Table of Contents
Chandigarh is the capital of Haryana. It is also the capital of Punjab. This city is special because it is the capital for two states. Chandigarh is known for its good design and buildings. It is an important city for both Haryana and Punjab. The choice of Chandigarh as the capital of Haryana is a big part in the history of Haryana.
Capital of Haryana State
Chandigarh, the capital of Haryana State, is unique as it also serves as the capital of Punjab. This city, established post-Indian independence, is renowned for its modern design, planned by architect Le Corbusier. Its creation followed the division of Punjab in 1966, leading to Haryana’s formation.
As a joint capital, Chandigarh is an important administrative and cultural hub. It’s known for its well-planned layout and green spaces, making it one of India’s most livable cities. The city’s governance is unique too; it’s a union territory, governed directly by India’s Central Government.
Chandigarh’s role as the capital of Haryana has been pivotal in the state’s political and historical narrative, symbolizing modern urban development and effective administrative planning.
Why Chandigarh is Capital of Punjab and Haryana
Reason behind the Chandigarh being the capital of both Punjab and Haryana due to historical and logistical reasons. Initially, after India’s partition in 1947, Punjab needed a new capital since its former capital, Lahore, became part of Pakistan. Chandigarh was designed as a modern city by the architect Le Corbusier for this purpose.
In 1966, when Punjab was divided to create the new state of Haryana, Chandigarh, with its developed infrastructure and central location, was chosen as the shared capital for both states. This decision also stemmed from its status as a well-planned, modern city.
Moreover, as a Union Territory, Chandigarh is directly governed by the Central Government of India. This unique governance model allows it to efficiently serve as a neutral administrative center for both Punjab and Haryana, justifying its role as a shared capital.
| Union Territories of India | Most Populated States in India |
| 7 Continents and 5 Oceans | List of US State Capitals |
Capital of Haryana Before Chandigarh
Before Chandigarh became the capital of Haryana, the region was part of the larger Punjab state, and did not have its own separate capital. Originally, Lahore was the joint capital of Punjab and Haryana when Haryana was still a part of Punjab. After India’s partition in 1947, Lahore became a part of Pakistan, and Chandigarh was planned and built as a new capital. In 1966, when Haryana was formed, Chandigarh was chosen as its capital. Thus, before the establishment of Chandigarh, the capital of Haryana was effectively shared with Punjab, first in Lahore and then in Chandigarh itself.
Capital of Haryana on Map
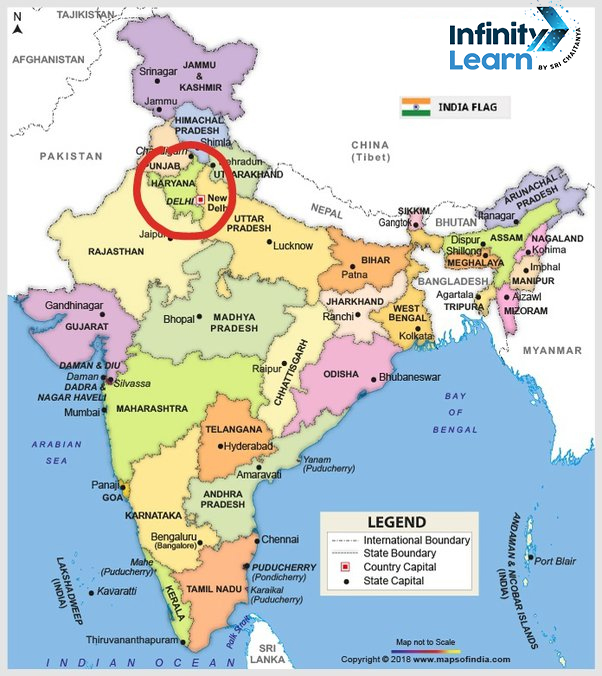
Chandigarh the Capital of Haryana
- Chandigarh’s Establishment: Designed by Swiss-French architect Le Corbusier, known for its modern architecture and urban planning.
- Unique Dual Capital: Serves as the capital of both Haryana and Punjab, a rare instance of a city being the capital for two states.
- Status as a Union Territory: Governed directly by the Central Government of India, unlike most other state capitals in India.
- Language Diversity: Predominantly Hindi-speaking, with widespread use of Punjabi, English, and other regional languages.
- Climate: Experiences distinct seasons, with hot summers, pleasant springs and autumns, and cool winters.
- Cultural Hub: Hosts various cultural events, festivals, and has a rich cultural heritage.
- Educational Excellence: Home to prestigious institutions, making it an educational hub in North India.
- Healthcare Facilities: Boasts advanced medical institutions, providing top-notch healthcare services.
- Tourist Attractions: Famous for its Rock Garden, Sukhna Lake, Rose Garden, and well-planned sectors.
- Green City: Notable for its greenery, with numerous parks and a well-maintained environment.
- Economic Growth: Chandigarh has a growing industrial base and is a key player in the region’s economy.
- Administrative Importance: As a capital, it holds significant administrative offices for both Haryana and Punjab.
- Urban Infrastructure: Known for its wide, tree-lined boulevards, and distinct urban layout.
- Public Transport: Efficient public transport system, including buses and a well-planned road network.
- Quality of Life: Often ranked high for its quality of living standards among Indian cities.
Overview of Haryana
- Formation of Haryana: Established in 1966 when it was carved out of the larger Punjab state.
- Capital of Haryana: Chandigarh, which is also the capital of Punjab and a Union Territory.
- Population of Haryana: Diverse population contributing significantly to agriculture and industry.
- Area of Haryana: Spans a considerable area in North India, sharing borders with several states.
- Language of Haryana: Primary language is Haryanvi, a Hindi dialect; Punjabi, Hindi, and English are also widely spoken.
- History of Haryana: Rich cultural heritage, with historical significance dating back to Vedic times and the epic Mahabharata.
- Climate of Haryana: Experiences extreme weather, including hot summers, cold winters, and a distinct monsoon season.
- Haryana CM (Chief Minister): Plays a vital role in state governance, focusing on development sectors like agriculture and industry.
- Agricultural Dominance: Known for its significant contributions to India’s wheat and rice production.
- Industrial Growth: Haryana has a growing industrial base, contributing to India’s economy.
- Cultural Diversity: Hosts various cultural festivals and events, reflecting a rich tradition.
- Educational Hub: Home to several prestigious educational institutions.
- Tourism in Haryana: Attractions include historical sites, natural parks, and cultural landmarks.
- Economic Contributions: Apart from agriculture, Haryana is known for its automobile, IT, and biotechnology industries.
- Sports Culture: Has a strong tradition in sports, particularly wrestling and boxing, producing many renowned athletes.
- Transport Infrastructure: Well-connected by road, rail, and air, facilitating robust intra-state and inter-state connectivity.
- Environmental Initiatives: Focus on sustainable development and green practices in urban areas.
- Healthcare Services: Boasts a network of hospitals and healthcare centers, focusing on public health.
- Rural Development: Continuous efforts in improving rural infrastructure and living standards.
- Governance and Administration: Effective administrative framework for the development and management of the state.
FAQs on Capital of Haryana
Which state has a joint capital with Haryana?
The Indian state of Punjab shares its capital, Chandigarh, with the neighboring state of Haryana. Chandigarh serves as the union territory and capital for both states, symbolizing cooperation and shared administration.
Which state has two capitals with the same name?
Both Haryana and Punjab have chosen Chandigarh as their capital city. This unique arrangement results in two states having the same capital, Chandigarh, which is centrally located between them.
What is the capital of Punjab and Haryana?
The capital of both Punjab and Haryana is Chandigarh. It is a well-planned city that serves as the seat of government for both states, facilitating administrative efficiency and collaboration.
What is the capital of Haryana?
The capital of Haryana is Chandigarh. This carefully planned city serves as the political and administrative center of Haryana, facilitating governance and public services for the state's residents.
Why is Chandigarh the capital of Punjab and Haryana?
Chandigarh was selected as the capital for both Punjab and Haryana due to its strategically central location between the two states. This decision aimed to promote unity and equitable access to the capital city, fostering cooperation and development between the neighboring states.








