Table of Contents
Introduction to Ammonium Carbonate Formula
Ammonium carbonate is an inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2CO3. It is composed of:
Ammonium ions (NH4+) and
Carbonate ions (CO32-).
The compound is a white, crystalline solid with a strong ammonia odour.
Structural formula of Ammonium Carbonate Formula
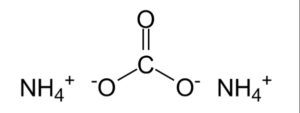
It is a chemical compound which consists of ammonium and carbonate ions. The chemical or molecular formula for Ammonium Carbonate is (NH4)2CO3.
Uses of Ammonium Carbonate
Ammonium carbonate is commonly used in various applications, such as a leavening agent in baking, a fertilizer in agriculture, and a reagent in chemical laboratories. It is known for its ability to release carbon dioxide gas when heated, making it useful in baking and as a raising agent. However, it is important to handle ammonium carbonate with care as it can release toxic ammonia gas when exposed to moisture or acidic conditions.
Physical Properties of Ammonium Carbonate Formula
- Appearance: Ammonium carbonate usually appears as a white powder or solid. It can sometimes have a slight ammonia-like odour.
- Solubility: It is soluble in water, with solubility increasing at higher temperatures. The solubility of ammonium carbonate in water allows it to readily dissociate into ammonium (NH4+) and carbonate (CO32-) ions.
- Melting and Boiling Point: Ammonium carbonate decomposes upon heating without melting. It undergoes sublimation, directly converting from a solid to a gas. The decomposition starts around 58 °C (136 °F), releasing ammonia gas, carbon dioxide, and water vapour.
- Density: The density of solid ammonium carbonate is around 1.5 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
- pH: When dissolved in water, ammonium carbonate forms ammonium and carbonate ions. These ions make the solution slightly alkaline, resulting in a pH greater than 7.
- Hygroscopicity: Ammonium carbonate has hygroscopic properties, meaning it can absorb moisture from the air.
- Stability: Ammonium carbonate is relatively unstable and tends to decompose over time, especially in the presence of moisture and heat. It breaks down into ammonia (NH3), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O).
Chemical Properties of Ammonium Carbonate Formula
- Decomposition: Ammonium carbonate is a salt that readily decomposes when exposed to heat or moisture. The decomposition reaction is endothermic, meaning it absorbs heat energy. It breaks down into ammonia (NH3), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O). This decomposition process is often used to generate ammonia gas. (NH4)2CO3 → 2NH3 + CO2 + H2O
- Volatility: Ammonium carbonate is volatile and tends to sublime at temperatures below its decomposition point. Sublimation is the process by which a substance directly converts from a solid to a gas without passing through the liquid phase.
- Ammonia Release: Ammonium carbonate readily releases ammonia gas when heated or dissolved in water. The ammonia gas has a strong, pungent odour.
- Acid-Base Properties: When dissolved in water, ammonium carbonate undergoes hydrolysis and produces ammonium ions (NH4+) and carbonate ions (CO32-). The presence of ammonium ions makes the solution slightly acidic, while the presence of carbonate ions contributes to the alkalinity of the solution. (NH4)2CO3 + H2O ↔ 2NH4+ + CO32-
- Reactivity: Ammonium carbonate can participate in various chemical reactions due to the presence of ammonium and carbonate ions. It can undergo reactions such as neutralization with acids to form ammonium salts and precipitation reactions with metal ions to form insoluble carbonates.
- Sensitivity to Moisture: Ammonium carbonate is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air. Exposure to moisture can accelerate its decomposition process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ammonium carbonate is a white crystalline salt with the chemical formula (NH4)2CO3. It is composed of ammonium ions (NH4+) and carbonate ions (CO32-). Ammonium carbonate has a strong odor of ammonia and is soluble in water. It is primarily used in baking and food preparation as a leavening agent and in the manufacturing of certain pharmaceuticals. Ammonium carbonate decomposes upon heating, releasing ammonia, carbon dioxide, and water. It is important to handle ammonium carbonate with care due to its strong odor and potential irritant properties.
Solved Examples of Ammonium Carbonate Formula
Example 1: Preparation of Ammonium Carbonate Solution
Question: How many grams of ammonium carbonate are required to prepare 500 mL of a 0.2 M ammonium carbonate solution?
Solution:
Step 1: Calculate the molar mass of ammonium carbonate:
Molar mass of (NH4)2CO3 = (2 * 14.01 g/mol) + (4 * 1.01 g/mol) + 12.01 g/mol + (3 * 16.00 g/mol) = 96.09 g/mol
Step 2: Calculate the number of moles of ammonium carbonate needed:
Moles = Molarity * Volume Moles = 0.2 mol/L * 0.5 L = 0.1 mol
Step 3: Calculate the mass of ammonium carbonate:
Mass = Moles * Molar mass
Mass = 0.1 mol * 96.09 g/mol = 9.609 g
9.609 grams of ammonium carbonate are required to prepare 500 mL of a 0.2 M ammonium carbonate solution.
Example 2: Decomposition Reaction
Question: When 5 grams of ammonium carbonate decompose, how many grams of ammonia, carbon dioxide, and water will be produced?
Solution:
Step 1: Write the balanced decomposition equation: (NH4)2CO3 → 2NH3 + CO2 + H2O
Step 2: Calculate the molar mass of ammonium carbonate:
Molar mass of (NH4)2CO3 = (2 * 14.01 g/mol) + (4 * 1.01 g/mol) + 12.01 g/mol + (3 * 16.00 g/mol) = 96.09 g/mol
Step 3: Calculate the number of moles of ammonium carbonate:
Moles = Mass / Molar mass
Moles = 5 g / 96.09 g/mol ≈ 0.052 mol
Step 4: Use the mole ratio to calculate the number of moles of products:
Ammonia: 2 moles of NH3 are produced for every 1 mole of (NH4)2CO3
Moles of NH3 = 2 * 0.052 mol = 0.104 mol
Carbon Dioxide: 1 mole of CO2 is produced for every 1 mole of (NH4)2CO3
Moles of CO2 = 1 * 0.052 mol = 0.052 mol
Water: 1 mole of H2O is produced for every 1 mole of (NH4)2CO3
Moles of H2O = 1 * 0.052 mol = 0.052 mol
Step 5: Calculate the mass of each product:
Mass = Moles * Molar mass
Mass of NH3 = 0.104 mol * 17.03 g/mol = 1.771 g
Mass of CO2 = 0.052 mol * 44.01 g/mol = 2.282 g
Mass of H2O = 0.052 mol * 18.02 g/mol = 0.938 g
Frequently Asked Questions on Ammonium Carbonate Formula
What is ammonium carbonate used for?
Ammonium carbonate has various uses, including as a leavening agent in baking, a smelling salt for reviving consciousness, and a pH regulator in certain industrial processes.
Is ammonium carbonate a smelling salt?
Yes, ammonium carbonate is commonly used as a smelling salt. It releases ammonia gas when crushed, which can help revive someone who has fainted.
Is ammonium carbonate safe to use?
Ammonium carbonate should be used with caution. It can release ammonia gas, which is irritating to the eyes and respiratory system. Proper ventilation and handling procedures are necessary.
How do you write Ammonium Carbonate?
The chemical formula for ammonium carbonate is (NH4)2CO3. It consists of two ammonium ions (NH4+) and one carbonate ion (CO3^2-) bonded together.
What is in Ammonium Carbonate?
Ammonium carbonate contains ammonium ions (NH4+) and carbonate ions (CO3^2-) held together in a chemical compound.
What is the Criss Cross formula for ammonium carbonate?
The Criss Cross formula for ammonium carbonate is determined by balancing the charges of the ammonium ion (NH4+) and the carbonate ion (CO3^2-), resulting in the chemical formula (NH4)2CO3.
What is the chemical formula of ammonium sulphate by Criss Cross method?
The chemical formula of ammonium sulfate determined using the Criss Cross method is (NH4)2SO4. It consists of two ammonium ions (NH4+) and one sulfate ion (SO4^2-) bonded together.








