, sickle cell disease, and certain muscular dystrophies. Neural tube defects, severe birth defects of the foetal brain and/or spine, such as spina bifida and anencephaly can also be detected. By analysing the foetal cells, healthcare professionals can identify abnormal chromosome numbers or structural variations, offering expectant parents valuable information about their child’s health even before birth.
Developmental insights
Amniocentesis not only provides glimpses into the genetic realm but also offers insights into the development of the fetal nervous system. Elevated levels of specific substances like alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and acetylcholinesterase can indicate improper nervous system development, potentially leading to conditions such as spina bifida or anencephaly. Such insights allow for early interventions and tailored medical care plans, improving the quality of life for affected individuals.
Challenges
Despite its undeniable medical benefits, amniocentesis is not without its challenges and controversies. One major concern is the risk of miscarriage following the procedure. While advancements in medical techniques and technology have significantly reduced this risk, it still hovers around 0.5%, prompting healthcare providers to offer the procedure only to individuals at a higher risk of genetic defects.
Ban with social implications
The banning of amniocentesis for sex determination in India highlights the intersection of medical advancements, ethics, and societal norms. The practice of aborting female foetuses due to a cultural preference for male offspring, known as female foeticide, led to the prohibition of using amniocentesis solely to determine the sex of the foetus. This decision aimed to counter the alarming decline in the female-to-male ratio and the resulting gender imbalance.
As medical science continues to evolve, amniocentesis remains a critical tool in prenatal diagnostics and genetic testing. Balancing the benefits of early detection and intervention with ethical considerations is an ongoing challenge. Striking the right balance involves ensuring that the procedure is used judiciously and responsibly while safeguarding the rights of both the unborn child and the expectant parents.
Summary of Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis, a procedure extracting amniotic fluid, offers insights into foetal health and genetic disorders during pregnancy. This method aids in detecting conditions like Down syndrome, while also revealing nervous system development. Despite its benefits, it faces challenges, including a small miscarriage risk. Its ban for sex determination in India addresses gender imbalances caused by female foeticide. As medical science advances, amniocentesis plays a vital role in prenatal care, requiring a delicate balance between medical progress and ethical concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions on Amniocentesis
What is amniocentesis?
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure involving the extraction and analysis of amniotic fluid from the womb. This procedure provides valuable insights into foetal health and genetic makeup, aiding in the detection of genetic disorders and developmental anomalies.
When is amniocentesis usually performed?
Amniocentesis is typically performed during the second trimester of pregnancy, usually between the 14th and 18th weeks of gestation.
How is amniocentesis done?
During amniocentesis, a thin needle is inserted through the mother's abdominal wall and into the amniotic cavity within the uterus, guided by ultrasound imaging. A small amount of amniotic fluid is carefully withdrawn for analysis.
What genetic disorders can be detected through amniocentesis?
Amniocentesis can detect genetic disorders such as Down syndrome, hemophilia, Tay-Sachs disease, sickle cell disease, certain muscular dystrophies, and neural tube defects like spina bifida and anencephaly.
How does amniocentesis reveal developmental insights?
Elevated levels of specific substances like alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and acetylcholinesterase in the amniotic fluid can indicate improper nervous system development, potentially leading to conditions such as spina bifida or anencephaly.
What are the challenges associated with amniocentesis?
One major challenge is the small risk of miscarriage following the procedure, which stands at around 0.5%. Advances in medical techniques and technology have reduced this risk significantly.
Why is amniocentesis banned for sex determination in India?
Amniocentesis was banned for sex determination in India due to the practice of female foeticide, where female fetuses were selectively aborted due to a cultural preference for male offspring. The ban aimed to counter the resulting gender imbalance.
Is amniocentesis performed on all pregnant women?
Amniocentesis is usually performed when there is a suspicion of genetic defects or developmental anomalies. It is not a routine procedure for all pregnant women.
What are the benefits of amniocentesis?
Amniocentesis provides early detection of genetic disorders, allowing for informed decision-making and preparation for the child's health needs before birth. It also aids in understanding developmental issues, enabling timely interventions.








