Table of Contents
Introduction to Ammonium Phosphate Formula
Ammonium phosphate refers to a family of chemical compounds that contain the ammonium cation (NH4+) and the phosphate anion (PO43-). It is commonly represented by the chemical formula (NH4)3PO4. In this compound, three ammonium ions are combined with one phosphate ion.
Ammonium phosphate is an important source of both nitrogen and phosphorus, which are essential nutrients for plant growth. It is widely used as a fertilizer in agriculture to provide these nutrients to crops. Additionally, ammonium phosphate is also utilized in various industrial applications, such as flame retardants, water treatment, and as a reagent in chemical synthesis.
Structural Formula of Ammonium Phosphate Formula
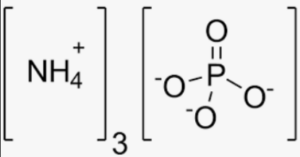
In this structure, each ammonium ion (NH4+) is connected to the phosphate ion (PO43-) through ionic bonds. The nitrogen atom (N) in each ammonium ion is bonded to four hydrogen atoms (H), and the phosphate ion consists of one phosphorus atom (P) bonded to four oxygen atoms (O).
Uses of Ammonium Phosphate
- Fertilizer: Ammonium phosphate is widely used as a fertilizer in agricultural practices. It provides a source of nitrogen and phosphorus, essential nutrients for plant growth and development. It is particularly beneficial for promoting root growth, flowering, and fruiting in crops.
- Flame Retardant: Ammonium phosphate compounds, such as monoammonium phosphate (MAP) and diammonium phosphate (DAP), are used as flame retardants in various applications. They are added to materials like textiles, plastics, and wood products to reduce their flammability and enhance fire safety.
- Food Additive: Ammonium phosphate is approved as a food additive by regulatory authorities and is used in certain food products. It serves as a leavening agent in baked goods, helping them rise during baking. It is also used as a nutrient source in some food products.
- Water Treatment: Ammonium phosphate is used in water treatment processes, particularly for controlling algae growth in water bodies. It inhibits the growth of algae by limiting the availability of phosphorus, which is essential for their growth.
- Industrial Applications: Ammonium phosphate finds applications in various industrial processes. It is used in the production of fire extinguishing agents, such as ABC dry chemical fire extinguishers. It is also utilized in the formulation of cleaning agents, metal treatment solutions, and as a catalyst in certain chemical reactions.
Physical Properties of Ammonium Phosphate Formula
- Appearance: Ammonium phosphate is typically a white crystalline solid.
- Solubility: It is soluble in water, meaning it can dissolve in water to form an aqueous solution.
- Density: The density of ammonium phosphate depends on the specific form and conditions, but it is generally around 1.62 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
- Melting Point: Ammonium phosphate has a melting point of approximately 155 degrees Celsius (311 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Odor: It is odorless.
- Hygroscopicity: Ammonium phosphate has hygroscopic properties, meaning it has a tendency to absorb moisture from the air.
- pH: In aqueous solution, ammonium phosphate can exhibit a slightly acidic to neutral pH, depending on the concentration and specific conditions.
Chemical Properties of Ammonium Phosphate Formula
- Acid-Base Reaction: Ammonium phosphate can act as both an acid and a base. It can react with strong bases to form ammonium salts and with strong acids to form phosphates. Example: (NH4)3PO4 + 3NaOH → 3NH4OH + Na3PO4
- Decomposition: Ammonium phosphate can undergo thermal decomposition when heated to high temperatures, breaking down into ammonia gas (NH3) and phosphoric acid (H3PO4). Example: (NH4)3PO4 → 3NH3 + H3PO4
- Reaction with Metal Ions: Ammonium phosphate can react with metal ions to form insoluble precipitates of metal phosphates. Example: (NH4)3PO4 + CuSO4 → (NH4)2SO4 + Cu3(PO4)2
- Reaction with Alkalis: Ammonium phosphate can react with alkalis to form ammonium salts and phosphates. Example: (NH4)3PO4 + KOH → NH4OH + KH2PO4
- Reaction with Strong Oxidizing Agents: Ammonium phosphate is a reducing agent and can react with strong oxidizing agents, such as potassium permanganate (KMnO4), leading to the formation of various products depending on the specific reaction conditions.
Solved Examples on Ammonium Phosphate Formula
Example 1: Balance the following chemical equation: (NH4)3PO4 + CaCl2 → NH4Cl + Ca3(PO4)2
Solution: To balance the equation, we need to ensure that the number of each type of atom is the same on both sides of the equation. The balanced equation is: 2(NH4)3PO4 + 3CaCl2 → 6NH4Cl + Ca3(PO4)2
Example 2: Calculate the molar mass of ammonium phosphate, (NH4)3PO4.
Solution: The molar mass can be calculated by summing the atomic masses of each element in the formula.
Molar mass of (NH4)3PO4 = (3 * 1.01 g/mol for N) + (12.01 g/mol for C) + (12.01 g/mol for H) + (4 * 16.00 g/mol for O) + (4 * 1.01 g/mol for H) + (31.00 g/mol for P) + (4 * 16.00 g/mol for O)
= 149.09 g/mol
Frequently Asked Questions on Ammonium Phosphate Formula
How ammonium phosphate is used in food?
Ammonium phosphate is used in the food industry as a food additive, specifically as a leavening agent in baked goods like bread, cakes, and cookies. It helps dough rise and contributes to the texture and fluffiness of these products.
What are ammonium phosphate crystals?
Ammonium phosphate crystals are solid formations of ammonium ions (NH4+) and phosphate ions (PO4³-) bonded together. They can exist in various forms and are often used as a fertilizer due to their nutrient content.
Is ammonium phosphate harmful to humans?
Ammonium phosphate, when used in food within permissible limits, is generally considered safe for human consumption. However, excessive consumption of phosphates in various forms can have health implications, so moderation is advised.
Why is phosphate needed in plants?
Phosphate is essential for plant growth because it plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including energy transfer (ATP), photosynthesis, and DNA synthesis. It helps plants develop strong roots, flowers, and seeds.
What type of bond is ammonium phosphate?
Ammonium phosphate contains both ionic and covalent bonds. The ammonium ion (NH4+) and the phosphate ion (PO4³-) are held together by ionic bonds due to their opposite charges, while the atoms within each ion share covalent bonds.
Why is ammonium phosphate soluble?
Ammonium phosphate is soluble in water because the ionic bonds between the ammonium (NH4+) and phosphate (PO4³-) ions are broken in the presence of water molecules, allowing the ions to separate and disperse in the solution.
Which two elements in ammonium phosphate are important for plant growth?
Two essential elements for plant growth found in ammonium phosphate are nitrogen (N), provided by the ammonium ion (NH4+), and phosphorus (P), supplied by the phosphate ion (PO4³-).
What is the use of ammonium phosphate?
Ammonium phosphate is primarily used as a fertilizer in agriculture to supply plants with essential nutrients, specifically nitrogen and phosphorus. It promotes healthy plant growth and is crucial for crop production.








