Table of Contents
Introduction
In the world of biology, the study of tissues is an essential aspect of understanding the complex structure and functioning of organisms. Tissues are groups of cells that work together to perform specific functions. Just as bricks come together to build a strong and functional wall, cells unite to form tissues, which in turn contribute to the overall functioning of organs and organ systems.
Types of Tissues
In the study of tissues, scientists have identified four primary types:
-
Epithelial Tissue
-
Connective Tissue
-
Muscular Tissue
-
Nervous Tissue
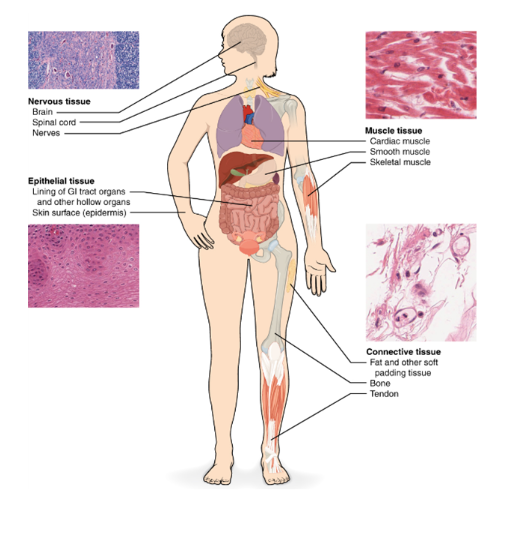
Each type has distinct characteristics and performs specific functions.
Epithelial Tissue
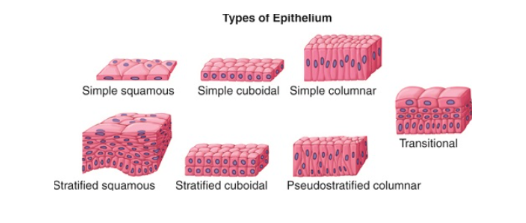
Epithelial tissue is found on the outer surfaces of the body, lining various organs and forming protective barriers. It can be further classified into simple epithelium (one layer of cells) and stratified epithelium (multiple layers of cells), depending on its structure and location. Epithelial tissue functions include absorption, secretion, and protection.
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is responsible for connecting and supporting different body parts. It includes various types such as loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, adipose tissue (fat tissue), and cartilage. Connective tissue provides structural support, protection, and insulation.
Muscular Tissue
Muscular tissue is responsible for movement and contraction. It is divided into three types: skeletal muscle, which is attached to bones and enables voluntary movements; smooth muscle, which is found in organs and controls involuntary movements; and cardiac muscle, which makes up the heart and enables its rhythmic contractions.
Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue is specialized for communication and control within the body. It includes neurons, which transmit signals, and supporting cells called neuroglia. Nervous tissue plays a crucial role in receiving sensory input, processing information, and coordinating responses.
Concept of Tissues
The concept of tissues arises from the fact that cells are the building blocks of life, and when they come together, they form tissues with specialized functions. Tissues are not just random collections of cells; they are organized and structured in a way that allows them to perform specific tasks efficiently. Each tissue type is composed of cells that have similar structures and work together to carry out specific functions.
Tissues are not limited to human beings; they are found in all multicellular organisms. From plants to animals, tissues are vital for maintaining the structure, regulating body processes, and ensuring the proper functioning of organs and organ systems.
Function of Tissue
- Protection: Epithelial tissues form protective barriers, such as the skin, lining of the digestive tract, and respiratory passages, shielding underlying tissues from physical injury, pathogens, and harmful substances.
- Support: Connective tissues provide structural support to organs, joints, and body structures. They maintain the shape and integrity of organs and hold them in place.
- Movement: Muscular tissues, including skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles, enable body movement, locomotion, and internal organ contractions.
- Sensation: Nervous tissues, particularly neurons, are responsible for receiving and transmitting sensory information, allowing us to perceive and respond to stimuli from the environment.
- Absorption and Secretion: Certain epithelial tissues, such as those lining the intestines and glands, are involved in absorbing nutrients, water, and other substances from the external environment, as well as secreting hormones, enzymes, and other essential substances.
- Transportation: Vascular tissues, including blood and lymphatic vessels, transport oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and immune cells throughout the body, ensuring proper distribution and delivery.
- Defense: Connective tissues, such as lymphoid tissue, play a vital role in the body’s immune response, helping to identify and eliminate foreign substances, pathogens, and abnormal cells.
- Coordination and Control: Nervous tissues, comprising neurons and supporting cells, allow for rapid communication and coordination within the body, regulating various physiological processes and maintaining homeostasis.
These functions highlight the diverse and essential roles that tissues play in maintaining the proper functioning of the body and contributing to overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
The study of tissues is fundamental to understanding the organization and functioning of living organisms. Tissues are the building blocks of organs, and organs, in turn, form systems that work harmoniously to support life. By studying the different types of tissues, scientists gain insights into how cells collaborate and specialize to perform a wide range of functions necessary for survival. Understanding tissues helps us comprehend the intricate complexity of life and provides a foundation for further exploration into the fascinating world of biology.
Frequently Asked Question on Tissue
What are tissues in biology?
Tissues are groups of specialized cells that work together to perform specific functions in living organisms.
How many types of tissues are there?
There are four main types of tissues in biology: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, and nervous tissue.
What is the function of epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue functions include protection, absorption, secretion, and forming barriers between different environments within the body.
What is the role of connective tissue?
Connective tissue provides support, connects and anchors body structures, protects organs, and helps transport nutrients and waste materials.
What is the function of muscular tissue?
Muscular tissue enables movement and contraction, allowing for voluntary and involuntary movements in the body.
What are the characteristics of nervous tissue?
Nervous tissue is responsible for receiving, transmitting, and processing sensory information, facilitating communication and control within the body.
How do tissues work together to maintain homeostasis?
Different tissues collaborate and communicate to maintain the body's internal balance, regulating temperature, pH levels, and other physiological processes.
Can tissues regenerate or repair themselves?
Some tissues, such as epithelial and connective tissues, have a higher regenerative capacity and can repair themselves to a certain extent. However, other tissues, like nervous tissue, have limited regenerative abilities.
How are tissues related to organs and organ systems?
Tissues form the building blocks of organs, and organs work together in organ systems to carry out specific functions necessary for the overall functioning of the organism.








