Table of Contents
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2015 Delhi
Time allowed : 3 hours
Maximum marks: 70
General Instructions :
- There are 22 questions in all.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question number 1 to 7 are very short-answer questions carrying 1 mark each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 40
- Question numbers 8 to 13 are short-answer questions carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 80-100 words.
- Question numbers 14 to 20 are long-answer questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 150
- Question numbers 21 to 22 are related to identification or locating and labelling of geographical features on maps, carrying 5 marks each.
- Outline maps of the World and India provided to you must be attached within your answer-book.
- Use of templates or stencils for drawing outline maps is allowed.
** Answer is not given due to change in present syllabus
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2015 Delhi Set – I
Question 1.
Define the term ‘population distribution’. [1]
Answer:
The term ‘population distribution’ refers to the way people are spaced over the earth’s surface. The population distribution is in even through out the world.
Question 2.
What are economic activities ? [1]
Answer:
Economic activity defines as any activity which results in production and distribution of goods and services. They are undertaken by the people to satisfy their economic needs.
Question 3.
Define the term ‘Transport Network’. [1]
Answer:
Several places (nodes) joined together by a series of routes (links) to form a pattern which permit vehicular moment or flow of some commodity is called transport network.
Question 4.
Distinguish between towns and villages on the basis of occupation. [1]
Answer:
The difference between towns and villages on the basis of occupation is that in towns the main occupation of the people is related to secondary and tertiary sectors, while in the villages most of the people are engaged in primary occupations such as agriculture, fishing, lumbering, mining, animal husbandry etc.
Question 5.
How is the level of urbanization measured in India ? [1]
Answer:
The level of urbanization is measured in terms of percentage of urban population to total population in any country.
Question 6.
Why did Sher Shah Suri built the Shahi (Royal) Road ? [1]
Answer:
Sher Shah Suri built the Shahi (Royal) road from Indus valley to the Sonar valley in Bengal to strengthen and consolidate his empire.
Question 7.
What is criterion for the classification of pollution ? [1]
Answer:
Different types of pollution are classified on the basis of medium through which pollutants are transported and diffused.
Question 8.
What is the subject-matter of the study of human geography ? Explain any three facts. [3]
Answer:
- To establish relationship between the physical world and the human world.
- To study the spatial distribution of human phenomena.
- To study the social and economic differences between different parts of the world.
- To understand the earth as home of human beings and to study all those elements which have sustained them.
- Nature and human are inseparable elements and should be see holistically.
Question 9.
Explain any three factors responsible for the location of rural settlements in the world. [3]
Answer:
The following three factors are responsible for the location of rural settlemen in the world :
(i) Water Supply : Usually rural settlements are located near water bodies such as rivers, lakes, ponds and springs where water can be easily obtained. Most water-based wet point settlements have many advantages such as water for drinking, cooking and washing. Rivers and lakes can be used for irrigation. Water bodies also have fish. Navigable rivers and lakes can be used for transportation.
(ii) Defence: During the times of political instability, war, hostility of neighbouring groups villages were built on defensive hills and islands. In India, most of the forts are located on higher grounds or hills.
(iii) Planned settlements : Sites that are not spontaneously chosen by villagers themselves. Planned settlements are constructed by government by providing shelter, water and other infrastructures on acquired land.
Question 10.
What are metropolitan cities and mega cities ? Give two examples of each of metropolitan cities and mega cities from India. [3]
Answer:
Cities which have population size between one to five million are called metropolitan cities and cities that accomodate a population of more than five million are called mega cities. As per 2011 census, any other city can also be considered metropolitan city as declared by authorities.
Examples :
- Metropolitan cities: Surat, Kanpur, Jaipur, Lucknow etc.
- Mega cities : Mumbai, Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai,
- Empowerment : It is the freedom of the
Question 11.
“Land resource is more crutial to the people whose livelihood is depending on agriculture in India.” Support this statement by any three suitable arguments. [3]
Answer:
Land resource is more crucial to people whose livelihood is depending on agriculture in India because;
- Agriculture is land based activity.
- Agricultural productivity is linked with quality of land. %
- Land ownership has a social and Economic value.
- Standard of living of the agrarian society depends on the agricultural productivity.
Question 12.
“The assessment, efficient use and conservation of water are necessary to ensure development.” : Explain in the light of values regarding ( conservation of water resources.** [3]
Question 13.
Define the term ‘air pollution’. Explain any two harmful effects of air pollution. [3]
Answer:
Air pollution defined as addition of contaminants like dust, fumes, gas, fog, odour, smoke or vapour to the air in large proportional duration that may have harmful effect. The harmful effects of air pollution are :
- It causes various diseases like respiratory, nervous and circulatory systems.
- It causes urban smog which has adverse effect on respiratory system.
- It can cause acid rain which can damage flora, fauna and property.
Question 14.
What is ‘Human Development’ ? Explain the four t pillars of human development. [5]
Answer:
Human development concept was developed by economist Mahbub ul Haq. Human development is defined as the process of enlarging people’s freedom , and opportunities and improving their well-being.
The four basic pillars of human development are : equity, sustainability, productivity, empowerment, and security.
- Equity : It is the idea of fairness for every person, between men and women; we each have the / right to an education and health care.
- Sustainability : It refers that we all have the right to earn our living that can sustain our lives and have access to a more even distribution of goods,
- Productivity: It refers to the full participation of people in the process of income generation.
Question 15.
Explain five factors that influence the industrial location in the world. [5]
Answer:
Factors influencing the industrial location are :
(i) Access to Market : Industries are looking for locations as near as possible to their markets. It helps in reducing the transport cost and enables the consumer to get things at cheaper rates. Ready market is also essential for perishable and heavy commodities.
(ii) Access to Raw Material: The raw materials is very important for the manufacturing industry. The raw materials which get reduced in weight during manufacturing process influence the industry to be located near the source, for example, location of sugar mills in Maharashtra and western Uttar Pradesh and Iron and Steel industry in West Bengal-Bihar-Odisha belt.
(iii) Access to Labour Supply : The availability of both unskilled and skilled, or technically qualified manpower, is an important factor that influences the location of industries. Some of the small scale industries traditionally associated with labour is glasswork (Firozabad), brass-work (Moradabad), utensils (Yamunanagar in Haryana), silk sarees (Varanasi), carpets (Mirzapur), etc.
(iv) Access to Sources of Energy: Regular supply of power is a prerequisite for the localization of industries. Coal, mineral oil and hydro-electricity are the three important conventional sources of power. Most of the industries are located near the source of power; for example, the iron and steel industry which depends on large quantities of cooking coal as source of power are located near the coal fields.
(v) Access to Transport and Communication : A good network of transport and communication facilities are essential for industrial development as it helps in procurrent of raw materials and distribution of finished products to the market.
Question 16.
Define the term ‘nomadic herding’. Explain its any four characteristics. [5]
Answer:
Nomadic herding is a primitive subsistence activity in which the herders rely on animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools and transport. They move from one place to another along with their livestock.
Characteristics :
- Simplest form of pastoralism in which herds and flocks graze on natural vegetation called pastures.
- It ancient activity where each nomadic community occupies a well defined territory as per their traditions and culture.
- Nomads have different type of animals in the herd according to local cultural and physical characteristics. The camel is the most desired animal in North Africa and the Middle East followed by sheep and goats. Horses, yaks, reindeers and Llamas are other important animals.
- The life of the nomadic herders is dependent upon their animals, which provides food, clothing (from their wool, hair or skins), transport-and for materials from which their houses can be made.
- They move with their herds from one place to another place with change in seasons. This is known as Transhumance for example sheep or other animals may graze in alpine meadows in the summer and be heralded back down into valleys for the winter.
Question 17.
Name the longest trans-continental railway of the world. Describe its any four features. [5]
Answer:
Trans-Siberian railway is the longest trans-continental railway of the world.
Characteristics :
- It is 9289 km long railway route.
- It extends between St. Petersburg in the east to Vladivostok in the west.
- It is double track route which is electrified.
- It is the most important route in Asia.
- There are several connecting links to the south.
- It connects Asian region to the European region.
Question 18.
What is density of population ? Describe the spatial variation of population density in India. [5]
Answer:
Density of population is the number of people per unit of area. It is expressed as number of people per unit area/per sq. km.
Spatial Variation in the density of population are :
- Very low : Arunachal Pradesh 13/17 persons/ sq. km.
- Low : The hill states of Himalayan region and North Eastern states excluding Assam has relatively low densities.
- Moderate : Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana has moderate density of population.
- High : West Bengal, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Kerala, Tamil Nadu has higher densities among the peninsular Indian states.
- Very High : Delhi has very high density of population 11,297 persons/sq. km.
Question 19.
Why is the area under pastures decreasing in India ? How do the changes in the economy effect the changes in land use ? Explain. [5]
Answer:
The area under pasture is decreasing in India due to pressure from agricultural land and illegal encroachment due to expansion of cultivation on common pasture land.
Changes in economy effect the change in land use :
- Size of Economy : Growth of the economy over the period of time result in increasing population, change in income levels, available technology and associated factors. As a result, the pressure on land will increase and marginal lands will come under use.
- Composition of Economy : The secondary and the tertiary sectors are growing much faster than the primary sector, specifically the agricultural sector. This type of change is common in developing countries like India. This process would result in a gradual shift of land from agricultural uses to non- agricultural uses.
- Declining contribution of Agriculture: The contribution of the agricultural activities reduces over time. In developing countries, the share of population dependent on agriculture declines slowly as compared to the decline in the sector’s share in GDP. The number of people that the agricultural sector has to feed is increasing day by day.
Question 20.
“The distribution of roads is not uniform in India.” Support this statement with suitable arguments. [5]
Answer:
The distribution of roads isomer in India due to the following reasons :
- The land in India is uneven. Higher slopes of the Himalayas have less density of roads as compared to the Ganga plains.
- India has unused distribution of population. Kerala has dense population, so there are more roads. While Rajasthan is sparsely populated and thus have less roads.
- Areas which are rich in agricultural resources have high density of roads. It helps them in the collection and distribution of agricultural products e.g., the Ganga plains.
- In India, the industrially developed areas have high road density. This is essential for connecting the industries to the sources of raw materials and the markets.
Question 21.
In the given political outline map of the world, five features A, B, C, D and E have been shown. Identify these features with the help of the information given below and write their correct names on the lines drawn near them. [5]
(A) The country having the highest rank in Human Development Index-2003
(B) Railway terminal station
(C) An important airport
(D) A major seaport
(E) A mega city
Answer:
Question 22.
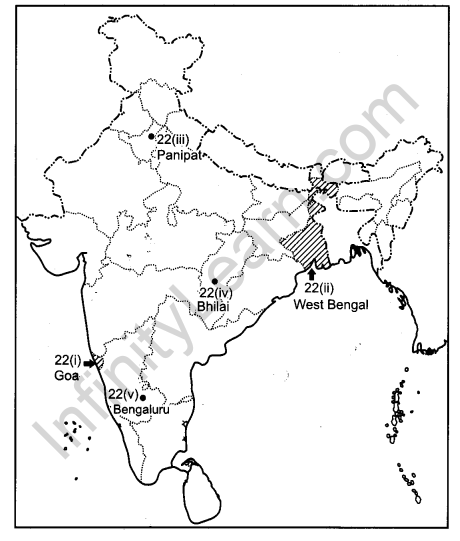
On the given political outline map of India, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols :
(i) The state having the smallest area.
(ii) The leading jute producing state.
(iii) An oil refinery in Haryana.
(iv) An integrated Iron and Steel Plant in Chhattisgarh.
(v) The international airport in Karnataka.
Answer:
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2015 Delhi Set – II
Note : Except for the following questions, all the remaining questions have been asked in previous set.
Question 10.
What makes rural settlement different from urban settlement in India ? Explain. [3]
Answer:
Difference between rural and urban settlements in India are :
Rural Settlements :
- Most of the people are engaged in primary activities to support their life.
- The people in the rural society had homogeneity and thus enjoyed more or less the same social status and had informal social relationships with each other.
- Inadequate educational facilities.
- Inadequate infrastructure.
- Life in the society was very simple and reflected in the way of living, dressing, food, habits, shelter and manners etc., showing low standard of living.
Urban Settlements :
- Most of the people are engaged in secondary and tertiary activities/other than primary activities.
- The people in the city belong to different castes, creeds, religions and cultures, thus do not enjoy the same social status and had formal social relationships with each other.
- Adequate educational facilities.
- Adequate infrastructure.
- Life in the city is not simple but very complex and complicated showing high living standard.
Question 13.
How is environment pollution caused ? Mention the four types of pollution responsible for the environmental degradation. [3]
Answer:
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that causes adverse change. Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light.
Types of pollution:
- Air pollution
- Water pollution
- Land pollution
- Noise pollution
Question 14.
When does positive population growth takes place ? Explain the geographical factors that influences the distribution of population in the world. [5]
Answer:
Positive growth of population takes place when the birth rate is more than the death rate between two points of time or when people from other countries migrate permanently to a region. Geographical factors that influence the distribution of population in the world :
- Availability of water : Availability of water is very important in determining the population of a given area. Water is the basic necessity for several purposes including irrigation, industries, transport and domestic affairs. Rivers are the source of fresh clean water as a result; most of the population is concentrated in the river valleys.
- Landforms : Terrain is one of an important factor which influences the concentration and growth of population, plain areas has higher density of population as compared to mountain regions. The steep slope in mountain areas restrict the availability of land for agriculture, development of transport, industries and other economic activities which discourage concentration of population.
- Climate : Climatic factors such as rainfall and temperature play the most important role in determining the population of an area. Extremes of climate discourage the concentration of population. Climates include the too cold climate of Himalayas and the too hot and dry climate of the Thar Desert. A moderate climate, on the other hand, is favourable for population.
- Soils : Soil is an important factor in determining the density of population. Fertile soil supports higher population density while infertile soil leads to low density. In the northern plain of India, the soil is regularly enriched by annual floods of the rivers like the Indus, the Ganga and the Brahmaputra and their tributaries. Therefore, this area has high population density. On the other hand, desert soils, mountain soils, laterite soils are infertile so there is low densities in those areas.
Question 17.
Describe the journey of development of land transport from the days of humans as carriers and the cable ways of todays. [5]
Answer:
Land transport is an important part of India’s economy as most of the moment of goods takes place over land. In the early days, human beings themselves carried palki or doli on certain occasions such as marriage and ceremonies. Later, animals were used to carry load and treated as beasts of burden. Invention of the wheel revolutionised the means of transport-carts and wagons, railways steam engine, invention of combustion engine-motors, cars and trucks, pipelines, ropeways and cableways have made the life of human easy.
Question 18.
Census of India is the source of population data in India. [5]
Answer:
India has uneven distribution of the population. The population of India as per 2011 census was 1,210,193,422. India added 181.5 million to its population since 2001. India has 2.4% of the world’s surface area, accounts for 17.5% of its population. Uttar Pradesh is the most populous state with roughly 200 million people. A little over 5 out of 10 Indians live in the six states of Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Bihar, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh. The share of the population is very small in the states like Jammu and Kashmir, Arunachal Pradesh and Uttrakhand. This uneven spatial distribution of population in India suggests a close relationship between population and physical, social, economic and historical factors. Rugged terrain and unfavourable climatic conditions are primarily responsible for sparse population in some areas. Hilly, dissected and rocky nature of the terrain, moderate to low rainfall, shallow and less fertile soils influence population in hilly areas. Flat plains with fertile soils and abundant rainfall have resulted in large number of people to settle in the densely populated northern plains. The distribution of population in India is also governed by physical features, industrial development, urbanization, economic development, availability of natural resources, agricultural development, transport facilities etc.
Note : Except for the following questions, all the remaining questions have been asked in previous set.
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2015 Delhi Set – III
Question 10.
Explain any three physical factors responsible for different types of rural settlements in India. [3 × 1 = 3]
Answer:
Types of rural settlement are determined by the following physical factors :
- Climate : Very hot and very cold climate is unfavourable for rural settlements. Areas with favourable climate attract people to reside over that areas. North Indian plains, deltaic regions and coastal plains have larger population with compact settlements. In harsh climate regions scattered settlements are found.
- Fertile Soils : Fertile soils are important for agricultural and allied activities. Clustered settlements are generally found in fertile alluvial plains. They may be in rectangular, radical and linear shapes.
- Nature of Terrain : Shape and size of rural settlements are determined by the nature of terrain. In plain areas, the shape and size of rural settlements are compact or clustered and larger, having larger number of population. On the other hand, on hilly and mountain areas they are scattered and small in size. In such areas, dispersed settlements are found in the form of isolated huts. They are found in Meghalaya, Uttrakhand and Himachal Pradesh.
Question 13.
How do industries pollute India’s water bodies ? Explain with examples. [3]
Answer:
Industry is a main source of water pollution, it produces pollutants such as wastes, polluted waste water, poisonous gases, chemical residuals, numerous heavy metals, dust, smoke etc., that are extremely harmful to people and the environment. Many industrial facilities use freshwater to dispose waste from the plant into the rivers, lakes and oceans by directly or indirectly discharging pollutants into water bodies without adequate treatment. Pollution affects the entire biosphere including plants and organisms living in these water bodies. Major polluting industries are leather, pulp and paper, textiles and chemicals.
Question 14.
How is the mortality rate of a region affected ? Explain any four push factors responsible for emigration. [5]
Answer:
Mortality rate is a measure of the number of deaths in a particular population, per unit of time.
Mortality rate is expressed in units of deaths per 1,000 individuals per year. Mortality rate is affected by a region’s demographic structure, social advancement and level of economic development.
Push factors responsible for emigration are :
- Unemployment carries a lot of people who are unable to fend for their living outside the cities and countries in search of better opportunities.
- Poor living conditions
- Political turmoil
- Unpleasant climate
- Natural disasters
- Outbreak of Epidemics causes various diseases which may be life-threatening as well. This causes a lot of people to move out of the affected areas.
- Socio-economic backwardness
Question 17.
Which means of transport is extensively used for carry water, petroleum, natural gas and other liquids ? Describe the network of this means of transport in the world. [5]
Answer:
Pipelines are extensively used to carry water, petroleum, natural gas and other liquids for uninterrupted flow.
- In U.S.A. there is a dense network of oil pipelines from the producing areas to the consuming areas. Big Inch is a famous pipeline, which carries petroleum from the oil wells of the Gulf of Mexico to the North-eastern states.
- In Europe, Russia and West Asia pipelines are used to connect oil wells to refineries. COMECON a 4800 km long is the largest pipeline of the world. It transports mineral oil from Volga and Ural in Russia to east European countries.
- In the Middle East the oil is transported through pipeline from Saudi Arabia to Iraq and other countries and to the refineries located on the Mediterranean coast (6550 Km).
- In North India pipelines connect the oil wells to the refineries and then to the industrial belts.
- HBJ pipeline runs through the North Western India and it is extended to Delhi, it is important for the economic development of the region.
- The oil producing countries of central Asia i. e., Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan supply petroleum and natural gas through pipeline to Turkey and Russia.
Question 18.
“Development is general and human development in particular is a complex concept used in Social Science.” Justify this statement with suitable arguments. [5]
Answer:
No doubt human development is a complex concept because for ages it was thought that the development is a substantive concept. Once it is achieved it will address all the socio-cultural and environmental ills of the society. Though development has brought improvement in the quality of life but more than one way it has increased regional disparties social inequalities,.discrimination, depriviation and displacement of people.
Considering the gravity and sensitivity of the issues involved, the UNDP in its human development report, 1993 tried to amend some of the implicit biases and prejudices. People participation and their security were the major issues in the human development report of 1993. It also emphasised on progressive democratisation and increasing empowerment of people as minimum conditions for human development.
The ‘civil societies’ should work to building up opinion for reduction in the military expenditure. In a nuclearised world, peace and well being are major global concerns.






