Sodium citrate is a compound represented by the formula Na3C6H5O7. It is a white crystalline powder that is highly soluble in water. It is commonly used as a food additive and preservative, as well as in medical and pharmaceutical applications. Sodium citrate is also utilized in industrial processes such as water treatment and metal cleaning.
Formula of Sodium citrate
The formula for sodium citrate is Na3C6H5O7.
The chemical formula for sodium citrate is Na3C6H5O7. Sodium citrate is a salt that consists of three sodium ions (Na+) and the citrate ion (C6H5O7-) combined together.
The citrate ion, C6H5O7-, is derived from citric acid, which is a weak organic acid. The citrate ion has three carboxyl groups (COOH) and one hydroxyl group (OH) attached to a six-carbon ring structure. In sodium citrate, three sodium ions replace three of the hydrogen ions in the citrate ion, resulting in a more stable ionic compound.
The formula Na3C6H5O7 indicates that sodium citrate contains three sodium ions for every citrate ion. This balanced combination ensures that the compound has a neutral charge overall.
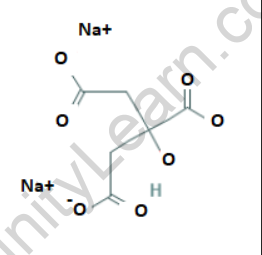
Structure of Sodium citrate
Sodium citrate consists of sodium ions (Na+) and citrate ions (C6H5O7-). The citrate ion is a tricarboxylate ion, composed of three carboxyl groups (-COO-) attached to a central carbon atom.
Physical properties of Sodium citrate
Sodium citrate is a white, crystalline powder or granules. It is highly soluble in water, but insoluble in organic solvents. The chemical formula of sodium citrate corresponds to a molar mass of approximately 258.07 g/mol.
Chemical properties of Sodium citrate
Sodium citrate is an alkaline compound and acts as a weak base in aqueous solutions. It can undergo acid-base reactions, forming citric acid when reacted with strong acids. Sodium citrate can also undergo hydrolysis, releasing citrate ions in solution.
Uses of Sodium citrate
Sodium citrate has various uses in different fields, including:
– Food and beverage industry: Sodium citrate is commonly used as a food additive, particularly as a preservative, flavor enhancer, and pH regulator. It can stabilize and emulsify food products, prevent crystallization in certain foods, and improve the shelf life of processed foods.
– Medical applications: Sodium citrate is used in medical settings as an anticoagulant for blood and plasma. It helps prevent blood clotting by binding to calcium ions and inhibiting coagulation. Sodium citrate is also used as a urine alkalizer to treat certain urinary tract disorders.
– Pharmaceutical formulations: Sodium citrate is used in the formulation of various pharmaceutical products, including tablets, powders, and solutions. It can act as a buffering agent, providing pH stability to medications.
– Laboratory applications: Sodium citrate is utilized in laboratories for various purposes, such as in chemical analysis and as a component of buffer solutions. It can help maintain a constant pH in reactions and experiments.
Sodium citrate Conclusion
Sodium citrate is commonly used as a food additive, pharmaceutical ingredient, and buffering agent. It is used in food and beverage applications as a flavoring agent, preservative, and acidity regulator. In pharmaceuticals, sodium citrate is used as a buffering agent to control the pH of medications and as an anticoagulant in blood transfusions. It also finds applications in cosmetics and personal care products.
Overall, the chemical formula Na3C6H5O7 represents sodium citrate, a versatile compound with various uses in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Solved example on Sodium citrate Example 1: How many moles of Sodium citrate (Na3C6H5O7) are present in 100 grams of the compound?
Solution: To calculate the number of moles, we need to divide the given mass by the molar mass of Sodium citrate.
Molar mass of Sodium citrate = (3 * Na) + (6 * C) + (5 * H) + (7 * O)
= (3 * 22.99) + (6 * 12.01) + (5 * 1.01) + (7 * 16.00)
= 258.07 g/mol
Moles = Mass / Molar mass
= 100 g / 258.07 g/mol
≈ 0.387 moles
Therefore, there are approximately 0.387 moles of Sodium citrate in 100 grams of the compound.
Example 2: How many atoms of oxygen are present in 5 moles of Sodium citrate (Na3C6H5O7)?
Solution: To calculate the number of oxygen atoms, we need to multiply the number of moles by the number of oxygen atoms present in one molecule of Sodium citrate.
Number of oxygen atoms = Number of moles * Avogadro’s number * Number of oxygen atoms per molecule
Number of oxygen atoms per molecule = 7 (from the formula Na3C6H5O7)
Avogadro’s number = 6.022 × 10^23
Number of oxygen atoms = 5 moles * 6.022 × 1023 * 7
= 2.1114 × 1025
Frequently asked Question on Sodium Citrate
1: What is the chemical formula of Sodium citrate?
Answer: The chemical formula of Sodium citrate is Na3C6H5O7.
2: What is the molar mass of Sodium citrate?
Answer: The molar mass of Sodium citrate is calculated by adding up the atomic masses of the elements present in the formula. In the case of Sodium citrate (Na3C6H5O7), the molar mass is approximately 258.07 g/mol.
3: What is the structure of Sodium citrate?
Answer: Sodium citrate has a triclinic crystal structure. It consists of sodium ions (Na+) and citrate ions (C6H5O7-) arranged in a specific three-dimensional arrangement.
4: What are the physical properties of Sodium citrate?
Answer: Sodium citrate is a white crystalline powder that is highly soluble in water. It has a salty taste and is odorless. It has a melting point of around 300°C and is stable under normal conditions.
5: What are the uses of Sodium citrate?
Answer: Sodium citrate has various applications in different fields. It is commonly used as a food additive and preservative, particularly in the food and beverage industry. It is also used in medical and pharmaceutical applications as an anticoagulant and as a component in oral rehydration solutions. Additionally, Sodium citrate is used in certain industrial processes, such as water treatment and metal cleaning.
6: Is sodium citrate soluble in water?
Answer: Sodium citrate is highly soluble in water. It readily dissolves in water, forming a clear and colorless solution. The solubility of sodium citrate in water is due to its ionic nature, where the sodium ions (Na+) and citrate ions (C6H5O7-) dissociate and become surrounded by water molecules.
7: What is another name for sodium acid citrate?
Answer: Another name for sodium acid citrate is sodium hydrogen citrate. Sodium acid citrate is the monosodium salt of citric acid, where one of the three hydrogen ions of citric acid is replaced by a sodium ion. It is also known by its chemical name, sodium 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate.
8: Is sodium citrate natural?
Answer: Sodium citrate can occur naturally, as it is found in citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, and limes. However, the sodium citrate used commercially is usually produced through a chemical process using citric acid and sodium hydroxide.
9: What is citric acid pH?
Answer: The pH of citric acid is relatively low. Pure citric acid has a pH around 2.2, indicating that it is acidic. However, the pH of a citric acid solution can vary depending on its concentration and dilution. When dissolved in water, citric acid acts as a weak acid and can lower the pH of the solution. The exact pH of a citric acid solution depends on the concentration of the acid and the presence of other substances in the solution.



