1. Circle: The collection of all points in a plane which are at a fixed distance from a fixed point in the plane is called a circle. The following examples of the circle are
2. Basic Definition
- Chord: Suppose, we take any two points on a circle, then the line segment PQ is called the chord of the circle.
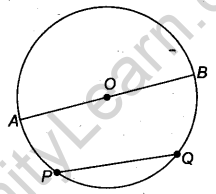
- Diameter: The chord which passes through the centre of the circle is called a diameter AB of the circle.
- Arc: A piece of a circle between two points is called an arc. If P and Q are any two points on them, the PQ is an arc of the circle and it is denoted by AB.
- Circumference: The length of the complete circle is called its circumference.
- Semi-circle: A diameter of a circle divides it into two equal parts which an arc. Each of these two arcs is called a semi-circle.
- Congruent Circles (Arc): Two circles are said to be congruent if and only if either of them can be superposed on the other so as to cover exactly.
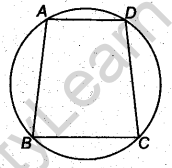
- Cyclic Quadrilateral: A quadrilateral ABCD is called cyclic if all the four vertices of it lie on a circle.
- Common Chord: The intersection point of two circles is the common chord of the circle.
3. Important Theorems
- The perpendicular from the centre of a circle to a chord bisects the chord and it is vice-versa.
- Equal chords of a circle (or of congruent circles) are equidistant from the centre.
- It two chords of a circle are equal, then their corresponding, arcs are congruent and conversely, if two arcs are congruent, then their corresponding chords are equal.
- Congruent arcs of a circle subtend equal angles at the centre.
- The angle subtended by an arc at the centre is double the angle subtended by it any point on the remaining part of the circle.
- Angle in the same segment of a circle is equal.
- The sum of either pair of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180° and vice-versa.
- The angle in a semi-circle is a right angle.
- If two chords of a circle are equal, then their corresponding arcs (minor, major or semi-circle) are congruent and vice-versa.


