Table of Contents
Introduction
Rainwater harvesting is the process of collecting and storing rainwater for future use. It involves the capture and storage of rainwater from rooftops, land surfaces, or other drainage areas. This harvested rainwater can be used for various purposes like irrigation, domestic use, and groundwater recharge. Rainwater harvesting helps to alleviate water scarcity, reduces the reliance on conventional water sources, and promotes sustainable water management. It is an environmentally friendly practice that conserves water resources, reduces storm water runoff, and mitigates the risk of flooding. By harnessing the power of rain, rainwater harvesting contributes to water security and supports sustainable development.
Advantages of Rainwater Harvesting
- Water Conservation: Rainwater harvesting allows us to capture and utilize a valuable natural resource that would otherwise go to waste. By collecting rainwater, we reduce our dependence on traditional water sources such as rivers, lakes, and groundwater, thereby conserving these limited resources.
- Mitigating Water Scarcity: Many regions around the world face water scarcity issues due to population growth, climate change, and other factors. Rainwater harvesting helps to supplement water supply during dry periods, particularly in areas where water availability is limited.
- Sustainable Water Management: Rainwater harvesting promotes sustainable water management practices. It reduces the strain on existing water sources, helps maintain ecological balance, and supports the overall sustainability of water resources.
- Cost Savings: Harvesting rainwater can lead to significant cost savings, especially for non-potable uses such as irrigation, toilet flushing, and washing vehicles. Using rainwater for these purposes reduces the demand for treated drinking water, resulting in lower water bills and operational costs.
- Flood and Erosion Control: By capturing rainwater, we can reduce stormwater runoff and minimize the risk of flooding and erosion. Rainwater harvesting systems help to control the flow of water, allowing it to infiltrate into the ground gradually and preventing excess runoff.
- Groundwater Recharge: Rainwater harvesting contributes to the replenishment of groundwater reserves. When rainwater is properly harvested and allowed to percolate into the ground, it helps recharge underground aquifers, which are vital sources of freshwater.
- Environmental Benefits: Rainwater harvesting has various environmental benefits. It reduces the pressure on natural water bodies, helps maintain their ecological balance, and protects aquatic ecosystems and biodiversity. Additionally, by relying less on energy-intensive water supply systems, rainwater harvesting helps to reduce carbon emissions and environmental impacts.
- Community Engagement and Empowerment: Rainwater harvesting initiatives promote community involvement and awareness about water conservation. They encourage individuals and communities to take responsibility for their water resources, fostering a sense of environmental stewardship and empowering people to make a positive impact.
Also Check
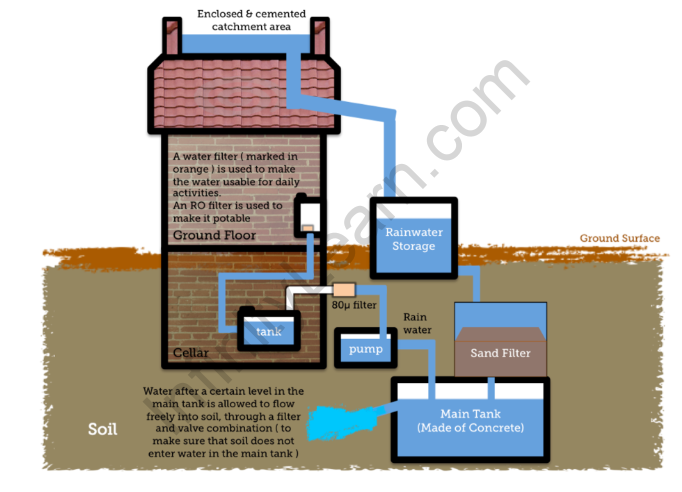
Mechanism of Rainwater Harvesting
- Assess the Catchment Area: Identify the area from which rainwater will be collected. This can include rooftops, paved surfaces, or any other suitable catchment area.
- Calculate Rainwater Yield: Determine the potential rainwater yield based on the catchment area and average annual rainfall in your region. This will help estimate the amount of water that can be harvested.
- Install Gutters and Downspouts: Install gutters along the edges of rooftops or structures to collect rainwater. Connect downspouts to guide the water into storage containers or underground storage tanks.
- Filter the Water: Install a first-flush diverter or a filter system to remove debris, leaves, and other contaminants from the collected rainwater. This ensures the water is clean and suitable for use.
- Direct the Water to Storage: Direct the filtered rainwater into storage containers or underground storage tanks. Ensure that the storage system is properly sealed to prevent contamination or breeding of mosquitoes.
- Use Overflow Mechanism: Install an overflow mechanism to divert excess water once the storage tanks or containers are full. This prevents overflow and potential damage to the system.
- Connect to Supply Systems: Connect the stored rainwater to the required supply systems based on its intended use. This can include connecting it to plumbing systems for non-potable uses such as toilet flushing, irrigation, or washing.
- Maintain the System: Regularly inspect and maintain the rainwater harvesting system. Clean filters, remove debris, and ensure proper functioning of storage tanks and distribution systems. Periodic maintenance helps maximize the efficiency and lifespan of the system.
- Monitor Water Usage: Keep track of the amount of rainwater being used and ensure its efficient use. Implement water-saving practices to optimize the benefits of rainwater harvesting.
- Educate and Promote Awareness: Raise awareness about the importance of rainwater harvesting in your community. Educate others about its benefits, encourage its adoption, and share knowledge on how to implement rainwater harvesting systems effectively.
By following these steps, individuals, communities, and organizations can effectively implement rainwater harvesting mechanisms to conserve water, mitigate water scarcity, and promote sustainable water management practices.
Need for Rainwater Harvesting
The need for rainwater harvesting arises from the growing global water crisis and the increasing demand for water in various sectors. Here are some key reasons highlighting the importance of rainwater harvesting:
- Water Scarcity: Many regions around the world are facing water scarcity issues due to population growth, urbanization, and climate change. Rainwater harvesting helps to augment water supply and reduce dependence on traditional water sources, such as rivers and groundwater.
- Sustainable Water Management: Rainwater harvesting promotes sustainable water management by utilizing a free and abundant natural resource. It reduces the strain on existing water sources, especially during drought periods, and helps maintain ecological balance.
- Mitigating Flooding and Erosion: In urban areas, excessive rainfall can lead to stormwater runoff, causing flooding and erosion. Rainwater harvesting systems capture and store rainwater, reducing the volume of runoff and minimizing the risk of floods and erosion.
- Groundwater Recharge: By collecting and infiltrating rainwater into the ground, rainwater harvesting aids in replenishing groundwater resources. This is particularly crucial in areas heavily dependent on groundwater for domestic and agricultural purposes.
- Conservation of Energy: Rainwater harvesting reduces the need for energy-intensive processes involved in pumping and treating water from distant sources. It promotes energy conservation and helps lower carbon emissions associated with water supply and distribution.
- Cost Savings: Implementing rainwater harvesting systems can lead to significant cost savings by reducing water bills, especially for non-potable uses such as landscaping, toilet flushing, and irrigation.
- Environmental Benefits: Rainwater harvesting reduces the pressure on rivers and other water bodies, which helps protect aquatic ecosystems and biodiversity. It also minimizes the need for dam construction and the associated environmental impacts.
- Community Engagement and Empowerment: Rainwater harvesting initiatives encourage community participation and awareness about water conservation. It empowers individuals and communities to take responsibility for their water resources and fosters a sense of environmental stewardship.
Disadvantages of Rainwater Harvesting
While rainwater harvesting has numerous advantages, it also has some disadvantages that should be considered:
- Seasonal Dependence: Rainwater harvesting is dependent on rainfall patterns and can be limited during dry seasons or in regions with low precipitation. In such cases, the availability of harvested rainwater may be insufficient to meet water demands, especially for regular or high-volume usage.
- Initial Cost and Maintenance: The installation of rainwater harvesting systems can involve significant upfront costs, including the purchase of storage tanks, filtration systems, and plumbing infrastructure. Additionally, regular maintenance is required to ensure the system functions efficiently, including cleaning filters, checking for leaks, and managing storage tank cleanliness.
- Water Quality Concerns: Rainwater is generally considered safe for non-potable uses like irrigation or washing. However, for potable purposes, additional treatment or filtration may be necessary to remove potential contaminants such as bacteria, pollutants, or debris. Without proper maintenance and treatment, there is a risk of water quality issues.
- Limited Storage Capacity: The storage capacity of rainwater harvesting systems is limited by the size of the storage tanks or containers. During heavy rainfall or extended periods of precipitation, the storage capacity may be exceeded, resulting in overflow and potential wastage of collected rainwater.
- Initial Water Flushing: In some cases, the initial rainfall at the beginning of a rain event may contain pollutants or debris accumulated on the catchment surface. This water may need to be diverted or flushed before collecting cleaner rainwater to avoid contamination of the stored water.
- Contamination Risks: If proper precautions are not taken, there is a potential risk of contamination of the harvested rainwater. Factors such as bird droppings, leaf litter, or chemical pollutants from nearby industries or sources can compromise the quality of collected water if appropriate filtration or treatment measures are not in place.
- Space Requirements: Rainwater harvesting systems, particularly large-scale ones, may require significant space for the installation of storage tanks or underground reservoirs. In urban areas or properties with limited space, finding suitable areas for these structures can be a challenge.
- Regulatory and Legal Considerations: Depending on the location and local regulations, there may be specific permits or legal requirements for rainwater harvesting systems. It is important to be aware of these regulations and comply with any necessary guidelines or restrictions.
Despite these disadvantages, with proper planning, maintenance, and adherence to water quality standards, the benefits of rainwater harvesting generally outweigh the drawbacks. It is important to assess the specific conditions and requirements of each situation to determine the suitability and feasibility of rainwater harvesting as a water management strategy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rainwater harvesting is a sustainable and practical solution to address water scarcity, promote water security, and protect the environment. By harnessing rainwater, we can conserve water, reduce reliance on conventional sources, and ensure a more sustainable and resilient future for generations to come. Rainwater harvesting is crucial for water conservation, mitigating water scarcity, promoting sustainable water management, and reducing the burden on traditional water sources. It offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, flood control, groundwater recharge, environmental protection, and community engagement. By harnessing rainwater, we can contribute to a more sustainable and resilient water future.
Frequently Asked Questions for Rainwater Harvesting
What is the importance of rainwater harvesting?
The importance of rainwater harvesting lies in its ability to provide a sustainable and decentralized water source. It helps to alleviate water scarcity, reduce reliance on traditional water sources, and promote self sufficiency in water supply. By capturing and storing rainwater, it can be used for various purposes such as irrigation, domestic use, groundwater recharge, and reducing stormwater runoff, thereby conserving water resources and mitigating the effects of droughts.
What are the different methods of rainwater harvesting?
There are several methods of rainwater harvesting, including: Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting: Collecting rainwater from rooftops and channeling it into storage tanks or underground reservoirs. Surface Water Harvesting: Collecting runoff from surfaces such as roads, pavements, or open areas and directing it into storage structures. Rainwater Ponds: Constructing ponds or small reservoirs to capture and store rainwater. Percolation Pits: Excavating pits in the ground to allow rainwater to percolate and recharge the groundwater table. Check Dams: Constructing small dams or barriers across streams or water channels to impound rainwater.
What are the factors affecting the amount of rainwater harvested?
The amount of rainwater harvested can be influenced by several factors, including: Rainfall Intensity: The volume and frequency of rainfall in a particular area affect the amount of water that can be harvested. Catchment Area: The size and type of the surface area where rainwater is collected, such as rooftops or open land, determines the quantity of water available for harvesting. Storage Capacity: The size and capacity of storage tanks or reservoirs limit the amount of rainwater that can be stored. Climate and Seasonal Variations: Different climatic conditions and seasonal patterns impact the availability of rainfall and, consequently, the amount of water that can be harvested.
What are 4 uses of rainwater harvesting?
The uses of rainwater harvested include: Irrigation: Rainwater can be used for watering plants, crops, gardens, and agricultural fields. Domestic Use: It can be treated and used for household activities like cleaning, washing, and flushing toilets. Groundwater Recharge: By allowing rainwater to percolate into the ground, it helps replenish the groundwater table. Stormwater Management: Capturing rainwater reduces stormwater runoff and the associated problems of flooding and soil erosion.
Who introduced rainwater harvesting in India?
Rainwater harvesting has been practiced in India for centuries, and it is difficult to attribute its introduction to a single individual. However, it has been an integral part of traditional water management systems in various regions of the country.
What are the principles of rainwater harvesting?
The principles of rainwater harvesting include: Catchment: Identifying suitable surfaces or areas to collect rainwater, such as rooftops, land, or paved surfaces. Conveyance: Establishing a system of gutters, pipes, or channels to transport rainwater from the catchment to the storage or recharge structures. Filtration: Implementing filtration mechanisms to remove debris, pollutants, and contaminants from collected rainwater. Storage: Utilizing storage tanks, reservoirs, or underground structures to store the harvested rainwater. Recharge: Allowing rainwater to percolate into the ground to recharge the groundwater aquifers.
What are the uses of rainwater?
Answer: Rainwater can be used for various purposes, including: Drinking and Cooking: Properly treated rainwater can be used for drinking and cooking purposes. Irrigation: It is suitable for irrigation, which helps in agricultural activities and maintaining gardens. Cleaning and Washing: Rainwater can be used for cleaning vehicles, outdoor surfaces, and general cleaning purposes. Groundwater Recharge: Allowing rainwater to percolate into the ground helps in recharging groundwater sources.
What are the types of rainwater harvesting?
1. Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting: This method involves collecting rainwater from rooftops and directing it into storage tanks or underground reservoirs. The water can be filtered and used for various purposes such as domestic use, irrigation, or groundwater recharge. 2. Surface Water Harvesting: This method involves collecting rainwater from open surfaces such as roads, pavements, or open land. The water is directed into storage structures such as ponds, tanks, or recharge pits for later use. 3. Rainwater Ponds: This method involves constructing small ponds or reservoirs to collect and store rainwater. The collected water can be used for irrigation, livestock watering, or replenishing groundwater. 4. Percolation Pits: This method involves excavating pits in the ground to allow rainwater to percolate and recharge the groundwater table. The pits are filled with layers of gravel, sand, and soil to facilitate the percolation process. 5. Check Dams: This method involves constructing small dams or barriers across streams or water channels to impound rainwater. The dams slow down the flow of water, allowing it to infiltrate into the soil and recharge groundwater. 6. Infiltration Trenches: This method involves digging long, narrow trenches filled with gravel or porous materials. Rainwater is directed into the trenches, where it infiltrates into the ground and replenishes groundwater. 7. Recharge Wells: This method involves drilling wells or boreholes into the ground and allowing rainwater to directly recharge the groundwater aquifers. The wells are designed to capture and store rainwater for gradual percolation into the aquifer. 8. Rainwater Harvesting in Urban Areas: In urban areas, rainwater can be harvested using innovative techniques such as rain gardens, green roofs, and rain barrels. These methods involve capturing rainwater on rooftops, in gardens, or through permeable pavements for localized use or recharge. Each type of rainwater harvesting method has its own advantages and suitability based on factors such as available space, rainfall patterns, soil conditions, and water requirements. The choice of method depends on the specific needs and circumstances of the location.
Which is the oldest rainwater harvesting system of India?
A 15th Century irrigation method, Khadin, were constructions designed to harvest surface runoff water for agriculture. Paliwal Brahmins of Jaisalmer were the first to bring this method of water conservation into implementation.








