Table of Contents
The human body is like a complicated machine. It does lots of tricky chemistry stuff to stay alive. One of the most important things it does is called respiration. Respiration changes food into energy.
There are two main types of respiration: one needs oxygen, and the other doesn’t. It’s important to know the Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration to understand how our bodies work well.
This knowledge helps us understand how living things, including people, make energy. When students learn about the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration, they can understand these important processes better. This is especially useful for students in the 10th grade when they learn about these ideas in more detail.
What is Aerobic Respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a process in which cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy, water, and carbon dioxide. This type of respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen and is the primary method by which cells in animals and plants generate energy.
An example of aerobic respiration is the process that occurs in human muscle cells during light exercise. When we discuss aerobic and anaerobic respiration, it’s important to note that aerobic respiration is more efficient in energy production compared to its anaerobic counterpart.
Examples of aerobic respiration:
- Cellular respiration in most organisms
- Fermentation of sugars by yeast to produce alcohol and carbon dioxide
- Breakdown of glucose in muscle cells for energy during exercise
What is Anaerobic Respiration?
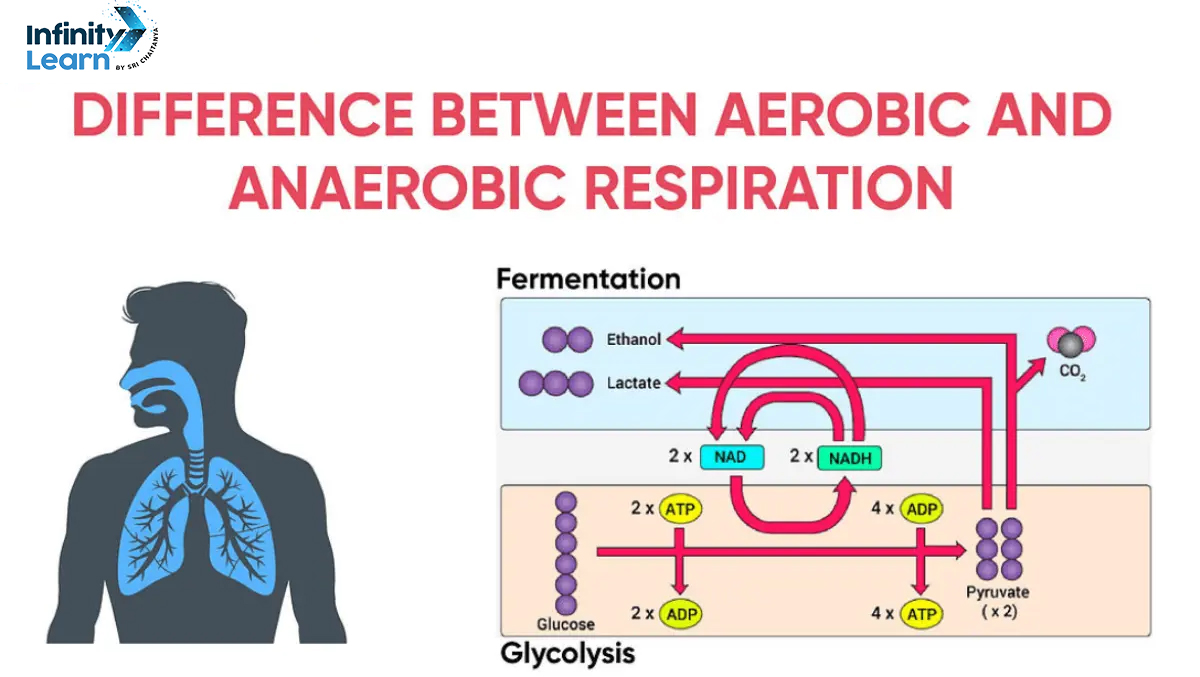
Anaerobic respiration, in contrast to aerobic, occurs in the absence of oxygen. This process involves the conversion of glucose into energy, with the end products being lactic acid in animals and ethanol and carbon dioxide in plants and yeast.
A common example of anaerobic respiration is the muscle fatigue experienced during intense exercise when oxygen supply is limited. Understanding the dynamics of aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration is essential to grasp how different organisms adapt to oxygen-deprived environments.
Examples of anaerobic respiration:
- Fermentation of lactic acid in muscle cells during intense exercise
- Fermentation of glucose by bacteria to produce yogurt, cheese, and other fermented foods
- Cellular respiration in some anaerobic organisms, such as yeast
While anaerobic respiration is less efficient, it allows organisms to survive in environments devoid of oxygen. Additionally, anaerobic respiration plays a vital role in several industrial and food production processes.
What are the Differences Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration?
| Aspect | Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| Oxygen Requirement | Requires oxygen | Does not require oxygen |
| Energy Efficiency | High energy yield (36-38 ATP) | Low energy yield (2 ATP) |
| By-products | Carbon dioxide and water | Lactic acid in animals, ethanol and carbon dioxide in yeast and plants |
| Location in Cell | Takes place in mitochondria | Occurs in the cytoplasm |
| Duration | Longer, sustained process | Rapid, short-term process |
| Organisms | Most animals, plants, and many microorganisms | Some bacteria, yeast, and muscle cells in animals under oxygen-deficient conditions |
| Pathway | Involves glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain | Involves only glycolysis |
| Use in Industry | Less direct industrial application | Used in brewing, baking (yeast fermentation), and certain types of waste treatment |
| Physiological Role | Major energy source for cellular activities | Temporary energy source during oxygen deficit or for organisms that live in anaerobic environments |
| End Products’ Fate | Carbon dioxide is exhaled, water is used metabolically or excreted | Lactic acid must be converted back to pyruvate; Ethanol is excreted or used in industrial processes |
Importance of Learning Difference between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
It is essential to learn the difference between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration for several reasons:
- Insights into Human Physiology: Knowledge of these respiratory processes helps students understand how the human body functions during different activities, such as resting, exercising, or when in oxygen-deprived conditions.
- Understanding Disease Mechanisms: Many diseases affect cellular respiration. Learning about aerobic and anaerobic respiration is crucial for understanding the pathology of these diseases.
- Environmental Impact: Anaerobic respiration plays a significant role in environmental processes, like decomposition and biogas production, showcasing how biological processes influence the environment.
- Agricultural Applications: Aerobic and anaerobic respiration are vital in understanding soil health and crop production, impacting sustainable agriculture practices.
- Enhances Analytical Skills: Studying these processes encourages analytical thinking by allowing students to compare and contrast the efficiency and outcomes of different types of respiration.
- Foundation for Advanced Study: For students pursuing higher education in biology, medicine, or environmental science, a solid understanding of these basic concepts is essential.
- Practical Everyday Applications: From exercise routines to understanding food preservation techniques like fermentation, the principles of aerobic and anaerobic respiration have everyday applications.
- Informed Health Choices: Understanding how the body uses oxygen during exercise can help in making informed decisions about physical health and exercise regimes.
- Contribution to Biotechnology: Knowledge of anaerobic processes is crucial in biotechnology applications like fermentation technology, used in creating pharmaceuticals, alcohol, and more.
- Interdisciplinary Learning: Studying these processes integrates concepts from chemistry, physics, and biology, promoting a more holistic approach to science education.
When students learn about how aerobic and anaerobic respiration are both similar and different, they can better understand important biological processes. This knowledge can have a big impact on their studies and careers in science-related fields.
| Check all the Biology Difference Between Articles | |
| Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell | Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell |
| Difference Between DNA and RNA | Difference Between Cold Blooded and Warm Blooded |
| Difference Between Flora and Fauna | Difference between mitosis and meiosis |
| Difference Between Weather and Climate | Difference Between Arteries and Veins |
| Difference Between Xylem and Phloem | |
FAQs on Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration Class 10 Ncert?
Aerobic respiration uses oxygen to break down glucose for energy, while anaerobic respiration does not. Aerobic is more efficient and produces more ATP, but anaerobic is used when oxygen is limited.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration exam question?
Aerobic Respiration — Takes place in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic Respiration –Takes place in the absence of oxygen
What are the 5 differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
Oxygen requirement: Aerobic requires oxygen, anaerobic does not. Location: Aerobic occurs in mitochondria, anaerobic in cytoplasm. Products: Aerobic produces carbon dioxide, water, and ATP, anaerobic produces lactic acid or alcohol and carbon dioxide. Efficiency: Aerobic is more efficient, producing 36 ATP molecules per glucose, while anaerobic produces 2. Energy production: Anaerobic is less efficient but allows survival in oxygen-depleted environments.






