Table of Contents
The greenhouse effect is a natural and vital process that regulates Earth’s climate, making it habitable for life. However, in recent decades, human activities have amplified this effect, leading to global climate change and its associated impacts. Understanding the greenhouse effect is crucial in comprehending the challenges posed by climate change and developing strategies to mitigate its consequences.
What is Greenhouse Effect?
The Greenhouse is a structure with transparent walls, typically made of glass, where plants are grown. The sunlight enters the greenhouse, warming the interior. The walls of the greenhouse trap some of this heat, preventing it from escaping into the atmosphere. As a result, the temperature inside the greenhouse rises, creating a suitable environment for plants to grow even during colder seasons.
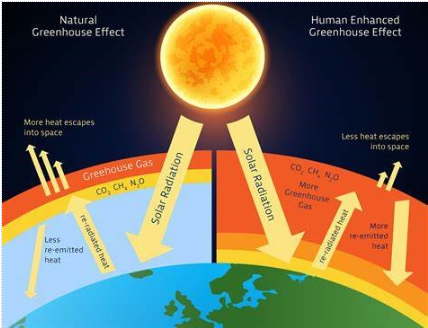
This same principle applies to the Earth’s atmosphere but on a much larger scale. The sun emits energy in the form of visible light and other electromagnetic radiation. Some of this solar radiation is absorbed by the Earth’s surface, warming it. In turn, the Earth re-emits some of this absorbed energy in the form of infrared radiation.
How does the Greenhouse Effect work?
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the Earth’s atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor (H2O), play a crucial role in the greenhouse effect. These gases are transparent to incoming solar radiation but effectively absorb and trap outgoing infrared radiation, preventing it from escaping into space. This trapped energy is then radiated in all directions, including back toward the Earth’s surface, causing further warming—much like the walls of a greenhouse trap heat.
Without the natural greenhouse effect, the Earth’s average surface temperature would be frigid, making it inhospitable for most life forms as we know them. It helps maintain an average temperature of about 15 degrees Celsius which enables a relatively stable and conducive climate for various ecosystems and human civilization.
Anthropogenic Influence on the Greenhouse Effect
While the natural greenhouse effect is essential for life on Earth, human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas), deforestation, industrial processes, and agriculture, have led to a significant increase in greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere. This enhanced greenhouse effect has caused the Earth’s average temperature to rise, a phenomenon known as global warming.
Effects of global warming
- Melting Polar Ice and Rising Sea Levels: As global temperatures rise, polar ice caps and glaciers are melting at an accelerated rate, leading to rising sea levels. This poses significant threats to low-lying coastal areas and island nations.
- Extreme Weather Events: Global warming intensifies heatwaves, droughts, hurricanes, and heavy rainfall events, causing more frequent and severe extreme weather events worldwide.
- Disruption of Ecosystems: Many plant and animal species face challenges due to shifting climate conditions, affecting their habitats, migration patterns, and interactions with other species.
- Ocean Acidification: The increased absorption of CO2 by the oceans leads to ocean acidification, which negatively impacts marine life, especially organisms with calcium carbonate shells or skeletons.
Control measures
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable agricultural and land-use practices can significantly reduce GHG emissions.
- Conservation and Reforestation: Protecting existing forests and restoring degraded lands through reforestation and afforestation initiatives can enhance carbon sequestration and help offset emissions.
- Adaptation and Resilience Building: Developing strategies to adapt to the impacts of climate change, such as building resilient infrastructure and promoting sustainable water management, is essential to minimize vulnerability.
- Global Cooperation: International agreements and cooperation are crucial in addressing climate change on a global scale. Treaties like the Paris Agreement aim to unite countries in their efforts to limit global warming and protect the environment.
Summary
The Greenhouse effect is a natural process that regulates Earth’s climate by trapping heat in the atmosphere. It explains how greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, play a crucial role in this process. However, human activities, like burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have intensified the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming and its adverse impacts, such as rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and ecosystem disruptions. To address climate change, the article emphasizes the need for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conservation efforts, adaptation strategies, and global cooperation through agreements like the Paris Agreement.
FAQs on Greenhouse Effect
What is greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect refers to the process by which certain gases in the Earth's atmosphere trap and retain heat, resulting in the warming of the planet's surface and lower atmosphere.
Which gases contribute to the greenhouse effect?
The main greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor (H2O). While water vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas, human activities primarily contribute to the increased concentrations of CO2, CH4, and N2O.
How does the greenhouse effect impact climate change?
Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, release large amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These additional gases enhance the greenhouse effect, causing the Earth's average temperature to rise, leading to global warming and climate change.
What are the consequences of the enhanced greenhouse effect?
The enhanced greenhouse effect has numerous impacts, including rising global temperatures, melting polar ice and glaciers, rising sea levels, more frequent and severe extreme weather events, disruption of ecosystems, and ocean acidification.
How can we reduce the greenhouse effect?
To mitigate the greenhouse effect and address climate change, it is essential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This can be achieved through transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, adopting sustainable agricultural practices, promoting afforestation and reforestation, and implementing international agreements and cooperation.
What is the difference between the greenhouse effect and global warming?
The greenhouse effect refers to the natural process of heat trapping in the atmosphere, while global warming specifically refers to the long-term increase in the Earth's average temperature due to the enhanced greenhouse effect caused by human activities.
Do natural factors contribute to enhanced greenhouse effect?
Natural factors, such as volcanic activity and variations in solar radiation, can influence the greenhouse effect to some extent. However, scientific research confirms that human activities are the primary drivers of the enhanced greenhouse effect observed in recent decades.
Does the greenhouse effect occur on other planets?
The greenhouse effect is not exclusive to Earth. It also occurs on other planets with atmospheres containing greenhouse gases. For example, Venus has an extreme greenhouse effect that has led to a surface temperature hot enough to melt lead.
What is the role of the greenhouse effect in climate change discussions?
The greenhouse effect is a fundamental concept in climate change discussions. It helps us understand how human activities impact the Earth's climate system, contributing to global warming and the need for mitigation strategies to address climate change effectively.








