Table of Contents
Introduction
Calcium nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(NO3)2. It is composed of one calcium ion (Ca2+) and two nitrate ions (NO3-) in its structure.
Calcium nitrate is produced by the reaction of calcium carbonate or calcium hydroxide with nitric acid.
CaCO3 + 2HNO3 → Ca(NO3)2 + CO2 + H2O
Structural Formula of Calcium Nitrate
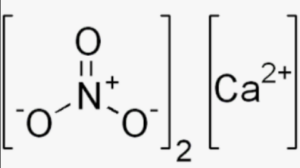
It consists of one calcium ion (Ca2+) bonded to two nitrate ions (NO3-). The calcium ion has a 2+ charge, while each nitrate ion carries a 1- charge. The nitrate ion consists of one nitrogen atom (N) bonded to three oxygen atoms (O).
Uses of Calcium Nitrate
- Fertilizer: Calcium nitrate is commonly used as a fertilizer in agriculture. It provides plants with a readily available source of calcium and nitrogen, essential nutrients for healthy plant growth. It is particularly useful in preventing calcium deficiency in crops and promoting strong root development.
- Concrete Accelerator: Calcium nitrate is used as a concrete accelerator in construction and building materials. By adding calcium nitrate to concrete mixtures, the setting time of the concrete can be shortened, allowing for faster construction and reduced waiting times.
- Wastewater Treatment: Calcium nitrate is employed in wastewater treatment processes to remove phosphates and nitrates from water. It acts as a coagulant, helping to precipitate and remove these contaminants, thereby improving the quality of the treated water.
- Explosives and Fireworks: Calcium nitrate is used as an oxidizing agent in the production of explosives and fireworks. It provides a source of oxygen that supports the combustion process, making it an essential component for these applications.
- <li”5″>Food Preservation: Calcium nitrate is sometimes used as a food additive to prevent spoilage and extend the shelf life of certain food products. It helps to inhibit the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms, contributing to food safety and preservation.
Also Check For: Zinc Nitrate Formula
Physical Properties of Calcium Nitrate Formula
- Appearance: Calcium nitrate typically exists as a white, crystalline solid.
- Melting Point: The melting point of calcium nitrate is approximately 561 degrees Celsius (1,042 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Solubility: Calcium nitrate is highly soluble in water, meaning it readily dissolves in water to form an aqueous solution.
- Density: The density of solid calcium nitrate is around 2.5 grams per cubic centimeter.
- Hygroscopicity: Calcium nitrate has hygroscopic properties, which means it can absorb moisture from the air.
- pH: An aqueous solution of calcium nitrate is typically slightly acidic due to the presence of nitrate ions.
- Odour: Calcium nitrate is odourless.
Chemical Properties of Calcium Nitrate Formula
- Decomposition: When heated, calcium nitrate decomposes into calcium oxide (CaO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and oxygen (O2). This decomposition reaction is endothermic, meaning it requires the input of energy.
Ca(NO3)2 -> CaO + 2NO2 + O2
- Oxidizing Properties: Calcium nitrate is an oxidizing agent, meaning it has the ability to donate oxygen or accept electrons in a chemical reaction. It can react with reducing agents, such as organic compounds or metals, promoting oxidation reactions.
- Reaction with Alkalis: Calcium nitrate reacts with alkalis to form calcium hydroxide and nitrates. For example, when calcium nitrate is treated with sodium hydroxide, it forms calcium hydroxide and sodium nitrate:
Ca(NO3)2 + 2NaOH -> Ca(OH)2 + 2NaNO3
- Reaction with Ammonia: Calcium nitrate can react with ammonia to form calcium hydroxide and ammonium nitrate:
Ca(NO3)2 + 2NH3 -> Ca(OH)2 + 2NH4NO3
Conclusion
In conclusion, calcium nitrate (Ca(NO3)2) is a versatile compound with various applications in different industries. It is primarily used as a fertilizer in agriculture to provide plants with calcium and nitrogen. Additionally, calcium nitrate serves as a concrete accelerator, helping to speed up the setting time of concrete in construction. It is also utilized in wastewater treatment to remove phosphates and nitrates from water, as an oxidizing agent in the production of explosives and fireworks, and as a food additive for preservation. However, it is important to handle calcium nitrate with care and follow safety guidelines due to its oxidizing properties.
Solved Examples on Calcium Nitrate Formula
Example 1: Calculation of Molar Mass Question:
Calculate the molar mass of calcium nitrate (Ca(NO3)2).
Solution: The molar mass of calcium (Ca) is 40.08 g/mol.
The molar mass of nitrogen (N) is 14.01 g/mol.
The molar mass of oxygen (O) is 16.00 g/mol.
Calculation: Molar mass of Ca(NO3)2 = (1 * molar mass of Ca) + (2 * molar mass of N) + (6 * molar mass of O)
= (1 * 40.08 g/mol) + (2 * 14.01 g/mol) + (6 * 16.00 g/mol)
= 164.10 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of calcium nitrate is 164.10 g/mol.
Example 2: Calculation of Mass Percent
A sample of calcium nitrate (Ca(NO3)2) weighing 25.0 g contains 8.0 g of calcium. What is the mass percent of calcium in the sample?
Solution: Mass percent = (mass of component / total mass) * 100
Calculation: Mass percent of calcium = (8.0 g / 25.0 g) * 100 = 32.0%
Therefore, the mass percent of calcium in the sample is 32.0%.
Frequently Asked Questions on Calcium Nitrate Formula
What is the most common formula for calcium nitrate?
The most common formula for calcium nitrate is Ca(NO3)2.
What is another name for calcium nitrate?
Calcium nitrate is also called as Norgessalpeter or Norwegian salpeter. Another name is Lime nitrate.
What is the purpose of preparation of calcium nitrate?
Calcium nitrate is prepared for various purposes, including: Fertilizer: Calcium nitrate is commonly used as a fertilizer due to its high content of both calcium and nitrogen. It provides essential nutrients to plants, promoting their growth and enhancing their ability to withstand stress. Concrete admixture: Calcium nitrate is used as a concrete admixture to accelerate the setting and hardening of concrete. It helps to improve the early strength development and overall durability of concrete structures. Oxidizing agent: Calcium nitrate is also used as an oxidizing agent in various chemical processes. It can provide a source of oxygen for combustion reactions or act as an oxidizer in certain chemical reactions. Cooling agent: Calcium nitrate is used in some industrial cooling systems, such as refrigeration units and air conditioning systems, to lower the temperature by absorbing heat during the dissolution process.
What is the natural source of calcium nitrate?
Calcium nitrate is not typically found in significant quantities in natural sources. It is predominantly produced synthetically through chemical reactions. However, calcium nitrate can be indirectly obtained from certain natural sources: Nitrate-rich soils: Some soils naturally contain nitrates, which can be converted into calcium nitrate through chemical processes. Certain regions with nitrate-rich soils may serve as a source for the production of calcium nitrate. Nitrate deposits: Some natural deposits, such as nitrate minerals and salt beds, may contain nitrates. These deposits can be processed to extract nitrate compounds, which can then be used in the production of calcium nitrate. It's important to note that the primary commercial production of calcium nitrate is through the reaction of calcium carbonate (from limestone or marble) with nitric acid. This synthetic process is the most common method for obtaining calcium nitrate on a large scale.
What is the pH of calcium nitrate?
Calcium nitrate in solution has a pH of 6.5. It is used for foliar and soil feeding, especially in acidic areas.
What is the use of CN fertilizer?
CN fertilizer typically refers to calcium nitrate fertilizer, which is commonly used in agriculture. It provides plants with essential nutrients, specifically calcium and nitrogen. The calcium in calcium nitrate helps promote strong cell walls and overall plant structure, while the nitrogen serves as a vital component for protein synthesis and growth. Calcium nitrate fertilizer is effective in preventing calcium deficiency in crops and promoting healthy plant development. It is particularly beneficial for crops that require higher levels of calcium, such as fruits, vegetables, and certain field crops. By supplying plants with these essential nutrients, CN fertilizer helps improve crop yield, quality, and overall plant health.
Can I mix NPK with calcium nitrate?
Yes, you can mix NPK (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) fertilizers with calcium nitrate. Mixing these fertilizers can be beneficial as it provides plants with a comprehensive range of essential nutrients. NPK fertilizers typically contain varying ratios of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are primary nutrients necessary for plant growth and development. Calcium nitrate, on the other hand, provides a good source of calcium and nitrogen. Combining these fertilizers can help meet the nutritional needs of plants more effectively, promoting balanced growth and improving overall crop productivity. However, it is important to carefully follow recommended application rates and consider the specific requirements of the plants you are fertilizing to avoid over-fertilization or nutrient imbalances.
How do you apply calcium nitrate to plants?
Calcium nitrate can be applied to plants in various ways depending on the specific needs and preferences. Here are a few common methods of application: Foliar Spray: Dissolve calcium nitrate in water according to the recommended dosage and spray the solution onto the leaves of the plants. This method is effective for providing a quick supply of calcium and nitrogen directly to the plant foliage. Soil Drench: Mix calcium nitrate with water and apply it directly to the soil around the base of the plants. This allows the nutrients to gradually release into the soil and be taken up by the plant roots. Irrigation System: If you have an irrigation system, you can dissolve calcium nitrate in water and apply it through the system. This ensures even distribution of the nutrients throughout the soil. Side Dressing: For larger plants or crops, you can apply calcium nitrate as a side dressing. This involves spreading the granules or prills of calcium nitrate alongside the plant rows or at the drip line.




