Table of Contents
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2017 Outside Delhi
Time allowed : 3 hours
Maximum marks: 70
General Instructions :
- There are 22 questions in all.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question number 1 to 7 are very short-answer questions carrying 1 mark each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 40
- Question numbers 8 to 13 are short-answer questions carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 80-100 words.
- Question numbers 14 to 20 are long-answer questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 150
- Question numbers 21 to 22 are related to identification or locating and labelling of geographical features on maps, carrying 5 marks each.
- Outline maps of the World and India provided to you must be attached within your answer-book.
- Use of templates or stencils for drawing outline maps is allowed.
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2017 Outside Delhi Set – I
Question 1.
State the two groups of factors which affect the profitability of mining. [1/2 + 1/2 = 1]
Answer:
Several factors affecting the profitability of mining operations are :
- Richness or Grade of the Ore,
- Size of Deposit,
- Method of Mining,
- Accessibility,
- Stage of Industrial Development
Question 2.
Which country of the world has the highest road density ? [1]
Answer:
Japan with respect to country size/area, Japan has highest road density and is 327 km length of roads per 100 sq. km area.
Question 3.
Name any two garrison (cantonment) towns of India. [1/2 + 1/2 = 1]
Answer:
Main cantonment towns of India are :
- Ambala,
- Jalandhar,
- Mhow,
- Babina and
- Udhampur.
Question 4.
Why is West Asia the least developed in rail facilities ? Explain one reason. [1]
Answer:
West Asia is the least developed in terms of rail facilities because of vast deserts and sparsely populated regions.
Question 5.
Examine the twin environmental problems that have emerged in the ‘Indira Gandhi Canal Command Area’. [1]
Answer:
Due to intensive irrigation and excessive use of water has led to the emergence of problems of water logging and soil salinity and both these have adverse effect on soil fertility and agricultural productivity.
Question 6.
Classify minerals on the basis of chemical and physical properties. [1/2 + 1/2 = 1]
Answer:
Minerals are divided into groups on the basis of chemical and physical properties. These are :
- Metallic and
- Non-Metallic minerals. Examples of metallic minerals are iron, copper, gold, silver and non-metallic minerals are salt, coal, copper etc.
Question 7.
How can you help in improving the quality of water in your locality ? [1]
Answer:
Quality of water suffers from large scale of pollution almost throughout the country. In the populated locality, we can avoid dumping all waste matter into water and into our rivers.
Question 8.
Study the map given below carefully and answer the questions that follow : [3]
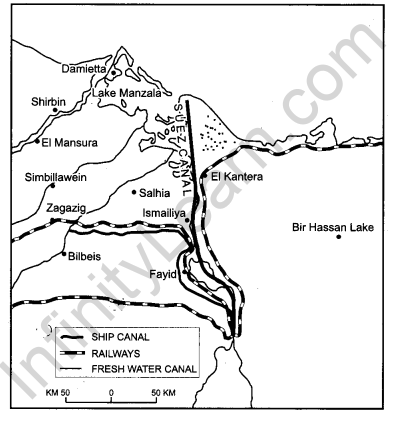
Question 8.1.
Identify and name the canal shown in the map.
Answer:
The canal shown in map is Suez Canal, constructed in 1869 between Port Said and Port Suez in Egypt.
Question 8.2.
Write any four characteristics of this canal.
Answer:
The main characteristics of this canal are :
- It gives Europe a new gateway to the Indian ocean and reduces sea-route distance between Liverpool and Colombo by 6400 km compared to Cape of Good Hope route.
- It is a sea level canal without locks which is 130 km long and 11 to 15 meter deep.
- About 100 ships travel daily and each ship takes around 10-12 hours to cross the canal.
- As the tolls are heavy, some find it cheaper to go by the longer Cape Route whenever the consequent delay is not important.
- A navigable fresh canal also follows from Nile.
Question 9.
Describe any three characteristics of chain stores in the world. [3 × 1 = 3]
Answer:
The distinctive features of multiple shops are as under :
- Chain stores are able to purchase merchandise most economically to their specification.
- They often direct the manufacturers. They employ highly skilled specialists.
- The main objective of the chain stores is to establish direct contact with the consumers by eliminating middlemen.
- They operate under centralised control and are horizontally integrated.
- The layout of these shops is simple and similar. They have the ability to experiment in one store and apply the results to many.
Question 10.
Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow : [3 × 1 = 3]
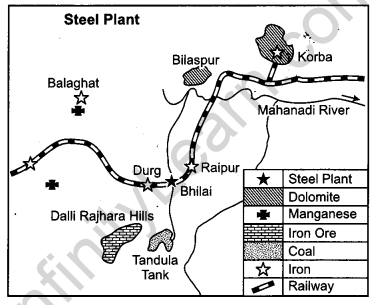
Question 10.1.
Identify and name the steel plant given above. In which state this plant located ?
Answer:
Steel plant is “Bhilai” and located in Chhattisgarh State.
Question 10.2.
Which is the main source of power for this steel plant ? Which rail route provides transport facilities to this plant ?
Answer:
Main power source is “Korba Thermal Power Station”. The rail route connecting to this plant is Kolkata-Mumbai rail route.
Question 10.3.
What are the major sources of Iron ore and water for this steel plant ?
Answer:
Major source of rich Hemetite Iron Ore for this plant is “Dalli-Rajhara range” of mines. The water source is “Tandula Tank”.
Question 11.
“There is no consensus on what exactly defines a village or a town.” Analyse the statement by using different criteria. [3]
Answer:
We all live in cluster of houses which can be called as village or a town. It is widely accepted that settlements can be differentiated in terms of rural (village) and urban (town), but there is no consensus on what exactly defines a village or a town. Although population size is an important criterion, it is not a universal criteria since many villages in densely populated countries in like India and China have population exceeding than some towns of Europe and USA.
In certain countries, urban settlements are defined on the economic basis. For example, in India, towns are called urban towns cities when it has 75% of its work force engaged in non-agricultural activities, whereas in some western countries an urban area is if more than 50% of the economically productive population are engaged in non-agricultural pursuits.
Question 12.
“Nature provides opportunities and humans make use of these and slowly nature gets humanised and starts bearing the imprints of human endeavour.” Justify the statement. [3]
Answer:
When the human being makes use of opportunities provided by nature, it starts bearing the imprints of human endeavour and this situation is known as humanisation of nature. Human beings interact with their physical environment with the help of technology. Technology indicates the level of cultural development of society.
Knowledge about nature is extremely important to develop technology and advanced technology loosens the shackles of environment on human beings. In the early stages of their interaction with their natural environment humans were greatly influenced by it. They adapted to the dictates of nature. This is so because the level of technology was very low and the stage of human social development was also primitive. They create possibilities with the resources obtained from the environment. The human activities create the cultural landscape. The imprints of human activities are created everywhere; health resorts on highlands, huge urban sprawls, fields, orchards and pastures in plains and rolling hills, ports on the coasts, oceanic routes on the oceanic surface and satellites in the space.
Question 13.
“Indiscriminate use of water by increasing population and industrial expansion has led to degradation of the water quality considerably in India.” Explain the values that can help in maintaining the quality of water. [3]
Answer:
Indiscriminate use of water by increasing population and industrial expansion has led to degradation of the quality of water considerably. Values that can help in maintaining the quality of water are :
- Judicious/optimum use of water; controlling population and recycle and reuse of water; Watershed Management and Rainwater Harvesting.
- Haryali is the watershed development started by the government of India for the same reason.
- Industries which are located on the river banks should be monitored for the waste disposals. They should not be throwing the waste in the river.
Question 14.
Mention any four major objectives of the New Industrial Policy, 1991 of India. Describe the role of globalisation in achieving these objectives. [2 + 3 = 5]
Answer:
Major objectives of India’s New Industrial Policy 1991 are as follows :
- The New Industrial Policy, 1991 seeks to liberate the industry from the shackles of licensing system.
- Maintain a sustained growth in productivity.
- Encourage foreign participation in India’s industrial development.
- Gainful employment and attain international competitiveness.
The process of globalisation includes opening up of world trade, development of advanced means of communication, internationalization of financial markets, growing importance of MNCs, population migrations and increased mobility of persons, goods, capital, data and ideas. It refers to the integration of economies of the world through uninhibited trade and financial flows, as also through mutual exchange of technology and knowledge. It also contains free inter-country movement of labour. This implies opening up the economy to foreign direct investment by providing facilities to foreign companies to invest in different fields of economic activity in India, removing constraints and obstacles to the entry of MNCs, allowing Indian companies to enter into foreign collaborations and also encouraging them to set up joint ventures abroad; carrying out massive import liberalisation programs by switching over from quantitative restrictions to tariffs and import duties, therefore globalisation has been identified with the policy reforms of 1991 in India.
Question 15.
“The size of a territory and per capita income are not directly related to human development.” Support the statement with examples. [5]
Answer:
Yes, it is true that the size of territory and per capita income are not directly related to human development.
- Growth of economy and productivity is generally assessed with the help of gross national product and per capital income.
- There are few rich and developed states like Maharashtra, Punjab, Haryana, Gujarat and Delhi have per capita income more than ₹ 4,000/month.
- Poverty is reflected in poor quality of life. Hundreds of people suffer malnutrition, deprivation, illiteracy and consequent low level of human development. It does not depend upon the size of territory.
- Often Smaller Countries have done better than larger ones in human development. Similarly, relatively poorer nations have been ranked higher than richer neighbours in terms of human development.
For example Sri Lanka, Trinidad and Tobago have a higher rank than India in the human development index despite having smaller economies. Similarly, within India, Kerala performs much better than Punjab and Gujarat in human development despite having lower per capita income. - Some large states like Odisha, Bihar, MP, UP and Tamilnadu have more than 50% population below poverty line while Delhi is much smaller areawise but is a prosperous state.
Question 16.
How is migration a response to the uneven distribution of opportunities over a space ? Explain the economic consequences of migration in India. [2 + 3 = 5]
Answer:
Migration is a response to the uneven distribution of opportunities because of the following reasons :
- In India many people live in rural areas and they migrate to urban areas mainly due to poverty, high population pressure on land, lack of basic infrastructural facilities like health, education, etc. This proves that migration is responsible for the uneven distribution over space.
- People tend to move from place of low opportunities and less safety to a place which has more opportunities and safe.
Economic Consequences :
- People migrating send remittance to their families at home and add to economic prosperity. Remittance from international migrants is one of the major sources of foreign exchange. In 2002, India received US $11 billion as remittances from international migrants.
- Remittance are used for food, repayment of debts, treatment, marriages, children education, agricultural development, construction of houses, etc. Thousands of poor villages of many states works as live blood for economy.
- Punjab, Kerala and Tamil Nadu receive very significant amount from their international migrants. Internal Migrants play an important role in the growth of economy of the source area.
Question 17.
“In modem times international trade is the basis of the world economy.” Support the statement with examples. [5]
Answer:
Trade is the base of world economy. The exchange of surplus goods between different countries is called international trade. It is the index of economic development of the country. The countries which export the commodities earn foreign exchange. Developed countries are major trading countries. It also helps to raise the standards of living of the people of developing countries. Some densely populated countries have to import raw materials to meet their demands for their economic and industrial development.
Such countries are Japan, Sri Lanka and other countries. The actual tonnage of goods traded makes up the volume. However, services traded cannot be measured in tonnage. Therefore, the total value of goods and services traded is considered to be the volume of trade. The total volume of world trade has been steadily rising over the past decades. Trade of primary products was dominant in the beginning of the last century. Later manufactured goods gained prominence and currently, though the manufacturing sector commands the bulk of the global trade, service sector which includes travel, transportation and other commercial services have been showing an upward trend.
Question 18.
Review any five measures adopted to solve the problems of Indian agriculture. [5 × 1 = 5]
Answer:
Measures adopted to solve the problems are :
(i) Indian agriculture is totally dependent on monsoon. The crop production in the cultivated land is directly dependent on rainfall. Excessive rainfall causes flood and less rainfall causes drought conditions. For expansion of irrigation dams, rivers and canals have played a crucial role enhancing agriculture output in country.
(ii) The yield of the crops in country is low in comparison to international level. Output of most of the crops such as rice, wheat, cotton and oil seeds in India is much lower than that of USA, Russia, Japan. Use of modern agricultural technologies such as high yield variety of seeds, chemical fertilisers, pesticides and farm machinery are introduced in India.
(iii) The inputs of modern agriculture are very expensive for the farmers to afford. So government is supporting them by introducing the facilities like farmer loans, machinery loans at very low interest rates.
(iv) A large number of farmers produce crops for self consumption. These farmers do not have enough land and resources to produce more than their requirement. Government is encouraging them to use high yield seeds, fertilisers and provide it in competitive rates.
(v) New seed varieties of wheat (Mexico) and rice (Philippines) known as high yielding varieties (HYVs)
were available for cultivation by mid-1960s. India took advantage of this and introduced package technology comprising HYVs, along with chemical fertilisers in irrigated areas of Punjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat.
Question 19.
Classify intensive subsistence agriculture into two categories practised in the world. How are they different from each other ? Explain. [1 + 4 = 5]
Answer:
Basically, there are two types of intensive subsistence agriculture :
Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by Wet paddy cultivation : This type of agriculture is characterised by dominance of the rice crop. Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by Non Paddy crops : This type of agriculture is characterised mainly by wheat.
|
Paddy |
Non-Paddy |
| (i) Rice is the dominant crop. | Wheat, Soyabean, Barley and Sorghum are the main crops. |
| (ii) Land holdings are very small due to high density of population. | Land holdings are big. |
| (iii) Labour is supplied by the farmer and his family members.
|
Machinery is deployed for cultivation of non-paddy crops. |
| (iv) Fertility of soil is maintained by using farm manure. | Fertilisers, pesticides are highly used for increasing soil fertility. |
Question 20.
Classify means of communication on the basis of scale and quality into two categories. Explain any two characteristics of each category. [1 + 4 = 5]
Answer:
Classification of means of communication on the basis of scale and quality : Personal Communication System:
- It is the most effective and advanced one and widely used in urban areas.
- It enables the user to establish direct connect through Email to get access to world of knowledge and information.
- It is used for e-commerce and carrying out monetary transaction.
- It is a huge central warehouse of data, with detailed information on various items.
(Letters, Telephone, Fax, Email, Internet, etc).
Mass Communication System :
- Radio broadcasting started in India in 1923 by the Radio club of Bombay and changed the socio-cultural life of people.
- Television broadcasting emerged as the most
- Use of satellite and synoptic view of larger area effective audio visual medium for information and for economic and strategic reasons.
(Radio, Television, Cinema, Satellite, Newspaper, Magazine and Books, Seminar and Conference, etc.).
Question 21.
Identify the five geographical features shown on the given political outline map of the world as A, B, C, D and E and write their correct names on the lines marked near them with the help of the following information: [5 × 1 = 5]
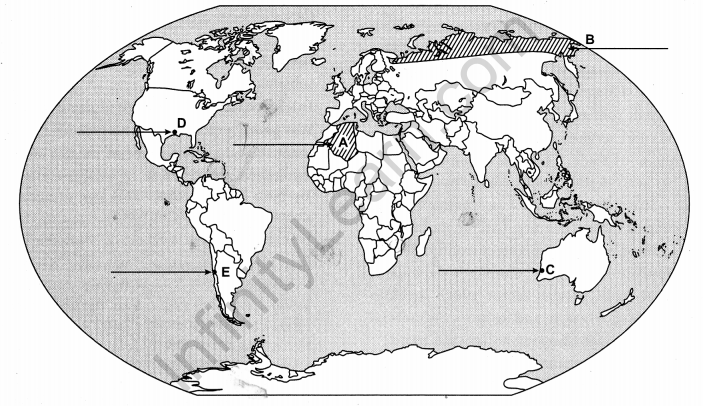
(A) A large country of Africa in terms of area
(B) A major area of subsistence gathering
(C) The terminal station of a ‘Transcontinental Railway’
(D) A major seaport
(E) An international airport
Answer:
Question 22.
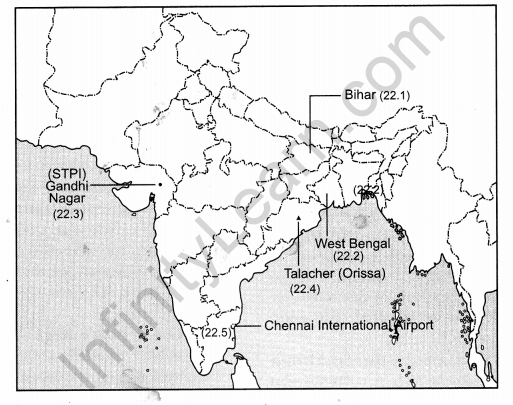
Locate and label the following features with appropriate symbols on the given outline political map of India: [5 × 1 = 5]
22.1. The state having the highest density of population according to census 2011.
22.2. The leading rice producing state.
22.3. The software technology park located in Gujarat.
22.4. The major coalfield located in Odisha.
22.5. An international airport located in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2017 Outside Delhi Set – II
Note : Except for the following questions, all the remaining questions have been asked in previous set.
Question 1.
What are the two types of Intensive subsistence agriculture ? [1]
Answer:
It is of the following two types :
- Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by wet paddy cultivation.
- Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by crops other than paddy.
Question 2.
Which country has the largest rail network in Africa ? [1]
Answer:
South Africa, with 18,000 km of railways has the densest rail network because of the gold, copper and diamond activities.
Question 3.
Name any two towns of India, initially developed as mining towns. [1/2 + 1/2 = 1]
Answer:
Raniganj, Jharia, Digboi and Singrauli were all developed as mining towns initially.
Question 9.
Describe any three characteristics of agro-based industries in the world.
Answer:
Agro-based industries are those industries which obtains raw materials from agricultural activities. Cotton textile, jute textile, silk, sugar, vegetable oil and paper industry are main industries of agro-based group of industries.
Its characteristics are :
- Agro-based industries are part of small scale industry which needs very nominal investment.
- Major agro processing industries are food processing industries.
- Most crucial factor is the availability of the raw materials. It should be available within a radius of 60 kms. In addition, water, power and other infrastructure facilities like access to road, railways, ports and airports as well as the markets for the products have to be ensured.
Question 15.
What is meant by human development ? Classify countries into four groups on the basis of the human development scores earned by them. Explain one feature of each group. [1 + 2 + 2 = 5]
Answer:
Human Development: The concept of human development was introduced by Dr. Mahbub-ul-Haq. Dr. Haq has described human development as development that enlarges people’s choices and improves their lives. People’s choices are not fixed but keep on changing. The basic goal of development is to create conditions where people can live meaningful lives. A meaningful life is not just a long one. It must be a life with some purpose. This means that people must be healthy, be able to develop their talents, participate in society and be free to achieve their goals.
Countries can be classified into four groups on the basis of the human development scores earned by them.

- Countries which are classified under High Human Index or Very High Human Index have a score of over 0.8; this group includes 57 countries. These countries provide higher human development through proper investment in people and good governance.
- Countries which are classified under High Human Index also include a good number of countries who provide appropriate human development through investment in right areas.
- Countries with Medium Human Index have more than 50 countries who have emerged after the Second World War. Some were former colonies while others appeared after the Soviet Union collapsed. They have a high social diversity however, they have faced social or political instability and uprising in history.
- About 32 countries record Low Level of Human Development because they have been going through political turmoil.
Question 18.
Explain the importance of five non-conventional sources of energy with suitable examples. [5]
Answer:
Importance of non-conventional sources of energy are :
(i) Solar Energy : Sun rays tapped in photovoltaic cells can be converted into energy, known as solar energy. The two effective processes considered to be very effective to tap solar energy are photovoltaics and solar thermal technology. It is cost competitive, environment friendly and easy to construct. It is generally used more in appliances like heaters, crop dryers, cookers, etc. The Western part of India has greater potential for the development of solar energy in Gujarat and Rajasthan.
(ii) Wind Energy : Wind energy is absolutely pollution free, inexhaustible source of energy. The mechanism of energy conversion from blowing wind is simple. The kinetic energy of wind, through turbines is converted into electrical energy. The permanent wind systems such as the trade winds, westerlies and seasonal winds like monsoon have been used as source of energy. Besides these, local winds, land and sea breezes can also be used to produce electricity. India, already has started generating wind energy. It has an ambitious programme to install 250 wind-driven turbines with a total capacity of 45 megawatts, in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Karnataka, favourable conditions for wind energy exists.
(iii) Tidal and Wave Energy : Ocean currents are the store-house of infinite energy. Since the beginning of seventeenth and eighteenth century, persistent efforts were made to create a more efficient energy system from the ceaseless tidal waves and ocean current. Large tidal waves are known to occur along the west coast of India. Hence, India has great potential for the development of tidal energy along the coasts but so far these have not yet been utilised.
(iv) Geothermal Energy: When the magma from the interior of earth, comes out on the surface, tremendous heat is released. This heat energy can successfully be tapped and converted to electrical energy. Apart from this, the hot water that gushes out through the geyser wells (hot wells) is also used in the generation of thermal energy. It is popularly known as geothermal energy. This energy is now considered to be one of the key energy sources which can be developed as an alternate source. The hot springs and geysers are being used since medieval period. In India, a geothermal energy plant has been commissioned at Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh.
(v) Bio-energy: Bio-energy refers to energy derived from biological products which includes agricultural residues, municipal, industrial and other wastes. Bio energy is a potential source of energy conversion. It can be converted into electrical energy, heat energy or gas for cooking. It will also process the waste and garbage and produce energy. One such project converting municipal waste into energy is Okhla in Delhi.
Question 19.
Analyse the significance and growth of service sector in the modern economic development of the world. [5]
Answer:
- Services are provided to individual consumers who can afford to pay for them. For example gardener, launderers and barber do primarily physical labour. Teachers, lawyers, physicians, musicians and others perform mental labour.
- Many services have now been regulated. Making and maintaining highways and bridges, maintaining fire fighting departments and supplying or supervising education.
- Customer care is among the important services often supervised or performed by governments or companies.
- Professional services are primarily healthcare, engineering, law and management. The location of recreational and entertainment services depends on the market.
- In modern times, Service sector has grown at a very fast speed all over the world. Economy of most of the developed countries is based on the earnings of service sectors.
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2017 Outside Delhi Set – III
Note : Except for the following questions, all the remaining questions have been asked in previous set.
Question 1.
Mention any two main regions of commercial dairy farming. [1/2 + 1/2 = 1]
Answer:
The main regions for dairy farming on commercial basis in the world are :
- The largest is North-Western Europe.
- Canada and North-Eastern USA.
- South-Eastern Australia, New Zealand and Tasmania.
Question 2.
Which inland waterway of the world is most heavily used ? [1]
Answer:
Rhine Waterways.
Question 3.
Name any two towns of India, initially developed as educational centres. [1/2 + 1/2 = 1]
Answer:
Some towns of India were initially developed as education as their primary function are : Roorkee, Varanasi, Aligarh, Pilani, etc.
Question 9.
Describe any three features of open-cast mining. [3]
Answer:
Features of open-cast mining are :
- This is the cheapest and easiest method of mining and is used for mining those minerals which occur close to the surface.
- The overhead costs such as safety precaution and equipment is relatively low.
- The output is both large and rapid.
Question 15.
Classify the population of the world on the basis of their residence into two groups. How are they different ‘from each other ? Explain. [1 + 4 = 5]
Answer:
The division of population into rural and urban is based on the residence.
| Rural Population | Urban Population |
| (i)The population living in a village is known as rural population. | The population living in towns and cities is known as urban population. |
| (ii) It supports small size population. | Urban population is engaged in secondary and tertiary activities. |
| (iii) Rural population is mostly engaged in agricutural and other primary occupation. | Urban population is engaged in secondary and tertiary activities. |
| (iii) Share of the rural population is 55% of the whole population of the world. | Share of the urban population is 45% of the whole population of the world. |
Question 18.
What was the main aim of the ‘Tribal Sub-Plan’ introduced in 1974 in Bharmaur area ? Review its contribution in the development of the Bharmaur region. [1 + 4 = 5]
Answer:
The process of development of tribal area of Bharmaur started in 1970s when Gaddis were included among ‘scheduled tribes’. Under the Fifth Five Year Plan, the tribal sub-plan was introduced in 1974 and Bharmaur was designated as one of the five Integrated Tribal Development Projects (ITDP) in Himachal Pradesh. This area development plan was aimed at improving the quality of life of the Gaddis and narrowing the gap in the level of development between Bharmaur and other areas of Himachal Pradesh. This plan laid, the highest priority on development of transport, communications, agriculture and allied activities, social and community services.
The most significant contribution of tribal sub plan in Bharmaur region is the development of infrastructure in terms of schools, health care facilities, potable water, roads, communications and electricity. But the villages located along the river Ravi in Holi and Khani areas are the main beneficiaries of infrastructural development. The female literacy rate in the region increased from 1.88 per cent in 1971 to 65 per cent in 2011. Traditionally, the Gaddis had subsistence agricultural-cum-pastoral economy having emphasis on food grains and livestock production. But during the last three decades of twentieth century, the cultivation of pulses and other cash crops has increased in Bharmaur region. But the crop cultivation is still done with traditional technology. The declining importance of pastoralism in the economy of the region can be gauged from the fact that at present only about one-tenth of the total households practise transhumance.
Question 19.
Classify trading centres into two categories. How are they different from each other ? Explain. [1 + 4 = 5]
Answer:
Classification of trading center :
- Rural Marketing Centres :
- Rural marketing centres cater to nearby settlements.
- These are quasi-urban centres.
- They serve as trading centres of the most rudimentary type.
- Here personal and professional services are not well developed. These form local collecting and distributing centres. Most of these have mandis (wholesale markets) and also retailing areas.
- Urban Marketing Centres :
- Urban marketing centres have more widely specialized urban services.
- They provide ordinary goods and services.
- Urban centres offer manufactured goods or finished products.
- Service of educational institution and professionals such as teachers, lawyers, consultants, physicians, dentists and veterinary doctors are available.






