Table of Contents
Nitric acid, with the chemical formula HNO3, is a strong and highly corrosive acid. It plays a crucial role in various industrial processes and has several applications. Let’s explore the formula, structure, physical properties, and chemical properties of nitric acid in detail.
Formula and Structure of Nitric Acid
The chemical formula of nitric acid is HNO3. It consists of one hydrogen (H) atom, one nitrogen (N) atom, and three oxygen (O) atoms. The structure of nitric acid can be represented as follows:
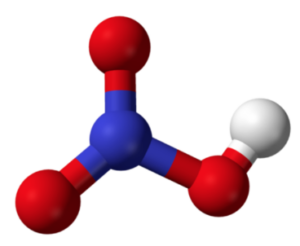
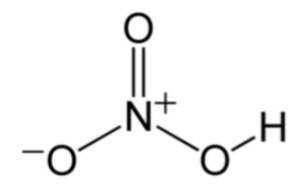
Nitric acid (HNO3)
In the structure, the nitrogen atom is bonded to three oxygen atoms. One of the oxygen atoms is bonded to a hydrogen atom.
Nitric Acid Physical Properties
- State: Nitric acid is a colourless liquid at room temperature.
- Odour: It has a pungent and distinct odour.
- Boiling Point: The boiling point of nitric acid is approximately 83 degrees Celsius (181 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Melting Point: Nitric acid freezes at approximately -42 degrees Celsius (-44 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Density: The density of nitric acid is about 1.51 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
- Solubility: Nitric acid is highly soluble in water and forms a stable aqueous solution.
Also Check: Zinc Nitrate Formula
Nitric Acid Chemical Properties
- Acidity: Nitric acid is a strong acid and dissociates completely in water, releasing hydrogen ions (H+). It is a potent oxidizing agent.
- Reaction with Metals: Nitric acid reacts vigorously with various metals, including copper, zinc, and iron, producing metal nitrates and liberating hydrogen gas.
- Oxidizing Properties: Nitric acid is a powerful oxidizing agent and can oxidize many organic and inorganic compounds. It is commonly used in oxidation reactions in laboratories and industries.
- Corrosive Nature: Due to its strong acidity, nitric acid is highly corrosive to many substances, including metals, organic materials, and tissues.
- Decomposition: Nitric acid is thermally unstable and decomposes upon heating, releasing toxic gases such as nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and oxygen (O2).
Applications of Nitric Acid
- Chemical Manufacturing: Nitric acid is used in the production of fertilizers, explosives, dyes, and various organic and inorganic compounds.
- Pickling Agent: It is employed as a pickling agent for metals, such as steel and stainless steel, to remove rust and scale.
- Etching: Nitric acid is used in the etching process for metals, ceramics, and electronic components.
- Cleaning Agent: It is utilized as a cleaning agent for laboratory glassware and equipment.
- Analytical Reagent: Nitric acid is used as a reagent in various analytical techniques, including spectroscopy and titration.
Solved Examples on Nitric acid Formula
Example 1: What is the molar mass of nitric acid (HNO3)?
Solution: To determine the molar mass of nitric acid, we need to calculate the sum of the atomic weights of its constituent elements.
The atomic weights are as follows:
H (hydrogen) = 1.008 g/mol
N (nitrogen) = 14.01 g/mol
O (oxygen) = 16.00 g/mol
Now, let’s calculate the molar mass:
Molar mass of nitric acid (HNO3) = H + N + (3 * O)
= 1.008 + 14.01 + (3 * 16.00)
≈ 63.01 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of nitric acid (HNO3) is approximately 63.01 g/mol.
Example 2: What is the common use of nitric acid in industries?
Answer: Nitric acid has several applications in industries. One common use is in the production of fertilizers. It is a key ingredient in the manufacturing of ammonium nitrate, which is a widely used nitrogen-based fertilizer. Nitric acid is also utilized in the production of explosives, such as dynamite and TNT (trinitrotoluene). Additionally, it is employed in the manufacturing of dyes, pigments, and various organic and inorganic compounds. Nitric acid’s strong oxidizing properties make it valuable in oxidation reactions, including the production of nitrobenzene and nitrocellulose. These applications highlight the significance of nitric acid in various industrial processes.
Frequently asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the chemical formula of nitric acid?
The chemical formula of nitric acid is HNO3.
How many hydrogen atoms are present in the formula of nitric acid?
Nitric acid contains one hydrogen H atom.
What is the oxidation state of nitrogen in nitric acid?
The oxidation state of nitrogen in nitric acid is plus 5.
What are the elements present in the formula of nitric acid?
The formula of nitric acid consists of hydrogen H, nitrogen N, and oxygen O atoms.
Is nitric acid a strong acid?
Yes, nitric acid is a strong acid. It completely dissociates in water, releasing hydrogen ions H plus.








