Table of Contents
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the formula CaCO3. It is a versatile substance found in nature and has numerous applications. Let’s explore the formula, structure, physical properties, and chemical properties of calcium carbonate in detail.
Formula and Structure of Calcium Carbonate
The chemical formula of calcium carbonate is CaCO3. It consists of one calcium (Ca) atom, one carbon (C) atom, and three oxygen (O) atoms. The structure of calcium carbonate can be
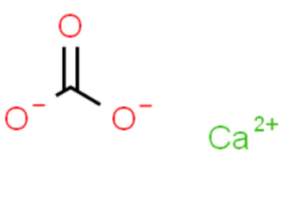
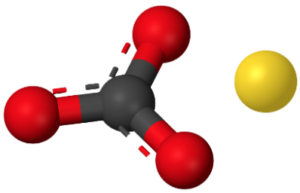
In the structure, the carbon atom is bonded to three oxygen atoms, with double bonds between the carbon and two of the oxygen atoms, and a single bond between the carbon and the remaining oxygen atom. The calcium atom is not directly involved in the bonding within the carbonate ion.
Calcium Carbonate Physical Properties
- State: Calcium carbonate can exist in various forms, including a solid (crystalline) state or as a fine powder.
- Colour: It is typically white or colourless.
- Density: The density of calcium carbonate varies depending on the form and crystal structure.
- Solubility: Calcium carbonate is sparingly soluble in water, but its solubility increases in the presence of carbon dioxide and decreases at higher temperatures.
Calcium Carbonate Chemical Properties
- Acid-Base Reaction: Calcium carbonate reacts with acids to produce carbon dioxide gas, water, and a calcium salt. For example, it reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl) to form carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and calcium chloride (CaCl2).
- Thermal Decomposition: When heated, calcium carbonate decomposes into calcium oxide (quicklime) and carbon dioxide gas. This process is known as thermal decomposition or calcination.
- Buffering Agent: Calcium carbonate acts as a buffering agent in various applications, helping to maintain pH levels and stabilize solutions.
- Formation of Sedimentary Rocks: Calcium carbonate plays a significant role in the formation of sedimentary rocks such as limestone, chalk, and marble, which are composed primarily of calcium carbonate.
- Industrial Applications: Calcium carbonate is widely used in various industries, including construction, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and food manufacturing.
Calcium Carbonate Applications
- Construction: Calcium carbonate is used as a filler and a coating pigment in the production of construction materials such as paints, coatings, adhesives, and sealants.
- Agriculture: It is utilized as a soil conditioner and pH regulator in agricultural practices to improve soil quality and enhance plant growth.
- Pharmaceuticals: Calcium carbonate is an essential ingredient in the manufacturing of antacids and dietary supplements.
- Environmental Remediation: It is employed in water treatment processes to remove impurities and adjust pH levels.
- Paper Production: Calcium carbonate is used in the paper industry as a filler and coating pigment to enhance the quality and brightness of paper.
Solved Examples on Calcium Carbonate Formula
Example 1: Calculate the molar mass of calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
Solution: To determine the molar mass of calcium carbonate, we need to calculate the sum of the atomic weights of its constituent elements.
The atomic weights are as follows:
Ca (calcium) = 40.08 g/mol
C (carbon) = 12.01 g/mol
O (oxygen) = 16.00 g/mol
Now, let’s calculate the molar mass:
Molar mass of CaCO3 = (1 * Ca) + (1 * C) + (3 * O)
= (1 * 40.08) + (1 * 12.01) + (3 * 16.00)
= 100.09 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is 100.09 g/mol.
Example 2: What happens when calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl)?
Solution: When calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, a chemical reaction takes place, resulting in the formation of calcium chloride (CaCl2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O).
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is as follows:
CaCO3 + 2HCl –> CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
In this reaction, the hydrochloric acid donates hydrogen ions (H+) to the carbonate ion (CO32) in calcium carbonate, leading to the formation of carbon dioxide gas. The calcium ion (Ca2+) from calcium carbonate combines with the chloride ion (Cl–) from hydrochloric acid to form calcium chloride, while water is also produced as a by-product.
This reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid is often used to demonstrate the effervescence of carbon dioxide gas, as it produces visible bubbles of gas when carried out in an open container.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The common name of calcium carbonate is limestone.
Calcium carbonate is composed of calcium Ca, carbon C, and oxygen O atoms, with the chemical formula CaCO3.
Many marine organisms, such as corals, mollusks, and some algae, utilize calcium carbonate to build their shells, exoskeletons, and coral reefs.
Calcium carbonate reacts with acids to form carbon dioxide gas, water, and a calcium salt. This process helps to neutralize acidic substances and regulate pH levels.
Calcium carbonate can be obtained from natural sources, including limestone, chalk, and marble. It is also produced synthetically for various industrial applications. What is the common name of calcium carbonate?
What is the chemical composition of calcium carbonate?
What is the role of calcium carbonate in marine organisms?
How does calcium carbonate neutralize acid?
What are the common sources of calcium carbonate?






