Table of Contents
CBSE Class 9 Maths Notes Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes
1. Cuboid: A figure which is surrounded by six rectangular surfaces is called cuboid.
The opposite surface of a cuboid is equal and parallel.
A cuboid has 12 edges and 8 corners. Each corner of a cuboid is called the vertex of a cuboid. The line segment joining the opposite vertices is called the diagonal of a cuboid. There are four diagonals in a cuboid.
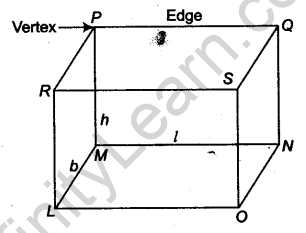
Volume of cuboid = Length × Breadth × Height = l × b × h
Lateral surface area = 2 (Length + Breadth) × Height = 2 (l + b) × h
Total surface area = 2 (Length × Breadth + Breadth × Height + Height × Length) = 2 (lb + bh + hl)
Total length of cuboid = 4 (l + b + h)
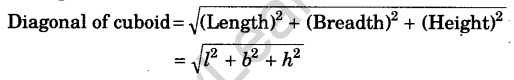
2. Cube: A cuboid, whose length, breadth and height are same is called a cube.
A cube has six surfaces, twelve edges, eight corners and four diagonals.
Volume of cube= (Side)3 = l3
Lateral surface area = 4 × (Side)2 = 4l2
Total surface area = 6 × (Side)2 = 6l2
Total length of cube = 12l
Diagonal of cube = √3 l
3. Right Circular Cylinder: A right circular cylinder is considered as a solid generated by the revolution of a rectangle about one of its sides.
The volume of a cylinder = πr2h
Curved surface area or lateral surface area = 2πrh
Total surface area = Curved surface + 2 × Base area = 2πrh + 2πr2 = 2πr(h + r)
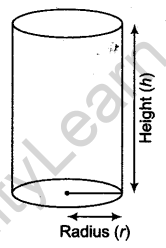
4. Cone: A right circular cone is a solid generated by revolving of a triangle about one of its sides (other than hypotenuse).
Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) πr2h
Curved surface area or lateral surface area = πrl
Total surface area = Curved surface area + Base area
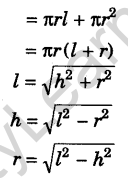
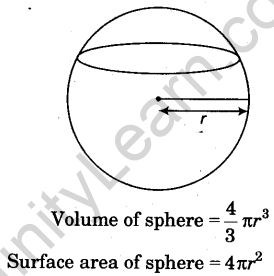
5. Sphere: A solid which is surrounded by a curved surface and each point of the surface is the same distance from a fixed point. The fixed point is called the centre of the sphere. The line segment joining from the centre of the sphere to any point of the surface is called the radius of the sphere.
6. Hemisphere: A plane passing through the centre of a sphere divides the sphere into two equal parts. Each part is called a hemisphere.
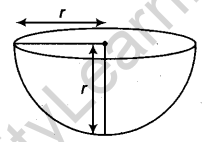
Volume of hemisphere = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) πr3
The curved surface area of hemisphere = 2πr2
Total surface area of hemisphere = 2πr2 + πr2 = 3πr2
NCERT Notes for Class 9 Maths
- Chapter 1 Number Systems Class 9 Notes
- Chapter 2 Polynomials Class 9 Notes
- Chapter 3 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry Class 9 Notes
- Chapter 4 Lines and Angles Class 9 Notes
- Chapter 5 Triangles Class 9 Notes
- Chapter 6 Coordinate Geometry Class 9 Notes
- Chapter 7 Heron’s Formula Class 9 Notes
- Chapter 8 Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 9 Notes
- Chapter 9 Quadrilaterals Class 9 Notes
- Chapter 10 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles Class 9 Notes
- Chapter 11 Circles Class 9 Notes
- Chapter 12 Constructions Class 9 Notes
- Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Class 9 Notes
- Chapter 14 Statistics Class 9 Notes
- Chapter 15 Probability Class 9 Notes
We hope the given CBSE Class 9 Maths Notes Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Pdf free download will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Class 9 Maths Notes Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.




