Table of Contents
Magnesium Nitrate Formula
Introduction
Magnesium nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Mg(NO3)2. It consists of one magnesium ion (Mg2+) and two nitrate ions (NO3-) per formula unit. It is a crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water.
Magnesium nitrate is commonly used as a source of magnesium in various applications, such as fertilizers, fireworks, and as a catalyst in certain chemical reactions. It is also used in the production of other magnesium compounds and as a component in the manufacture of explosives.
Structural Formula of Magnesium Nitrate
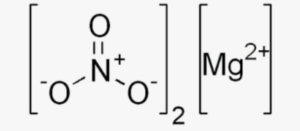
The structural formula of magnesium nitrate is written as Mg(NO3)2. This formula represents the arrangement of atoms in a molecule of magnesium nitrate. It consists of one magnesium (Mg) ion bonded to two nitrate (NO3-) ions. The magnesium ion has a 2+ charge, while each nitrate ion has a 1- charge.
Uses of Magnesium Nitrate
- Fertilizers: Magnesium nitrate is used as a source of magnesium and nitrogen in fertilizers. It provides essential nutrients to plants for healthy growth, chlorophyll production, and overall nutrient balance. It is particularly beneficial for crops that require additional magnesium, such as fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
- Fireworks: Magnesium nitrate is a common ingredient in fireworks and pyrotechnic compositions. When ignited, it produces a brilliant white light due to the intense burning of magnesium. It is often used in combination with other metal salts to create colorful flame effects in fireworks displays.
- Laboratory and Chemical Reagents: Magnesium nitrate is used in laboratory settings as a source of magnesium for various chemical reactions. It can also be used as a reagent in analytical chemistry, particularly in the determination of phosphates and other substances.
- Metal Surface Treatment: Magnesium nitrate is utilized in metal surface treatment processes. It can be used as a component in coatings and plating baths to provide corrosion resistance and improve the appearance of metal surfaces. It is commonly employed in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
- Preservation of Wood: Magnesium nitrate can be used as a wood preservative to protect against decay and insect infestation. It is applied as a solution or treatment to wood products, particularly in outdoor applications or areas prone to moisture and fungal growth.
- Concrete Additive: Magnesium nitrate can be added to concrete formulations as an admixture to improve its performance and durability. It helps to reduce the setting time of concrete, enhance workability, and increase the strength and resistance to freeze-thaw cycles.
Physical Properties of Magnesium Nitrate Formula
- Appearance: Magnesium nitrate is usually a crystalline solid. The crystals can vary in color from white to colorless or slightly yellowish.
- Solubility: Magnesium nitrate is highly soluble in water. It readily dissolves in water to form a clear and colorless solution.
- Melting Point: The melting point of magnesium nitrate is around 89-90°C (192-194°F). At this temperature, it undergoes a phase transition from a solid to a liquid state.
- Density: The density of magnesium nitrate is approximately 2.3 g/cm³. The density can vary slightly depending on the temperature and crystalline form.
- Hygroscopicity: Magnesium nitrate has hygroscopic properties, meaning it can absorb moisture from the surrounding environment. It tends to form hydrates, such as the hexahydrate form Mg(NO3)2 · 6H2O), which contains six water molecules per magnesium nitrate molecule.
- Odor: Magnesium nitrate is odorless.
Also Check For: Zinc Nitrate Formula
Chemical Properties of Magnesium Nitrate Formula
- Decomposition: Magnesium nitrate decomposes upon heating, releasing nitrogen dioxide (NO2) gas and oxygen (O2) gas as byproducts. The decomposition reaction can be represented as: 2Mg(NO3)2 → 2MgO + 4NO2 + O2
- Hydration: Magnesium nitrate can readily absorb water from the atmosphere, forming hydrates. The most common hydrate form is the hexahydrate (Mg(NO3)2· 6H2O), which contains six water molecules per magnesium nitrate molecule.
- Oxidizing Properties: Magnesium nitrate is an oxidizing agent. It can donate oxygen to other substances and promote oxidation reactions. It can react with reducing agents, such as organic materials or certain metals, releasing oxygen and potentially causing combustion.
- Reaction with Bases: Magnesium nitrate reacts with bases to form magnesium hydroxide. For example, when reacting with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), the following reaction occurs: Mg(NO3)2 + 2NaOH → Mg(OH)2 + 2NaNO3
- Solubility: Magnesium nitrate is highly soluble in water. It dissolves easily to form a clear and colorless solution. The solubility of magnesium nitrate increases with increasing temperature.
Conclusion
In conclusion, magnesium nitrate (Mg(NO3)2) is a chemical compound consisting of magnesium ions (Mg2+) and nitrate ions (NO3-). The formula represents the composition of the compound and the arrangement of its constituent elements. Magnesium nitrate has several applications and uses in various industries. It is commonly used as a fertilizer in agriculture to provide plants with essential nutrients, particularly magnesium and nitrogen, which are important for healthy plant growth and development. It can also be used as an oxidizing agent in certain chemical reactions and processes. Additionally, magnesium nitrate is utilized in the production of pyrotechnics and fireworks to produce vibrant colors when ignited. It is also employed in the manufacturing of ceramics, catalysts, and specialty chemicals. The formula for magnesium nitrate reflects its composition and plays a crucial role in determining its properties and applications in different fields.
Solved Examples on Magnesium Nitrate Formula
Example 1: Determine the molecular weight of magnesium nitrate hexahydrate (Mg(NO3)2 · 6H2O).
Solution: To calculate the molecular weight, we need to consider the atomic masses of magnesium (Mg), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), and hydrogen (H).
The atomic masses are as follows:
Mg: 24.31 g/mol
N: 14.01 g/mol
O: 16.00 g/mol
H: 1.01 g/mol
Now, let’s calculate the molecular weight of magnesium nitrate hexahydrate:
Mg(NO3)2: (1 × Mg) + (2 × N) + (6 × O)
= 24.31 + (2 × 14.01) + (6 × 16.00)
= 148.31 g/mol 6H2O: (6 × 2 × H) + (6 × O)
= (6 × 2 × 1.01) + (6 × 16.00) = 108.18 g/mol
Adding the molecular weights of Mg(NO3)2 and 6H2O: 148.31 + 108.18
= 256.49 g/mol
Therefore, the molecular weight of magnesium nitrate hexahydrate is 256.49 g/mol.
Example 2: Calculate the amount of magnesium nitrate required to prepare 500 mL of a 0.1 M solution.
Solution: To determine the amount of magnesium nitrate needed, we need to use the formula: Amount (in moles) = Concentration (in M) × Volume (in L)
Given: Concentration = 0.1 M Volume = 500 mL = 0.5 L
Using the formula: Amount (in moles) = 0.1 M × 0.5 L = 0.05 moles
The molar mass of magnesium nitrate is 148.31 g/mol, so the mass of magnesium nitrate needed can be calculated as:
Mass = Amount (in moles) × Molar mass
Mass = 0.05 moles × 148.31 g/mol = 7.42 g
Therefore, 7.42 grams of magnesium nitrate is required to prepare 500 mL of a 0.1 M solution.
Frequently Asked Questions on Magnesium Nitrate Formula
What is the Criss Cross method of magnesium oxide?
The Criss Cross method helps you find the formula of an ionic compound. For magnesium oxide, magnesium has a charge of +2 and oxygen has a charge of -2. When you criss-cross the numbers (without the signs), you get Mg1O2, but since the numbers are equal, we simplify to MgO.
What is mg2+ and NO3- combined?
When Mg²⁺ (a magnesium ion) combines with NO₃⁻ (a nitrate ion), they form magnesium nitrate.
What is the formula for magnesium nitrate?
The formula for magnesium nitrate is Mg(NO₃)₂.
What is the formula for magnesium nitrite by Criss Cross method?
Magnesium has a charge of +2 and nitrite has a charge of -1. Using the Criss Cross method, you'd get Mg1(NO₂)2 or simply Mg(NO₂)₂.
What are the uses of magnesium nitrate?
Magnesium nitrate is used in the manufacture of concentrated nitric acid, as a dehydrating agent in the preparation of concentrated nitric acid, and as a source of magnesium in horticulture and agriculture.
How do you write magnesium nitrite?
Magnesium nitrite is written as Mg(NO₂)₂.
What is Mg2 and NO3?
Mg²⁺ refers to a magnesium ion with a +2 charge. NO₃⁻ refers to a nitrate ion with a -1 charge.








