Table of Contents
Introduction to Oxygen Cycle
Imagine taking a deep breath of fresh air and feeling the surge of energy as oxygen fills your lungs. Oxygen is vital for all life forms on Earth, from tiny microorganisms to towering trees and majestic animals. But have you ever wondered how oxygen circulates and replenishes itself in our environment? Enter the fascinating world of the oxygen cycle.
The oxygen cycle is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the movement and transformation of oxygen molecules in various forms through the Earth’s biosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere. It is an essential process that ensures the continuous availability of oxygen for respiration and sustains life on our planet.
Process of Oxygen Cycle
Oxygen Production: The first stage of the oxygen cycle involves the production of oxygen through photosynthesis. Plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce oxygen and glucose. During this process, oxygen is released into the atmosphere as a by product.
Oxygen Consumption: In the second stage, organisms engage in respiration, consuming oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide as a waste product. Plants and animals alike rely on oxygen for cellular respiration, where glucose is broken down to produce energy. This stage ensures the availability of oxygen for metabolic processes in living organisms.
Oxygen Exchange: The third stage of the oxygen cycle involves the exchange of gases between the atmosphere, plants, and oceans. Through various processes such as diffusion, air currents, and weather systems, oxygen is distributed throughout the atmosphere. Additionally, the exchange of gases between the atmosphere and the oceans helps maintain oxygen levels in aquatic ecosystems, supporting marine life.
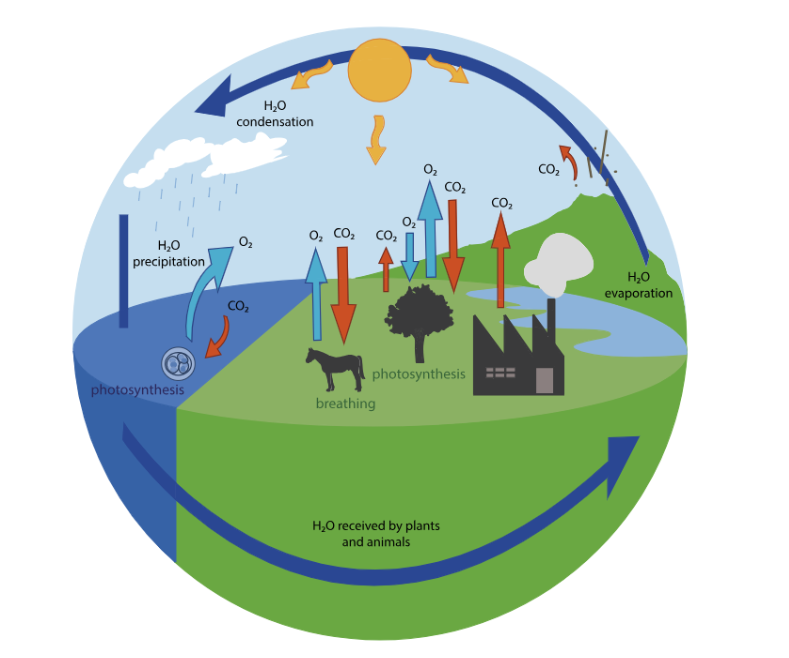
These three stages work together to maintain the balance of oxygen in the atmosphere, supporting life on Earth. It is important to note that human activities can disrupt this cycle through activities such as deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels, leading to imbalances in atmospheric composition and potentially affecting the health of ecosystems.
Oxygen Production
The primary source of oxygen in the atmosphere comes from photosynthesis, the remarkable process performed by plants, algae, and some bacteria. During photosynthesis, these organisms use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and glucose. Oxygen is released into the atmosphere as a by product, providing the breathable air that supports life.
Respiration
Respiration, both in plants and animals, plays a significant role in the oxygen cycle. During respiration, organisms consume oxygen and release carbon dioxide as a waste product. In this process, oxygen is used to break down glucose molecules, releasing energy that fuels various cellular activities. The released carbon dioxide can then be used by plants during photosynthesis to produce more oxygen, completing the cycle.
The Role of Decomposition
Decomposition is another crucial component of the oxygen cycle. When plants and animals die, their organic matter undergoes decomposition by bacteria and fungi. During this process, microorganisms consume the decaying matter and utilize oxygen for respiration. Decomposition returns carbon dioxide to the atmosphere and releases nutrients back into the soil, fostering the growth of new plants.
Oxygen in the Atmosphere
The Earth’s atmosphere contains approximately 21% oxygen, making it the second most abundant gas after nitrogen. The constant exchange of oxygen between the biosphere and the atmosphere ensures that there is a steady supply of this life-giving gas. Winds, air currents, and weather systems help distribute oxygen molecules across different regions, creating a balanced oxygen composition in the atmosphere.
The Ocean Connection
The oxygen cycle also encompasses the oceanic realm. The world’s oceans are vast reservoirs of oxygen. Marine plants, such as algae and phytoplankton, perform photosynthesis and contribute to the production of oxygen. Additionally, oceanic currents and wave action aid in the exchange of gases, allowing dissolved oxygen to be replenished in aquatic ecosystems and supporting the diverse marine life.
Human Impact on the Oxygen Cycle
Human activities have an impact on the delicate balance of the oxygen cycle. Deforestation, for example, reduces the number of trees available for photosynthesis, leading to decreased oxygen production. Burning fossil fuels and industrial emissions release excessive amounts of carbon dioxide, which can disrupt the balance of gases in the atmosphere. These changes can have profound effects on climate patterns, air quality, and overall environmental health.
The Oxygen Cycle and Climate Regulation
The oxygen cycle is closely intertwined with the carbon cycle and other biogeochemical cycles. Oxygen levels in the atmosphere play a crucial role in regulating climate. Through the process of photosynthesis, oxygen production helps remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, mitigating the greenhouse effect and stabilizing global temperatures. Therefore, the oxygen cycle and its interconnections with other cycles are essential for maintaining a habitable planet.
Uses of Oxygen cycle
- Oxygen is essential for the survival of living organisms, serving as a vital component of respiration.
- The oxygen cycle plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of oxygen in the atmosphere.
- It allows for the continuous production of oxygen through photosynthesis by plants, algae, and some bacteria.
- Oxygen is released into the atmosphere during photosynthesis, replenishing the oxygen levels.
- Organisms, including plants and animals, consume oxygen through respiration, using it for metabolic processes and energy production.
- During respiration, organisms release carbon dioxide as a byproduct, which can be utilized by plants during photosynthesis.
- The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, plants, and oceans helps distribute oxygen throughout the Earth’s systems.
- Oxygen is exchanged between the atmosphere and the oceans, supporting marine life and maintaining oxygen levels in aquatic ecosystems.
- The oxygen cycle is interconnected with other biogeochemical cycles, such as the carbon cycle, influencing the overall functioning of Earth’s ecosystems.
- Human activities can impact the oxygen cycle through activities like deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels, leading to imbalances in atmospheric composition and potential consequences for ecosystems and human health.
In conclusion, the oxygen cycle is a remarkable process that sustains life as we know it. From the photosynthetic prowess of plants to the respiration of organisms, it ensures a constant supply of oxygen in our environment. Understanding and appreciating the intricacies of the oxygen cycle can inspire us to protect and preserve the delicate balance.
FAQs on Oxygen Cycle
What is the oxygen cycle?
The oxygen cycle refers to the continuous movement of oxygen between the atmosphere, living organisms, and the Earth's systems.
How does oxygen enter the atmosphere?
Oxygen enters the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis carried out by plants, algae, and some bacteria.
What organisms produce oxygen during photosynthesis?
Plants, algae, and some bacteria produce oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis.
How is oxygen consumed in the oxygen cycle?
Oxygen is consumed by organisms through the process of res
How does the oxygen cycle impact the environment?
The oxygen cycle supports the survival of various organisms and helps maintain the balance of gases in the atmosphere, which is vital for sustaining life on Earth.
Can human activities affect the oxygen cycle?
Yes, human activities such as deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels can disrupt the oxygen cycle by reducing the number of oxygen-producing plants and releasing excess carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
What are the consequences of oxygen imbalance in ecosystems?
An oxygen imbalance can lead to disturbances in aquatic ecosystems, harming marine life and impacting the overall functioning of ecosystems.
How is the oxygen cycle related to the carbon cycle?
The oxygen cycle and carbon cycle are closely linked as oxygen is released during photosynthesis and consumed during respiration, while carbon dioxide is released during respiration and absorbed during photosynthesis.
Is the oxygen cycle affected by climate change?
Climate change can indirectly affect the oxygen cycle by altering the distribution and behavior of plants and organisms, potentially impacting oxygen production and consumption processes.








