Table of Contents
The national calendar of India is the Saka Calendar. It is used by the Government of India for official purposes alongside the Gregorian calendar. While the Saka Calendar is used for official and civil purposes, the Gregorian calendar is also widely used in India. The dual calendar system allows for coordination with international standards.
The Saka Calendar was officially adopted as the national calendar of India on March 22, 1957. This adoption aimed to promote a sense of national identity and pride. The Saka Calendar is based on the traditional Indian solar year and is used to determine the official dates of the Indian national holidays and other significant events. It is based on the Saka Era, which started in 78 CE when King Kanishka ascended the throne. The Saka Calendar is legally recognized in India and is used for official purposes, including determining dates for national holidays. The adoption of the Saka Calendar was a deliberate move to integrate India’s cultural and historical heritage into the nation’s official calendar, reinforcing a connection with traditional practices. There are several other regional calendars that are used in different states and communities in India, reflecting the country’s cultural diversity. Examples include the Vikram Samvat, Tamil calendar, and Bengali calendar.

Saka Calendar History
- The National Calendar of India, also known as the Saka calendar, is the official civil calendar in use in the country. The Saka Calendar starts from the year 78 AD of the Gregorian calendar. The beginning of the Saka Era is considered to be the conquest of the Saka ruler Kanishka over the Indo-Greeks.
- The calendar also accounts for the movement of the Sun and the Moon in relation to the constellations and assigns different zodiac signs to each month. This helps in determining the dates of various Hindu festivals and rituals. Important events, festivals and auspicious days in the Hindu calendar are acknowledged in the National Calendar of India. They are listed as gazetted holidays and people generally schedule their personal and professional activities based on these holidays.
- The Hindu calendar is used by Hindus for religious and social purposes. The Hindu calendar consists of different cycles of time, including days, months, years, and Yugas (ages). The months of the Hindu calendar are generally divided into two parts: the waxing phase of the moon and the waning phase of the moon. The months are named differently in different parts of India.
- The Saka Calendar aligns with various Hindu festivals and events. Its adoption aimed to synchronise national holidays with traditional Indian cultural and religious occasions.
- The Saka Calendar is a solar calendar, and its dates are determined based on the position of the sun. Festivals and holidays are calculated using astronomical principles.
- This calendar is used in many parts of India, particularly in government and administrative circles. However, many people also follow other regional calendars based on different traditions and lunar positions.
- The calendar consists of 12 months and each month is divided into two parts – Shukla Paksha (bright fortnight) and Krishna Paksha (dark fortnight). The first month in the National Calendar of India is Chaitra, which usually falls in March or April.
Types of Calendars in India
In Indian history, various calendars were established by rulers to mark the beginning of new eras or dynasties. Over time, these evolved into permanent calendars based on solar and lunar movements. In present-day India, there are four main types of calendars commonly used:
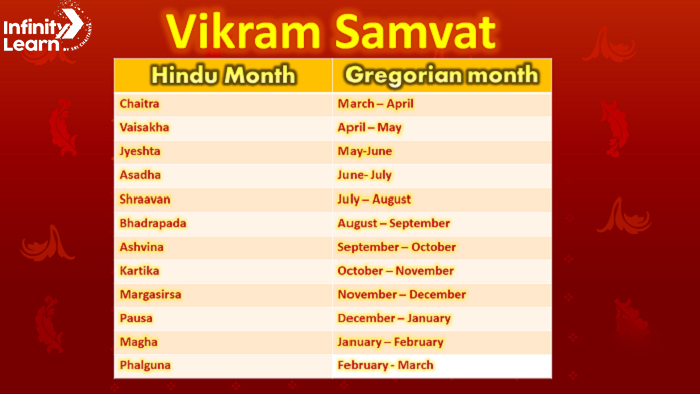
Vikram Samvat: This calendar is based on the Hindu solar calendar and begins in 57 BCE. It is named after King Vikramaditya and is widely used in North India, particularly by Hindus.
Saka Samvat: The Saka era calendar begins in 78 CE and is linked to the Shalivahana era. It’s used alongside the Vikram Samvat in some regions, especially in parts of western and southern India.
Hijri Calendar: The Islamic lunar calendar, also known as the Hijri calendar, is used by Muslims across India to mark religious events and festivals. It begins in 622 CE, which is the year of the Prophet Muhammad’s migration from Mecca to Medina.
Gregorian Calendar: Introduced by Pope Gregory XIII in 1582, this calendar is widely accepted internationally and is the standard civil calendar in India. It’s used for official purposes, administration, and in daily life, aligning with the global standard.
These calendars coexist and are often utilized for different purposes—religious, cultural, administrative, or personal—by various communities throughout India.
Saka Calendar Months Name List
The months of the National Calendar of India are:
1. Chaitra (March-April)
2. Vaisakha (April-May)
3. Jyeshtha (May-June)
4. Ashadha (June-July)
5. Shravana (July-August)
6. Bhadra (August-September)
7. Ashwin (September-October)
8. Kartika (October-November)
9. Agrahayana (November-December)
10. Pausha (December-January)
11. Magha (January-February)
12. Phalguna (February-March)
The first day of the year in this calendar is Chaitra 1, which usually falls on March 22 or 23. Each month contains important Hindu festivals and auspicious days, such as Diwali, Holi, Navratri, and more.
Saka Calendar and Gregorian Calendar
- The Saka calendar and Gregorian calendar are two different calendar systems used in different parts of the world. The Saka calendar, also known as the Indian national calendar, is the official calendar of India.
- Both the Saka calendar and Gregorian calendar are used in different parts of the world for different purposes.
While the Saka Calendar is used for official and civil purposes, the Gregorian calendar is also widely used in India, particularly in international contexts and for business transactions. - The Saka calendar is used to determine the dates of Hindu festivals and auspicious occasions. On the other hand, the Gregorian calendar is the most widely used calendar system in the world and is based on the solar cycle.
- The Gregorian calendar has 365 days in a year, except for leap years, which have an extra day. The calendar is divided into 12 months, and each month has either 30 or 31 days, except for February, which has 28 days, or 29 in a leap year. It was introduced by Pope Gregory XIII in 1582 and replaced the Julian calendar.
- The Gregorian calendar is used globally for scheduling and planning social and commercial activities.
Difference Between Saka Calendar and Gregorian Calendar
Below mentioned are some of the key differences between the Gregorian and Saka calendars:
1. Origin: The Gregorian calendar originated in Europe, while the Saka calendar originated in India.
2. Basis: The Gregorian calendar is a solar calendar, which means it is based on the movement of the Sun, while the Saka calendar is a lunar calendar.
3. Months: The Gregorian calendar consists of months with either 30 or 31 days, except for February, which has 28 days (or 29 days in a leap year), while the Saka calendar also consists of months with lengths ranging from 29 to 32 days.
4.Calendar day: In the Gregorian calendar, a new day starts at midnight, while in the Saka calendar, a new day starts at sunrise.
5. Usage: The Gregorian calendar is widely used across the world for civil and commercial purposes, while the Saka calendar is used primarily in India for determining the dates of Hindu festivals and auspicious occasions.
Important Facts about the National Calendar of India
● The saka calendar is a lunar calendar, and it consists of 12 months. Each month begins with a new moon day, and there are two fortnights in each month.
● The determination of dates in the Saka Calendar involves astronomical calculations.
● The Saka Calendar stands as a testament to India’s rich cultural history and its effort to blend tradition with the practicalities of contemporary life.
● The Saka Calendar consists of 12 months, and its months are named after the signs of the zodiac. For example, the month of Chaitra corresponds to Aries.
If you’re learning about India’s National Calendar, you can check out more about the country’s other important symbols in the table below.
Also Read Related Articles
| National Symbols of India | National Flag of India |
| National Emblem of India | National Anthem of India |
| National Bird of India | National Flower of India |
National Calendar Of India – Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the national calendar of India?
The national calendar of India is the Saka Calendar. It is used for official and civil purposes alongside the Gregorian calendar.
When was the Saka Calendar adopted as the national calendar?
The Saka Calendar was adopted as the national calendar of India on March 22, 1957, corresponding to the 1st day of Chaitra 1879 Saka Era.
How is the Saka Calendar different from the Gregorian calendar?
The Saka Calendar is a traditional Indian solar calendar, while the Gregorian calendar is a solar calendar used internationally. The starting point and calculation methods for these calendars differ.
What is the significance of adopting the Saka Calendar?
The adoption of the Saka Calendar aimed to emphasise India's historical and cultural heritage, aligning national holidays with traditional festivals and events.








