Table of Contents
Introduction Carbon Tetrachloride Formula
Carbon tetrachloride, with the chemical formula CCl4, is a colourless, heavy, nonflammable liquid compound. It is also known by the common name “tetrachloromethane.”
Carbon tetrachloride is a stable compound and is mainly used as a solvent, particularly in industrial applications. However, it is known to be toxic and has been phased out in many countries due to its harmful effects on human health and the environment.
Structural Formula of Carbon Tetrachloride
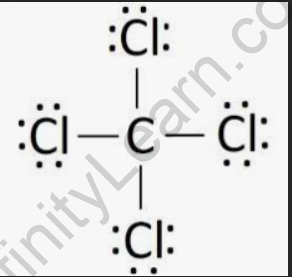
Carbon tetrachloride is composed of one carbon atom bonded to four chlorine atoms, arranged in a tetrahedral shape.
Uses of Carbon Tetrachloride
- Solvent: Carbon tetrachloride was commonly used as a solvent for various organic compounds, such as oils, fats, resins, and waxes. It was particularly useful in the dry cleaning industry for removing stains from fabrics.
- Fire Extinguisher: Carbon tetrachloride was utilized in fire extinguishers as a liquid that could be sprayed onto fires. However, it is no longer recommended for this purpose due to its toxicity and environmental impact.
- Refrigerant: In the past, carbon tetrachloride was employed as a refrigerant in cooling systems and air conditioners. However, it has largely been phased out due to its ozone-depleting properties.
- Chemical Intermediate: Carbon tetrachloride was used as a starting material for the synthesis of other chemicals, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), pesticides, and pharmaceuticals.
- Cleaning Agent: It was used as a degreasing agent and for cleaning electronic components, although safer alternatives are now preferred.
Physical Properties of Carbon Tetrachloride Formula
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is a colorless liquid compound that is also known as tetrachloromethane. Here are the physical properties of carbon tetrachloride:
- Molecular formula: CCl4
- Molecular weight: 153.82 g/mol
- Appearance: Colorless liquid
- Odour: Characteristic sweet odor
- Melting point: -22.92 °C (-9.28 °F)
- Boiling point: 76.72 °C (170.1 °F)
- Density: 1.586 g/cm³ at 25 °C (77 °F)
- Solubility: Carbon tetrachloride is relatively insoluble in water but dissolves in many organic solvents, such as ethanol, acetone, and benzene.
- Refractive Index: 1.461 at 20 °C (68 °F)
- Viscosity: 0.88 cP at 25 °C (77 °F)
- Flashpoint: Non-flammable, but it can ignite at high temperatures or in the presence of an open flame.
- Vapour Pressure: 11.7 mmHg at 25 °C (77 °F)
Chemical Properties of Carbon Tetrachloride Formula
- Stability: Carbon tetrachloride is a stable compound under normal conditions. It is non-reactive with most common substances, such as water, acids, and bases. However, it can react with strong reducing agents or reactive metals under certain conditions.
- Solvent properties: Carbon tetrachloride is an effective solvent for a wide range of organic compounds. It can dissolve oils, fats, resins, waxes, and many other nonpolar or weakly polar substances. Due to its nonpolar nature, it is not a good solvent for polar or ionic compounds.
- Inertness: Carbon tetrachloride is considered an inert compound in many chemical reactions. It is not easily involved in typical organic reactions, such as nucleophilic or electrophilic substitutions. This inertness makes it useful in certain applications, such as as a solvent for reactions that need an inert environment.
- Thermal decomposition: At high temperatures (above 900°C or 1652°F), carbon tetrachloride can undergo thermal decomposition. The decomposition products include toxic gases, such as chlorine gas (Cl2) and phosgene (COCl2), which can pose significant health hazards.
- Reaction with active metals: Carbon tetrachloride can react with highly reactive metals, such as sodium or magnesium, to form metal chloride compounds and release carbon. The reaction is typically exothermic and can be violent if not controlled.
Conclusion
In conclusion, carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is a chemical compound that was once widely used in various industries and applications. However, its use has significantly declined due to its harmful effects on human health and the environment. Carbon tetrachloride has been found to be toxic, carcinogenic, and damaging to the liver. It is also a potent greenhouse gas and ozone-depleting substance. As a result, its use has been restricted or banned in many countries. Safer alternatives have been developed to replace carbon tetrachloride in most applications, promoting the protection of human health and the environment.
Solved Examples on Carbon Tetrachloride Formula
Example 1: Calculating Molar Mass
What is the molar mass of carbon tetrachloride?
Solution: The molar mass of carbon (C) is approximately 12.01 g/mol, and the molar mass of chlorine (Cl) is approximately 35.45 g/mol. Since there are four chlorine atoms in carbon tetrachloride, we can calculate the molar mass as follows:
Molar mass of CCl4 = (Molar mass of C) + (4 × Molar mass of Cl) = (12.01 g/mol) + (4 × 35.45 g/mol)
= 12.01 g/mol + 141.8 g/mol
= 153.81 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of carbon tetrachloride is approximately 153.81 g/mol.
Example 2: Stoichiometry and Balanced Equation
What is the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between carbon tetrachloride and water (H2O)?
Solution: The balanced chemical equation for the reaction between carbon tetrachloride and water can be represented as follows:
CCl4 + 2H2O → CO2 + 4HCl
In this reaction, carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) reacts with water (H2O) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrochloric acid (HCl).
Example 3: Moles to Mass Conversion
How many grams of carbon tetrachloride are present in 0.25 moles of CCl4?
Solution: To determine the mass of carbon tetrachloride, we can use the molar mass of CCl4 calculated earlier.
Molar mass of CCl4 = 153.81 g/mol
Mass of CCl4 = Number of moles × Molar mass
= 0.25 moles × 153.81 g/mol
= 38.45 g
Therefore, there are 38.45 grams of carbon tetrachloride present in 0.25 moles of CCl4.
Frequently Asked Questions on Carbon Tetrachloride Formula
What is called CCl4?
CCl4 is the chemical formula for Carbon Tetrachloride, a compound consisting of one carbon atom and four chlorine atoms.
How do you write carbon tetrachloride?
Carbon tetrachloride is written as CCl4, denoting one atom of carbon and four atoms of chlorine in the molecular structure.
What is the valency of CCl4?
The valency of CCl4 is zero as the compound is stable and all the outer shell electrons of the carbon atom are shared with chlorine atoms.
What is CCl4 used for?
Historically, CCl4 was used as a cleaning agent, solvent, and in fire extinguishers. However, its use has been phased out due to environmental and health concerns.
What is the common name for carbon tetrachloride formula?
The common name for the carbon tetrachloride formula is Carbon Tetrachloride itself, but it was also known as Tetrachloromethane.
Why is CCl4 used as a solvent?
CCl4 was used as a solvent because of its ability to dissolve various organic compounds and its non-flammable nature, although it's largely phased out now.
Why is CCl4 used as a fire extinguisher?
CCl4 was used in fire extinguishers due to its ability to smother flames by inhibiting the availability of oxygen, although it’s no longer used due to its toxicity.
Is CCl4 organic or inorganic?
CCl4 is considered an inorganic compound despite it contains carbon, because it lacks hydrogen-carbon (C-H) bonds typical of organic compounds.
What is carbon tetrachloride used for?
Carbon tetrachloride was utilized as a solvent, cleaning agent, and in fire extinguishers, but its use is now restricted due to toxicity and environmental harm.








