Table of Contents
Annual Rainfall in India: India is a big country with different types of weather. Most of the rain comes from the Southwest Monsoon, which happens from June to September. There are two main types of rain – one in the southwest and the other in the northeast. The southwest rain is more, about 75% of the total rain we get each year. The northeast rain is less, about 25% of the yearly rainfall, and it comes from October to December.
Rainfall is a critical factor in shaping India’s diverse landscape and ways of life. India encounters different rainfall patterns, from the dry areas of Rajasthan to the green landscapes of the Western Ghats, with its vast size and varied topography. It is essential to Know how rainfall works in India to understand ecosystems, farming methods, and the daily routines of its people. This article will provide complete details about the Annual Rainfall in India and the Distribution of Annual Rainfall in India.
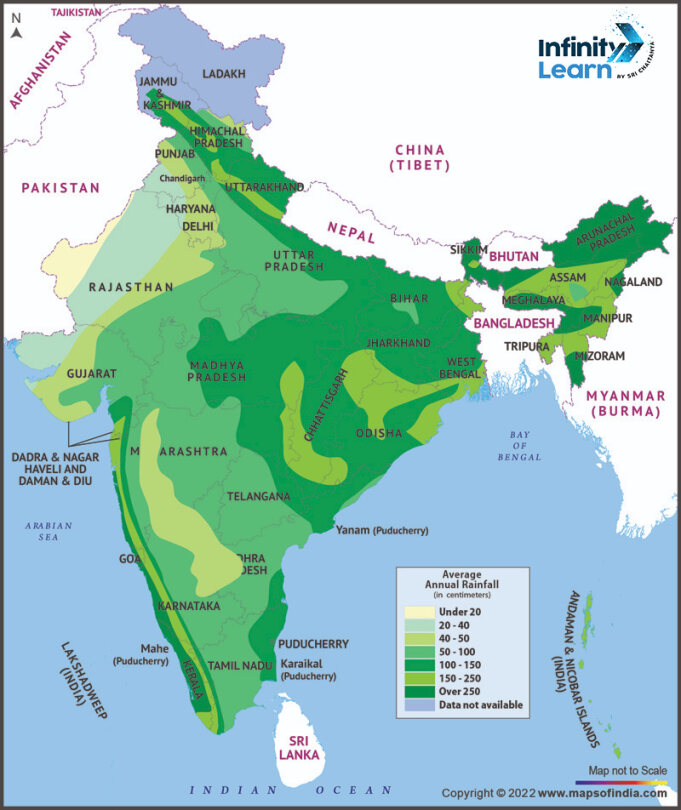
Annual Rainfall in India
India has different weather in different parts. Some places get lots of rain, while others get very little. India has two main types of monsoons: southwest monsoons (long rains) and northeast monsoons. Southwest monsoon happens when warm, wet air from the Indian Ocean meets cool, dry air over Central South Asia. Northeast monsoon comes from cold air in Siberia, meeting warm air over the Bay of Bengal.
In India, the western coast (Mumbai, Kerala) gets a lot of rain, but the eastern coast (Odisha, Kolkata) gets less. The northeast part (Assam, Meghalaya) gets heavy rain, around 2000mm every year. This happens because of how air masses interact, making India’s climate diverse.
Annual Rainfall Distribution in India
Rainfall in India is inconsistent throughout the year. It usually starts in June and ends in September. According to the Koppen Climate classification, India is divided into seven climatic regions:
- Alpine
- Sub-tropical arid desert
- Sub-tropical semi-arid
- Tropical semi-arid
- Tropical Savannah
- Sub-tropical humid
- Tropical rainforest
On average, Indian states receive 118 cm of rainfall annually, as per the Meteorological Department’s data. The distribution of Average Rainfall in India is further categorized into different regions:
Extreme Precipitation Regions: The areas in the Northeastern regions and the windward side of the Western Ghats experience around 400 cm of rainfall annually. This includes Assam, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, and the hilly areas of the Western Ghats, with Mawsynram in Meghalaya recording the highest average rainfall in India.
Heavy Precipitation Regions: Most parts of eastern India experience 200-300 cm of rainfall. States like West Bengal, Tripura, Nagaland, Manipur, Odisha, and Bihar fall under this zone, along with the sub-Himalayan belt.
Moderate Precipitation Regions: The areas with 100 to 200 cm of rainfall, including parts of West Bengal, Bihar, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, and the leeward area of the Western Ghats. The wet deciduous forests are common in this region.
Scanty Precipitation Region: The regions with 50 to 100 cm of rainfall contain parts of Maharashtra, Gujarat, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, and the western part of Uttar Pradesh. Usual flora includes common grasslands, savannahs, and dry deciduous forests.
Desert and Semi-desert Regions: The regions receiving less than 50 cm of annual rainfall in India are Rajasthan and Gujarat, and certain areas in Jammu and Kashmir, like Ladakh, are known as cold deserts. The savannah vegetation is found in wetter regions, and the lowest rainfall is in the Ruyli village in Rajasthan.
Highest Annual Rainfall in India
Mawsynram is located in Meghalaya, and it holds the record for the highest average rainfall in India. It receives about 11,873 mm (467 in) of rain. It is known as the “land of the clouds,” Meghalaya showcases India’s geographical diversity, ranging from the dry Thar Desert to the wettest place on Earth, Cherrapunji.
States with Highest Rainfall
Sikkim, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and West Bengal are states experiencing significant average rainfall in India. The key areas include Mawsynram, Agumbe (Karnataka), Cherrapunji, Mahabaleshwar (Maharashtra), Pasighat (Arunachal Pradesh), Amboli (Maharashtra), and Gangtok (Sikkim).
Average Annual Rainfall in India
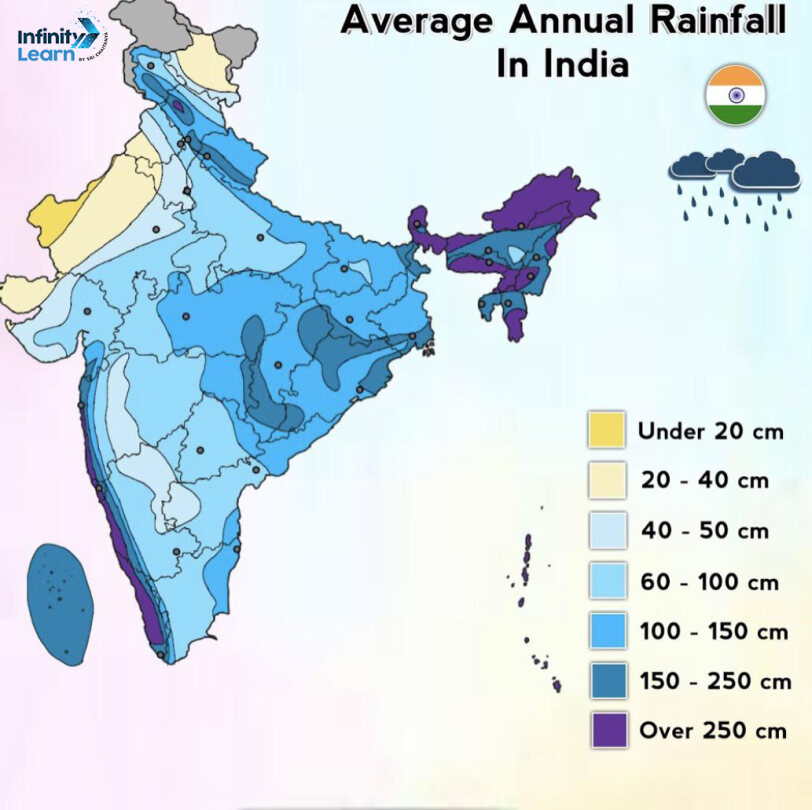
India’s average annual rainfall is around 125 cm (890 mm). However, the distribution varies due to factors like geographical features, closeness to the sea, and altitude. The coastal regions along the western coast and northeastern states receive higher average rainfall in India. It ranges from 2,500 to 5,000 mm annually.
Lowest Annual Rainfall in India
Jaisalmer district in Rajasthan, notably Ruyli, experiences the lowest average rainfall in India. The rainfall measured just 8.3 cm. Jaisalmer’s Ruyli witnesses minimal average rainfall in India, with an average of 210 mm.
Artificial Annual Rainfall in India
The cloud seeding is an artificial rainfall technique. It is gaining popularity in India. The successful experiments, including a reported 18% increase in Annual Rainfall in Maharashtra, have sparked increased investment. Scientists from the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune, conducted studies on cloud seeding and targets hygroscopic, warm convective clouds with a cloud base height below zero.
Average Rainfall in India UPSC
For UPSC aspirants, a focused study on the annual rainfall in India chapter is important. This topic holds immense significance as it constitutes a substantial portion of the UPSC Geography syllabus. It encompasses the physical, economic, and human aspects of India’s geography.
The UPSC syllabus includes a comprehensive questioning of the patterns of Average rainfall in India within the subject of geography. A deep understanding of this subject is vital for aspirants gearing up for the UPSC exams. It equips them with the knowledge to adeptly handle questions related to India’s climate and its far-reaching consequences across diverse sectors.
Annual Rainfall in India FAQs
Where does India experience its highest annual rainfall?
Mawsynram receives the highest annual rainfall in India.
What is the average annual rainfall in India?
The average annual rainfall in India is 118 cm, according to annual data from the Meteorological Department.
Which place holds the second position in terms of highest annual rainfall in India?
Cherrapunji is the second rainiest place in India. It is also located in Meghalaya.








