Table of Contents
Polymerase Chain Reaction MCQs for NEET Biology: Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a key technique in biology used to make many copies of a specific DNA or gene for study. This process is important when the available DNA is too small for analysis. PCR uses Taq DNA polymerase, an enzyme that works well in high temperatures, to replicate DNA. A machine called a thermocycler controls the temperature changes needed for the process. PCR is essential in biotechnology and is part of the CBSE Biology syllabus. For NEET preparation, understanding PCR concepts through MCQs is crucial for mastering topics in the biology syllabus and excelling in exams.
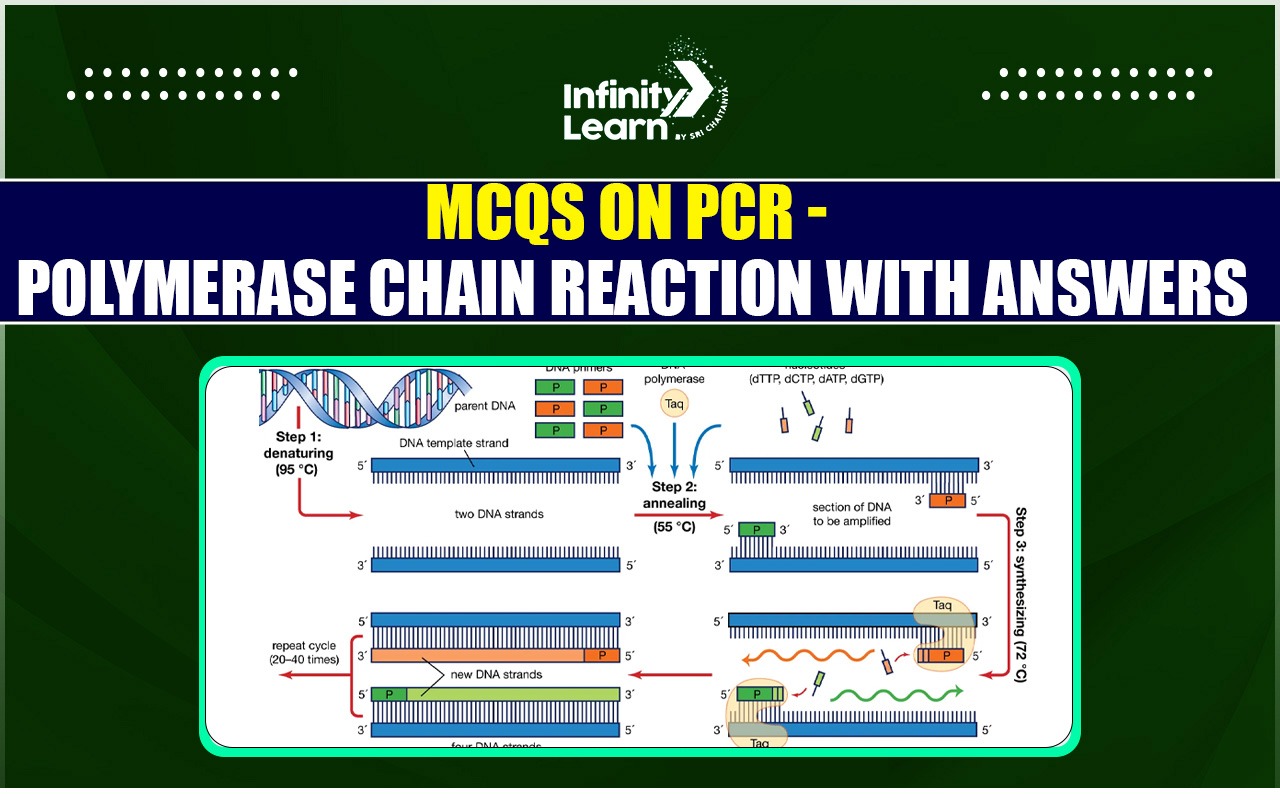
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) MCQ
In molecular biology, the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is an essential method for amplifying particular DNA segments. By replicating DNA sequences in a test tube, PCR allows for the creation of millions of copies of a target DNA fragment, which is crucial for further analysis. The process involves three key steps: denaturation, annealing, and extension, with the help of the enzyme Taq DNA polymerase. PCR has wide applications in genetic research, diagnostics, forensic science, and medical fields, including the detection of genetic disorders.
For Class 12 Biology, understanding PCR is essential as it forms a part of the syllabus and helps in answering questions related to biotechnology, genetics, and molecular biology. A solid grasp of PCR can significantly enhance a student’s ability to tackle related topics in the Class 12 and NEET exam.
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) MCQ with Answers
Q1. What is the primary purpose of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)?
a) To isolate DNA
b) To amplify DNA
c) To sequence DNA
d) To replicate cells
Answer: b) To amplify DNA
Q2. Which enzyme is used in PCR for DNA amplification?
a) DNA polymerase
b) RNA polymerase
c) Taq DNA polymerase
d) Ligase
Answer: c) Taq DNA polymerase
Q3. What temperature is used during the denaturation step of PCR?
a) 25°C
b) 50°C
c) 95°C
d) 75°C
Answer: c) 95°C
Q4. Which of the following is the correct order of steps in PCR?
a) Denaturation → Annealing → Extension
b) Annealing → Denaturation → Extension
c) Extension → Denaturation → Annealing
d) Denaturation → Extension → Annealing
Answer: a) Denaturation → Annealing → Extension
Q5. What is the role of primers in PCR?
a) To synthesize RNA
b) To provide a starting point for DNA synthesis
c) To cut the DNA
d) To heat the DNA
Answer: b) To provide a starting point for DNA synthesis
Q6. Which device is used to control the temperature during PCR?
a) Centrifuge
b) Thermocycler
c) Incubator
d) Gel electrophoresis unit
Answer: b) Thermocycler
Q7. In which stage of PCR does DNA replication take place?
a) Denaturation
b) Extension
c) Annealing
d) Termination
Answer: b) Extension
Q8. In PCR, which of the following is used to separate DNA strands?
a) Taq polymerase
b) High temperature
c) Restriction enzymes
d) Gel electrophoresis
Answer: b) High temperature
Q9. What is the typical number of cycles in a PCR reaction?
a) 5-10 cycles
b) 10-20 cycles
c) 20-40 cycles
d) 50-100 cycles
Answer: c) 20-40 cycles
Q10. What is the typical temperature for the annealing step in PCR?
a) 50-60°C
b) 70-80°C
c) 85-95°C
d) 25-30°C
Answer: a) 50-60°C
Q11. Which of the following is not essential for a PCR process?
a) Taq DNA polymerase
b) Nucleotides (dNTPs)
c) Reverse transcriptase
d) Primers
Answer: c) Reverse transcriptase
Q12. How many copies of the target DNA are typically produced after 30 cycles of PCR?
a) 1 million
b) 1 billion
c) 1 thousand
d) 10 billion
Answer: d) 10 billion
Q13. What is the role of magnesium ions (Mg²⁺) in PCR?
a) Stabilize the primers
b) Activate the polymerase enzyme
c) Help in DNA denaturation
d) Separate DNA strands
Answer: b) Activate the polymerase enzyme
Q14. What is the primary difference between PCR and DNA replication in cells?
a) PCR uses RNA primers
b) PCR occurs at room temperature
c) PCR amplifies specific DNA segments
d) DNA replication does not require enzymes
Answer: c) PCR amplifies specific DNA segments
Q15. Which of the following is NOT a type of PCR?
a) Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-PCR)
b) Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
c) Real-Time PCR (RT-PCR)
d) Microarray PCR
Answer: d) Microarray PCR
Q16. What is the final product of a PCR reaction?
a) Single-stranded RNA
b) Double-stranded DNA
c) Proteins
d) Single-stranded DNA
Answer: b) Double-stranded DNA
Q17. Which step of PCR involves lowering the temperature to allow primers to bind to the DNA?
a) Denaturation
b) Annealing
c) Extension
d) Replication
Answer: b) Annealing
Q18. Which of the following is NOT used in PCR?
a) Thermocycler
b) RNA polymerase
c) DNA primers
d) Taq DNA polymerase
Answer: b) RNA polymerase
Q19. Which type of DNA polymerase is used in PCR due to its heat resistance?
a) E. coli DNA polymerase
b) Taq DNA polymerase
c) Human DNA polymerase
d) Reverse transcriptase
Answer: b) Taq DNA polymerase
Q20. What is a key feature of PCR that allows it to amplify specific regions of DNA?
a) Use of RNA primers
b) High temperature denaturation
c) Sequence-specific primers
d) Use of enzymes to cut DNA
Answer: c) Sequence-specific primers
Q21. Which of the following is a limitation of PCR? a) Amplifies all DNA sequences equally
b) Requires a large amount of DNA
c) Cannot amplify DNA
d) Requires very specific primers
Answer: d) Requires very specific primers
Q22. How does a thermocycler work in PCR?
a) It supplies a constant temperature
b) It cycles through different temperature ranges
c) It separates DNA strands
d) It adds nucleotides to DNA strands
Answer: b) It cycles through different temperature ranges
Q23. Which of the following is used as the template in PCR?
a) mRNA
b) cDNA
c) DNA
d) Protein
Answer: c) DNA
Q24. Which type of PCR is used for measuring gene expression levels?
a) Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
b) Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-PCR)
c) PCR-RFLP
d) Nested PCR
Answer: a) Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
Q25. What is the function of the extension step in PCR?
a) To separate the DNA strands
b) To synthesize new DNA strands
c) To bind the primers to the DNA
d) To denature the DNA
Answer: b) To synthesize new DNA strands
Q26. What is the denaturation temperature required in PCR?
a) 70°C
b) 90°C
c) 95°C
d) 100°C
Answer: c) 95°C
Q27. What does PCR stand for?
a) Polymerase Catalyzed Reaction
b) Proliferation Chain Reaction
c) Polymerase Chain Reaction
d) Protease Chain Reaction
Answer: c) Polymerase Chain Reaction
Q28. Which of the following is true about PCR?
a) It can amplify a single DNA strand
b) It does not require a thermocycler
c) It can amplify DNA from minute amounts
d) It can replicate genes only in bacteria
Answer: c) It can amplify DNA from minute amounts
Q29. Which product is created during the extension step in PCR?
a) RNA
b) DNA
c) Protein
d) RNA primers
Answer: b) DNA
Q30. What does the term “thermocycling” in PCR refer to?
a) Rapid cooling of DNA
b) The use of Taq polymerase
c) Repeated temperature cycles for DNA amplification
d) Heating DNA to break bonds
Answer: c) Repeated temperature cycles for DNA amplification




