Table of Contents
Introduction to Ammonium Acetate Formula
Ammonium acetate (NH4C2H3O2) is an inorganic compound that consists of ammonium ions (NH4+) and acetate ions (C2H3O2-). It is commonly used in various scientific and industrial applications due to its unique properties. Ammonium acetate is a white, crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. It has a slightly acetic or vinegar-like odor
Structural Formula of Ammonium Acetate Formula
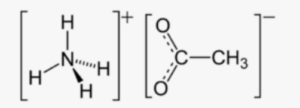
In the structural formula, the central nitrogen (N) atom is surrounded by four hydrogen (H) atoms, representing the ammonium ion (NH4+). The carbon (C) atoms are linked by a double bond, and one carbon atom is bonded to an oxygen (O) atom, representing the acetate ion (C2H3O2-).
Uses of Ammonium Acetate
- Buffer Solution: Ammonium acetate is commonly used as a buffer solution in laboratory settings. It helps maintain a stable pH in chemical reactions and biological experiments, particularly in the pH range of around 4 to 6.
- Chemical Reagent: Ammonium acetate is used as a chemical reagent in various organic synthesis reactions. It can act as a source of acetate ions, which can participate in various chemical transformations such as esterification, acetylation, and decarboxylation reactions.
- Analytical Chemistry: Ammonium acetate is utilized in analytical chemistry techniques such as liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. It is often added to mobile phases in liquid chromatography to improve separation and detection of analytes.
- Protein Purification: Ammonium acetate is used in protein purification processes. It can help precipitate proteins from a solution, allowing for their separation and purification.
- pH Adjustment: Due to its acidic nature, ammonium acetate can be used to lower the pH of solutions or to neutralize basic solutions.
- Food Additive: Ammonium acetate is an approved food additive with the European food additive number E264. It can be used as an acidity regulator and flavoring agent in certain food products.
Physical Properties of Ammonium Acetate Formula
- State: Ammonium acetate is typically found as a white, crystalline solid at room temperature
- Odor: It has a slightly acetic or vinegar-like odor.
- Solubility: Ammonium acetate is highly soluble in water. It readily dissolves in water to form a clear, colorless solution.
- Melting Point: The melting point of ammonium acetate is relatively low, around 114-116 degrees Celsius (237-241 degrees Fahrenheit). It can readily melt when subjected to heat.
- Density: The density of solid ammonium acetate is around 1.17 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
- Hygroscopicity: Ammonium acetate has hygroscopic properties, meaning it has a tendency to absorb moisture from the surrounding environment.
- pH: In aqueous solutions, ammonium acetate has a slightly acidic pH due to the dissociation of the ammonium ion (NH4+) and the acetate ion (C2H3O2-).
Chemical Properties of Ammonium Acetate Formula
- Acid-Base Behavior: Ammonium acetate is an example of a salt that can act as both an acid and a base. When dissolved in water, it dissociates into ammonium ions (NH4+) and acetate ions (C2H3O2-). The ammonium ion can act as an acid by donating a proton (H+), while the acetate ion can act as a base by accepting a proton.
- Buffering Capacity: Ammonium acetate is commonly used as a buffering agent in chemistry and biology laboratories. It helps maintain a stable pH in solutions by resisting changes in acidity or alkalinity when small amounts of acid or base are added.
- Volatility: Ammonium acetate has a relatively low boiling point and can readily vaporize at elevated temperatures. This property makes it useful in certain applications, such as in the preparation of volatile compounds or in mass spectrometry techniques.
- Organic Synthesis: Ammonium acetate is widely employed in organic synthesis as a source of the acetate ion. It can be used in reactions that involve the formation of esters, acylations, or as a catalyst for various transformations.
- Decomposition: When heated to high temperatures, ammonium acetate can undergo decomposition, releasing ammonia gas (NH3) and acetic acid (CH3COOH). This property is utilized in some laboratory procedures or industrial processes where ammonia or acetic acid are required.
- Salt Formation: Ammonium acetate can react with various acids or bases to form different salts. For example, it can react with hydrochloric acid to produce ammonium chloride or with sodium hydroxide to form sodium acetate.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the formula for ammonium phosphate is (NH4)3PO4. Ammonium phosphate is a compound commonly used in fertilizers and as a source of phosphorous and nitrogen for plants. It provides essential nutrients for plant growth and is particularly beneficial for promoting root development, flowering, and fruiting. Ammonium phosphate is also used in some fire extinguishers due to its fire-retardant properties. However, it should be handled with care as it can be corrosive and may cause skin and eye irritation. Proper usage and adherence to safety guidelines are important when working with ammonium phosphate.
Solved Examples on Ammonium Acetate Formula
Example: Calculate the mass of ammonium acetate needed to prepare 500 mL of a 0.2 M ammonium acetate solution.
Solution:
Given: Molarity (M) = 0.2 mol/L
Volume (V) = 500 mL = 0.5 L
Molar mass of ammonium acetate = 77.0825 g/mol
To calculate the mass of ammonium acetate, we can use the formula:
Mass = Molarity (M) × Molar mass (M.M.) × Volume (V)
Plugging in the values:
Mass = 0.2 mol/L × 77.0825 g/mol × 0.5 L
= 7.70825 g
Therefore, approximately 7.70825 grams of ammonium acetate are needed to prepare 500 mL of a 0.2 M ammonium acetate solution.
Frequently Asked Questions on Ammonium Acetate Formula
What is ammonium acetate used for?
Ammonium acetate is used in various applications, including as a buffer in chemical reactions, a reagent in analytical chemistry, and a food additive in some countries. It helps control the pH of solutions and is utilized in processes like DNA purification and chemical synthesis.
Is ammonium acetate a weak acid?
Yes, ammonium acetate is a weak acid. It can release a small number of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution, which makes it slightly acidic.
Is ammonium acetate an acidic salt?
Ammonium acetate can be considered an acidic salt because it contains the acetate ion, which can act as a weak base. When dissolved in water, it can slightly increase the acidity of the solution.
How do you write ammonium acetate?
The chemical formula for ammonium acetate is NH4CH3COO. It consists of ammonium ions (NH4+) and acetate ions (CH3COO-) bonded together.
How do you identify ammonium acetate?
You can identify ammonium acetate through its chemical formula (NH4CH3COO) and its characteristic odor, which is often described as mildly pungent or vinegar-like.
Is ammonium acetate soluble in water?
Yes, ammonium acetate is highly soluble in water. When added to water, it readily dissolves, forming an aqueous solution.
Is ammonium acetate safe?
Ammonium acetate is generally considered safe when used as directed. However, like any chemical, it should be handled with care, and exposure to large amounts or inhalation of its dust should be avoided.
Is ammonium acetate a strong salt?
No, ammonium acetate is not a strong salt. It is a weak salt due to its limited ability to dissociate into ions in water.








