Table of Contents
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Light
The NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Electric Current and its Effects are crucial for the students of 7th standard. The solutions are provided here to help students understand the chapter in an easy and interesting way. These NCERT Exemplar Solutions are created by subject experts according to the latest CBSE syllabus (2023-2024). Students must practice these solutions regularly to prepare effectively for their examinations. Check out Chapter 15 Class 7 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions given in PDF form.
Getting well versed with electric current Class 7 concepts is very crucial for students. Current topics given in NCERT Class 7 textbooks play a pivotal role in examinations. It is very important to practice the symbols, circuit diagrams, formulae, and problems to score good marks. At Infinity Learn, downloadable files of e-books, notes, pdf, solved previous year question papers are available for students to start their exam preparation without delay.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Boojho and Paheli were given one mirror each by their teacher. Boojho found his image to be erect and of the same size whereas Paheli found her image erect and smaller in size. This means that the mirrors of Boojho and Paheli are, respectively
(a) plane mirror and concave mirror.
(b) concave mirror and convex mirror.
(c) plane mirror and convex mirror.
(d) convex mirror and plane mirror.
Solution: (c) Plane mirror forms erect and same size image while convex mirror forms erect and smaller size image.
Question 2. Which of the following can be used to form a real image?
(a) Concave mirror only.
(b) Plane mirror only.
(c) Convex mirror only.
(d) Both concave and convex mirrors.
Solution: (a)
Question 3. If an object is placed at a distance of 0.5 m in front of a plane mirror, the distance between the object and the image formed by the mirror will be
(a) 2 m
(b) 1 m
(c) 0.5 m
(d) 0.25 m
Solution: (b) Distance between object and mirror + distance between mirror and image = (0.5 + 0.5) m = 1 m
Question 4. You are provided with a concave mirror, a convex mirror, a concave lens and a convex lens. To obtain an enlarged image of an object you can use either
(a) concave mirror or convex mirror.
(b) concave mirror or convex lens.
(c) concave mirror or concave lens.
(d) concave lens or convex lens.
Solution: (b)
Question 5. A rainbow can be seen in the sky
(a) when the sun is in front of you.
(b) when the sun is behind you.
(c) when the sun is overhead.
(d) only at the time of sun rise.
Solution: (b) Rainbow appears usually after the rain when the sun is low in the sky and you can see a rainbow only when your back is towards the sun.
Question 6. An erect and enlarged image can be formed by
(a) only a convex mirror.
(b) only a concave mirror.
(c) only a plane mirror.
(d) both convex and concave mirrors.
Solution: (b)
Question 7. You are provided with a convex mirror, a concave mirror, a convex lens and a concave lens. You can get an inverted image from
(a) both concave lens and convex lens.
(b) both concave mirror and convex mirror.
(c) both concave mirror and convex lens.
(d) both convex mirror and concave lens.
Solution: (c)
Question 8. An image formed by a lens is erect. Such an image could be formed by a
(a) convex lens provided the image is smaller than object.
(b) concave lens provided the image is smaller than object.
(c) concave lens provided the image is larger than object.
(d) concave lens provided the image is of the same size.
Solution: (b) Image formed by a concave lens is always virtual, erect and smaller in size than the object.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 9. The image formed by a lens is always virtual, erect and smaller in size for an object kept at different positions in front of it. Identify the nature of the lens.
Solution: Image formed by a concave lens is always virtual, erect and smaller in size than the object kept at different positions in front of it.
Question 10. Fill in the blanks:
(a) The inner surface of a steel spoon acts as a ________ mirror.
(b) The outer surface of a flat steel plate acts as a ________ mirror.
(c) The outer shining surface of a round bottom steel bowl acts as a ________ mirror.
(d) The inner surface of the reflector of a torch acts as a ________ mirror.
Solution:
(a) concave
(b) plane
(c) convex
(d) concave
Question 11. State whether the following statements are True or False.
(a) A concave lens can be used to produce an enlarged and erect image.
(b) A convex lens always produces a real image.
(c) The sides of an object and its image formed by a concave mirror are always interchanged.
(d) Art object can be seen only if it emits light.
Solution:
(a) False
(b) False
(c) True
(d) False
Question 12. What type of mirror is used as a side mirror in a scooter? Why is this type of mirror chosen?
Solution: Convex mirror is used as a side mirror in a scooter. This type of mirror is chosen as it forms a smaller and virtual image. So, it can be used to see a much larger area than the area visible by a plane mirror.
Question 13. Observe the given figures carefully.
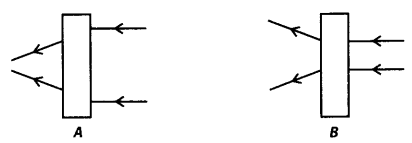
The given figures show the path of light through lenses of two different types, represented by rectangular boxes A and B. What is the nature of lenses A and B?
Solution: Lens A is convex lens or converging lens. Lens B is concave lens or diverging lens.
Question 14. Boojho made light from a laser torch to fall on a prism. Will he be able to observe a band of seven colours? Explain with a reason.
Solution: No, Boojho will not be able to observe a band of seven colours as laser torch is monochromatic so it gives out light of only one colour.
Question 15. State the correct sequence (1-7) of colours in the spectrum formed by the prisms A and B, shown in figure.
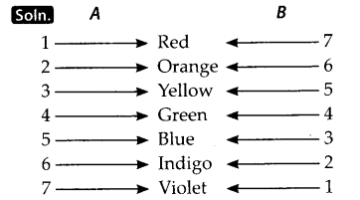
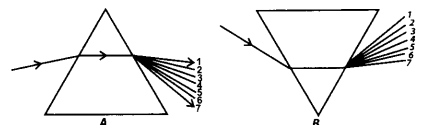
Question 16. The side mirror of a scooter got broken. The mechanic replaced it with a plane mirror. Mention any inconvenience that the driver of the scooter will face while using it?
Solution: Convex mirror is used as rear view mirror in vehicles. If it is replaced with a plane mirror then driver of the scooter will not be able to see traffic spread over a large area behind him.
Question 17. The concave reflecting surface of a torch got rusted. What effect would this have on the beam of light from the torch?
Solution: The beam of light from the torch will be diffused with lower intensity due to rusted reflecting surface.
Question 18. An erect and enlarged image of an object is formed on a screen. Explain how this could be possible.
Solution: An erect and enlarged image of an object can be obtained on a screen if the object is placed upside down between principal focus and twice the length of principal focus of the convex lens.
Question 19. Two different type of lenses are placed on a sheet of newspaper. How will you identify them without touching?
Solution: If it is a convex lens, then the letters of newspaper will appear bigger/magnified and if it is a concave lens, then the letters will appear smaller.
Question 20. A shopkeeper wanted to fix a mirror which will give a maximum view of his shop. What type of mirror should he use? Give reason.
Solution: He should use a convex mirror as it can form images of objects spread over a large area.
Question 21. The distance between an object and a convex lens is changing. It is noticed that the size of the image formed on a screen is decreasing. Is the object moving in a direction towards the lens or away from it?
Solution: In the case of convex lens, as the object moves away from it, the size of the image formed on a screen decreases.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 22. Suppose we wish to obtain the real image of a distant tree. Explain two possible ways in which we can do it.
Solution:
Two possible ways in which the real image of a distant tree can be obtained are given below :
(i) By using a concave mirror and a screen. In a concave mirror, a real image is formed if the distance between the mirror and the object is beyond the focus.
(ii) By using a convex lens and a screen. In a convex lens, when the object is far away from the lens, the image is very close to the lens, real and inverted.
Question 23. lt was observed that when the distance between an object and a lens decreases, the size of the image increases. What is the nature of this lens? If you keep on decreasing the distance between the object and the lens, will you still able to obtain the image on the screen? Explain.
Solution: It is a convex lens. If we keep on decreasing the distance between the object and the tens, the size of image increases. But when object comes between principal focus and lens then a magnified, virtual and upright image is formed. So, we will not be able to obtain the image on screen as it will be a virtual image.
Question 24. You are given three mirrors of different types. How will you identify each one of them?
Solution: We are given three different types of mirrors. To identify each one of them we will take an object and place it at different positions. Accordingly, we will get the positions of the image and nature of the image for each mirror, through which mirrors can be identified.
| Properties of image formed | Plane mirror | Concave mirror | Convex mirror |
| Real or virtual | Virtual | Real except when the object is near the mirror | Virtual |
| Erect or inverted | Always erect | Inverted when real and erect when virtual | Always erect |
| Size of image | Image formed is of the same size as the object | Diminished for certain positions and enlarged for others | Always diminished |
Also Read: NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 16 Water : A Precious Resource
FAQ’s 0n NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light
Where can I get the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15?
You can get the most detailed and accurate solutions from Infinity Learn. The top educators who possess excellent subject knowledge have designed these solutions as per the needs of the students. The solutions are framed according to the latest syllabus of the CBSE board to help students score well in the annual exam. So these solutions are present in PDF format which can be downloaded and accessed from the links available at Infinity Learn. The solutions can be referred by the students anywhere and at any time without any restrictions.
What are the concepts covered in Chapter 15 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science?
he concepts covered in Chapter 15 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science are – 1. Symbols of Electric Components, 2. Heating effect of electric current, 3. Magnetic effect of electric current, 4. Electromagnet, 5. Electric bell.
Are the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 free of cost?
Yes, the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 15 is absolutely free of cost. The chapter wise and exercise wise PDF links are present at Infinity Learn which can be downloaded and accessed by the students based on their needs. For a good score in the annual exam, students should refer to the solutions while answering the questions present in the textbook. All the important concepts are covered in the solutions to help students gain a grip on the concepts which are important from the exam point of view. By regular practice, students will be able to analyse the areas in which they are weak and work on them for better academic performance.






