Table of Contents
Oogenesis: Oogenesis is the process of forming female gametes, also known as ova. Once produced, the female gamete is referred to as an ovum. In general terms, these female gametes are commonly called “eggs,” but the term “egg” can encompass various developmental stages, leading to different interpretations across organisms.
For example, in birds, the entire development of an egg into a chick occurs within the egg after it is laid. On the other hand, in placental mammals, once the egg is fully developed and fertilized, it begins to divide, and it is no longer considered an egg. It’s important to remember that every ovum must be haploid, meaning it contains a single copy of each chromosome.
Oogenesis is the process of ovum differentiation. Spermatogenesis and oogenesis are two distinct forms of gametogenesis. In males, the process is known as spermatogenesis; in females, it is referred to as oogenesis, resulting in the formation of ova.
Oogenesis differs significantly from spermatogenesis in various ways. Let’s look at oogenesis, exploring its stages, ovulation, and fertilization.
What is Oogenesis?
Oogenesis is forming female gametes and begins inside the fetus before birth. The steps in oogenesis leading up to the production of primary oocytes occur before birth, and these primary oocytes do not divide further. Instead, they either become secondary oocytes or degenerate.
Oogenesis takes place in the ovaries’ outermost layers. It all begins with an oogonium, a germ cell that undergoes mitosis to multiply. The oogenesis process is divided into three stages:
- Pre-natal stage
- Antral stage
- Pre-ovulatory stage
During the pre-natal stage, the initial steps of oogenesis take place. The antral stage represents a more advanced phase of the process, and finally, the pre-ovulatory stage culminates in the development of mature ova, ready for potential fertilization.
Process of Oogenesis
The process of female gamete formation is called oogenesis. There are three distinctive Oogenesis stages:
- Pre-natal Stage:
During this stage, the primary oocyte grows while being arrested in meiosis-I. Simultaneously, the follicular cells multiply, forming a stratified cuboidal epithelium called granulosa cells. These granulosa cells secrete glycoproteins, resulting in the formation of zona pellucida around the primary oocyte. - Antral Stage:
In this stage, fluid-filled spaces between the granulosa cells merge to create a central fluid-filled cavity known as the antrum. The structures at this phase are referred to as secondary follicles. Each month during the cycle, these secondary follicles develop under the influence of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). - Pre-Ovulatory Stage:
The pre-ovulatory stage is triggered by an LH surge, leading to the completion of meiosis-I. Within the follicle, two haploid cells of unequal sizes are formed. One of these cells, which receives less cytoplasm, develops into a polar body and does not contribute to ovum formation. The other daughter cell, called the secondary oocyte, undergoes meiosis-II. Meiosis-II secondary oocyte arrests in the metaphase stage.
This sequence of stages marks the complex process of oogenesis, culminating in the development of mature ova, which are essential for reproduction.
Oogenesis Diagram
In the oogenesis flow chart, the process of oogenesis, which involves the formation of female gametes (oocytes) in the ovaries, is visually represented. Additionally, the flow chart highlights the spermatogenesis and oogenesis difference, the processes responsible for producing eggs and sperm, respectively.
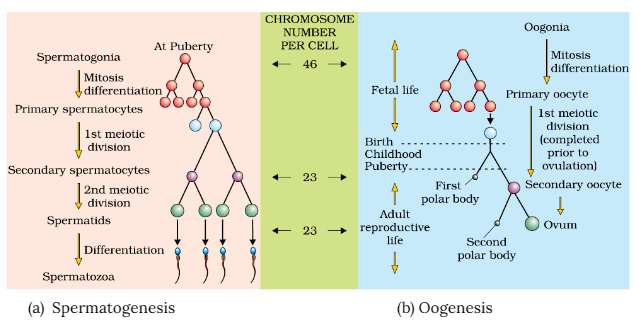
Ovulation
Ovulation is a critical phase in the oocyte development within the ovaries. Each oocyte is surrounded by follicle cells, collectively forming a follicle.
As the menstrual cycle commences, the primary oocytes begin to enlarge, and the number of follicle cells increases, leading to the enlargement of the follicle.
Some nurturing oocytes typically degenerate, leaving only one follicle to mature. In certain cases, this can result in the birth of fraternal twins, who are genetically distinct.
Once a follicle reaches maturity, the primary oocyte completes its primary meiotic division, transforming into a secondary oocyte. Subsequently, the follicle ruptures, releasing the secondary oocyte into the fallopian tube even before the second meiotic division has occurred. This release of the secondary oocyte from the ovaries is known as ovulation.
Ovulation is a crucial event in the female reproductive system, marking the release of the mature oocyte and its potential journey toward fertilization.
Fertilization
Fertilization results in the completion of Meiosis-II, leading to the release of a third polar body. In cases where fertilization does not occur, the oocyte degenerates 24 hours after ovulation while still arrested in the Meiosis-II cell division stage.
The key distinction between oogenesis and spermatogenesis lies in the timing of their initiation, as oogenesis commences during fetal development before birth.
Frequently Asked Questions on Oogenesis
What is oogenesis? Give a brief account of oogenesis.
Oogenesis is the process of egg or ovum formation in females. It involves developing and maturing oocytes (immature egg cells) within the ovaries. During oogenesis, oocytes undergo meiotic divisions, producing mature ova that are essential for sexual reproduction in female organisms.
Define oogenesis.
Oogenesis is the process of egg formation in females, where oocytes within the ovaries undergo meiotic divisions to develop and mature into ova, which is crucial for reproductive purposes.
What is the difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis PDF?
Spermatogenesis involves the production of sperm from male germ cells and spermatogonia in males, whereas oogenesis is the process of egg production from female germ cells, specifically oogonia, in females.
What are the stages of oogenesis Class 12?
The stages of oogenesis, which occur in the ovaries or female gonads, can be categorized into three phases: multiplication, growth, and maturation. These stages contribute to the development and formation of ova through the process of oogenesis.
What is Oogenesis in Hindi?
अंडाशय में अंडा कोशिका निर्माण की प्रक्रिया को अंडजनन कहा जाता है। भ्रूण अवस्था के दौरान अंडजनन आरंभ होता है। जब भ्रूण लगभग 7 महीने का हो जाता है, तो ओगोनिया का निर्माण होता है, जो कि ओओसाइट्स की पूर्ववर्ती कोशिकाएं होती हैं।








