Table of Contents
The periodic table of chemical elements is generally known as the periodic table. It is a chart in which all the discovered elements are organised in rows (called periods) and columns (called groups) based on their increasing atomic number. The periodic table is often used to get quick information about an element, like nuclear mass and chemical symbols. The regular table design also allows scientists to detect patterns in element properties such as electronegativity, ionization energy, and atomic radius.
Many scientists worked on the problem of grouping the elements, but in 1869, Dimitri Mendeleev published his version of the periodic table. Since then, the periodic table has changed to reflect almost 150 years of chemistry and physics technological progress and understanding. With 118 known elements today, it is often regarded as one of science’s most significant achievements in science.
Why was Mendeleev Periodic Table widely accepted?
Dimitri Mendeleev, often called the founding figure of the periodic table, introduced the initial version of the periodic table that resembles the one we currently use. However, there is a significant difference between Mendeleev’s approach and the way we organize the periodic table today.
Mendeleev organized his periodic table by arranging elements in order of increasing atomic mass. In contrast, the modern periodic table is organized by increasing atomic numbers.
Even though Mendeleev’s periodic table was based on the weight of atoms, he successfully predicted the existence and properties of certain elements. During his time, only about half of the elements we now know were discovered, and the information available about these elements was often incorrect. Mendeleev’s Periodic Table was published in the German Journal of Chemistry in 1869.
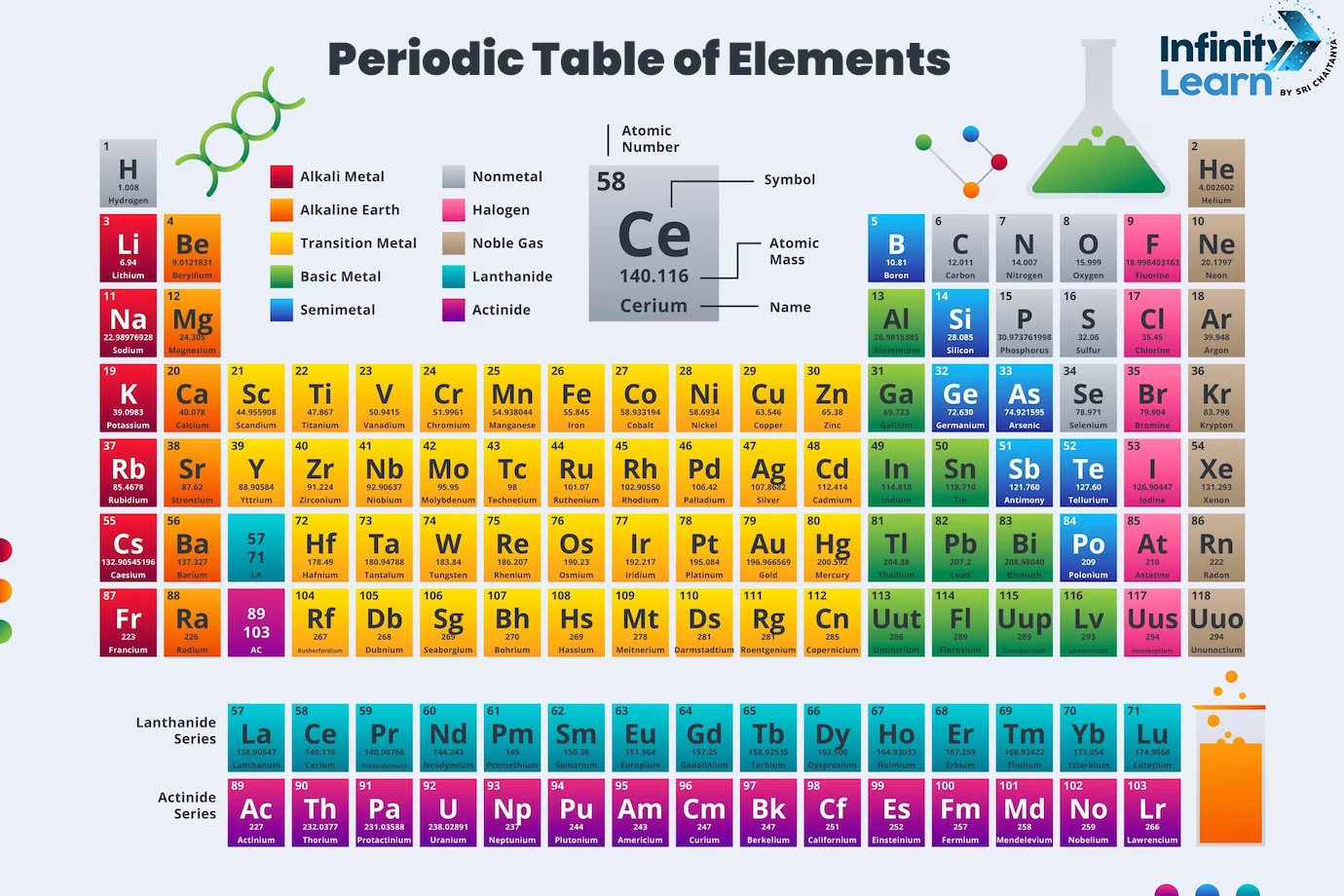
Periodic Table of Elements with Names, Symbols, and Atomic Number
All the elements of the Periodic Table are given below with their names and symbols.
| Periodic Table of Elements | ||||
| 1: H-
Hydrogen |
2: He-
Helium |
3: Li-
Lithium |
4: Be-
Beryllium |
5: B-
Boron |
| 6: C-
Carbon |
7: N-
Nitrogen |
8: O-
Oxygen |
9:F-
Fluorine |
10: Ne-
Neon |
| 11: Na-
Sodium |
12: Mg- Magnesium | 13: Al- Aluminum | 14: Si-
Silicon |
15: P- Phosphorus |
| 16: S-
Sulfur |
17. Cl-
Chlorine |
18: Ar-
Argon |
19: K- Potassium | 20: Ca-
Calcium |
| 21: Sc- Scandium | 22: Ti-
Titanium |
23: V-
Vanadium |
24: Cr-Chromium | 25: Mn- Manganese |
| 26:Fe- Iron |
27:Co-
Cobalt |
28: Ni-
Nickel |
29: Cu-
Copper |
30: Zn-
Zinc |
| 31: Ga-
Gallium |
32: Ge- Germanium | 33: As-
Arsenic |
34: Se- Selenium | 35: Br-
Bromine |
| 36: Kr-
Krypton |
37: Rb- Rubidium | 38: Sr- Strontium | 39: Y-
Yttrium |
40: Zr_Zirconium |
| 41: Nb-
Niobium |
42: Mo- Molybdenum | 43: Tc- Technetium | 44: Ru- Ruthenium | 45: Rh- Rhodium |
| 46: Pd-
Palladium |
47: Ag-
Silver |
48: Cd-
Cadmium |
49: In-
Indium |
50: Sn-
Tin |
| 51: Sb- Antimony | 52: Te-
Tellurium |
53: I-
Iodine |
54: Xe-
Xenon |
55: Cs-
Cesium |
| 56: Ba-
Barium |
57: La- Lanthanum | 58: Ce-
Cerium |
59: Pr-
Praseodymium |
60: Nd- Neodymium |
| 61: Pm- Promethium | 62: Sm-
Samarium |
63: Eu- Europium | 64: Gd- Gadolinium | 65: Tb-
Terbium |
| 66: Dy- Dysprosium | 67: Ho-
Holmium |
68: Er-
Erbium |
69: Tm
Thulium |
70: Yb- Ytterbium |
| 71: Lu-
Lutetium |
72: Hf-
Hafnium |
73: Ta-
Tantalum |
74: W-
Tungsten |
75: Re- Rhenium |
| 76: Os-
Osmium |
77: Ir-
Iridium |
78: Pt-
Platinum |
79: Au-
Gold |
80; Hg-
Mercury |
| 81: Tl-
Thallium |
82: Pb-
Lead |
83:Bi-
Bismuth |
84: Po- Polonium | 85: At-
Astatine |
| 86: Rn-
Radon |
87: Fr-
Francium |
88: Ra-
Radium |
89: Ac-
Actinium |
90: Th-
Thorium |
| 91: Pa- Protactinium | 92: U-
Uranium |
93: Np- Neptunium | 94: Pu- Plutonium | 95: Am- Americium |
| 96: Cm-
Curium |
97: Bk-
Berkelium |
98: Cf- Californium | 99: Es-
Einsteinium |
100: Fm- Fermium |
| 101: Md- Mendelevium | 102: No- Nobelium | 103: Lr-
Lawrencium |
104: Rf- Rutherfordium | 105: Db-
Dubnium |
| 106: Sg-
Seaborgium |
107: Bh- Bohrium | 108: Hs-Hassium | 109: Mt- Meitnerium | 110: Ds Darmstadtium |
| 111: Rg- Roentgenium | 112: Cn-
Copernicium |
113: Nh- Nihonium | 114: Fl-Flerovium | 115: Mc- Moscovium |
| 116: Lv- Livermorium | 117: Ts- Tennessine | 118: Og- Oganesson | ||
First 30 Elements of the Periodic Table with Chemical Symbols and Atomic Mass
- ATOMIC NUMBER: An atom’s atomic number equals the number of protons in its nucleus or the number of electrons in an electrically neutral atom.
- ATOMIC MASS: The mass of an atom is called its atomic mass. It shows how many times a bit of an element is heavier than one-twelfth (1/12th) the mass of one carbon atom. It is measured in amu (atomic mass unit).
The first 30 elements of the periodic table with chemical symbols and atomic mass are given below in the following table:
| ELEMENT | ATOMIC NUMBER | MASS NUMBER |
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 | 1 |
| Helium(He) | 2 | 4 |
| Lithium(Li) | 3 | 7 |
| Beryllium(Be) | 4 | 9 |
| Boron(B) | 5 | 11 |
| Carbon(C) | 6 | 12 |
| Nitrogen(N) | 7 | 14 |
| Oxygen(O) | 8 | 16 |
| Fluorine(F) | 9 | 19 |
| Neon(Ne) | 10 | 20 |
| Sodium(Na) | 11 | 23 |
| Magnesium(Mg) | 12 | 24 |
| Aluminum(Al) | 13 | 27 |
| Silicon(Si) | 14 | 28 |
| Phosphorous(P) | 15 | 31 |
| Sulfur(S) | 16 | 32 |
| Chlorine(Cl) | 17 | 35.5 |
| Argon(Ar) | 18 | 40 |
| Potassium(K) | 19 | 39 |
| Calcium(Ca) | 20 | 40 |
| Scandium (Sc) | 21 | 44.956 |
| Titanium (Ti) | 22 | 47.867 |
| Vanadium (V) | 23 | 50.942 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 24 | 51.996 |
| Manganese (Mg) | 25 | 54.938 |
| Iron (Fe) | 26 | 55.845 |
| Cobalt (Co) | 27 | 58.933 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 28 | 58.693 |
| Copper (Cu) | 29 | 63.546 |
| Zinc (Zn) | 30 | 65.38 |
What are the Types of Elements in the Periodic Table of Chemistry?
Elements are divided into four types;
-
- Metals: Metals are complex solid elements that are ductile, malleable, and good heat and electrical conductors. (Silver-Ag, Iron-Fe)
- Nonmetals: Nonmetals are drab and can exist as solids, liquids, or gases. (Oxygen-O, Carbon-C)
- Metalloids: Metalloids are elements with characteristics that fall somewhere between metals and nonmetals. (Silicon-Si, Germanium-Ge)
- Noble gasses: Noble gasses, often known as inert gasses, are a distinct class of elements that do not react with other ingredients. (Helium-He, Neon-Ne)
FAQs on Periodic Table of Elements
WHAT ARE ELEMENTS IN THE PERIODIC TABLE OF CHEMISTRY?
An element is a substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons: all traces of a given element have the same number of protons. Elements are the most basic chemical forms and cannot be broken down chemically.
WHAT ARE THE FIRST 20 ELEMENTS OF THE PERIODIC TABLE OF CHEMISTRY?
The first 20 elements are Hydrogen, Helium, Lithium, Beryllium, Boron, Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Fluorine, Neon, Sodium, Magnesium, Aluminium, Silicon, Phosphorus, Sulphur, Chlorine, Argon, Potassium, and Calcium
WHAT DOES THE MODERN PERIODIC TABLE MEAN?
The modern periodic table is based on contemporary periodic law. The table is an arrangement of elements in increasing atomic number order. In its current form, the periodic table is known as the modern periodic table. It has 18 vertical columns and 7 horizontal rows.
How many metals and non-metals are there in 118 elements?
The current periodic table contains 118 different elements. Out of these, 18 are non-metals, 7 are metalloids, and 93 are various kinds of metals.
What are the 4 blocks on the periodic table?
The elements in the periodic table are organized into groups based on the way their outermost electrons move. There are four groups called s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block.
Who found the first element of Periodic table?
In 1669, a chemist named Hennig Brandt made the first chemical discovery of an element called phosphorus.
How many elements are there in periodic table?
There are 118 different elements on the Periodic Table. According to the periodic law, the characteristics of these elements change in a regular pattern as you move from one element to another, based on their atomic numbers.
What is a group in a periodic table?
A group in the periodic table is like a vertical row of elements. Elements in the same group have similar features in the outermost part of their atoms, either in how they look or how they react with other substances.