CBSE Class 11 Maths Notes Chapter 13 Limits and Derivatives
Limit
Let y = f(x) be a function of x. If at x = a, f(x) takes indeterminate form, then we consider the values of the function which is very near to a. If these value tend to a definite unique number as x tends to a, then the unique number so obtained is called the limit of f(x) at x = a and we write it as \(\lim _{ x\rightarrow a }{ f(x) }\).
Left Hand and Right-Hand Limits
If values of the function at the point which are very near to a on the left tends to a definite unique number as x tends to a, then the unique number so obtained is called the left-hand limit of f(x) at x = a, we write it as
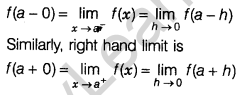
Existence of Limit
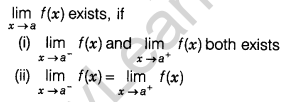
Some Properties of Limits
Let f and g be two functions such that both \(\lim _{ x\rightarrow a }{ f(x) }\) and lim \(\lim _{ x\rightarrow a }{ g(x) }\) exists, then
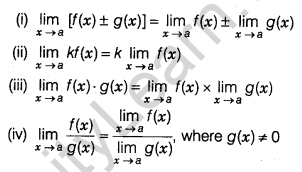
Some Standard Limits
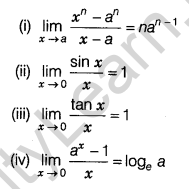
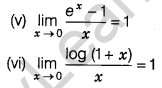
Derivatives
Suppose f is a real-valued function, then

Fundamental Derivative Rules of Function
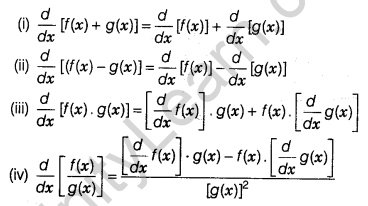
Let f and g be two functions such that their derivatives are defined in a common domain, then
Some Standard Derivatives






