Table of Contents
Introduction to Zinc Carbonate Formula
Zinc carbonate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula ZnCO3. It is a white crystalline solid that occurs naturally as the mineral smithsonite, but it can also be synthesized artificially. Zinc carbonate is commonly used in various industrial applications and has some interesting properties.
Structural Formula of Zinc Carbonate
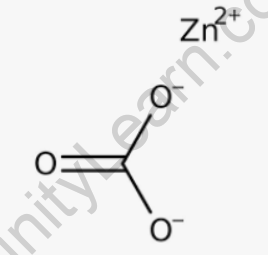
The structural formula of zinc carbonate can be represented as ZnCO3. It consists of a zinc ion (Zn2+) bonded to a carbonate ion (CO32-). The carbonate ion is composed of one carbon atom bonded to three oxygen atoms, forming a trigonal planar arrangement. The zinc ion is located in the center, surrounded by the carbonate ion. The structural formula indicates the arrangement and bonding of the atoms in the compound, providing a visual representation of its molecular structure.
Uses of Zinc Carbonate
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Zinc carbonate is used in the production of medicinal products such as ointments, lotions, and creams. It is often included as an active ingredient in various skin medications and treatments.
- Cosmetics: Zinc carbonate is found in cosmetics, particularly in powders, foundations, and mineral makeup. It functions as a pigment and provides coverage and a matte finish to the skin.
- Rubber Manufacturing: Zinc carbonate is used as an activator in the vulcanization process of rubber. It helps improve the elasticity, strength, and durability of rubber products.
- Paints and Coatings: Zinc carbonate is utilized as a filler and pigment in the production of paints, coatings, and varnishes. It contributes to the opacity, color, and texture of the final product.
- Ceramics and Glass: Zinc carbonate is used as a flux in ceramic and glass manufacturing processes. It helps lower the melting point of materials, aids in glaze formation, and enhances the overall quality of the finished products.
- Fireproofing Materials: Zinc carbonate is sometimes added to fireproofing compounds and coatings due to its ability to release carbon dioxide when exposed to high temperatures. This property helps create a protective barrier against fire and heat.
- Agriculture: Zinc carbonate can be used as a zinc supplement in agriculture, primarily to address zinc deficiencies in crops and promote healthy plant growth.
Physical Properties of Zinc Carbonate Formula
- Appearance: Zinc carbonate is a white, odorless solid.
- Density: The density of zinc carbonate varies depending on the form and structure, but it is typically around 4.4 g/cm³.
- Melting Point: Zinc carbonate has a melting point of approximately 315°C (599°F).
- Solubility: Zinc carbonate is sparingly soluble in water, meaning it dissolves only to a limited extent. The solubility increases with decreasing pH or in the presence of acidic solutions.
- Crystal Structure: Zinc carbonate crystallizes in various crystal structures, including both the aragonite and calcite forms.
- Stability: Zinc carbonate is stable under normal conditions. However, it can decompose when exposed to high temperatures, releasing carbon dioxide gas (CO2).
- Electrical Conductivity: Zinc carbonate is an insulator, meaning it does not conduct electricity.
Chemical Properties of Zinc Carbonate Formula
- Dissociation: Sodium phosphate readily dissociates in water to release sodium ions (Na+) and phosphate ions (PO43-). The dissociation of sodium phosphate is influenced by pH, temperature, and concentration.
- Acid-Base Reactions: Sodium phosphate can act as both an acid and a base depending on the reaction conditions. It can react with strong bases to form salts and water, and it can also react with strong acids to form salts and water. For example, it can react with hydrochloric acid (HCl) to form sodium chloride (NaCl) and phosphoric acid (H3PO4).
- Precipitation Reactions: Sodium phosphate can form insoluble salts with certain metal ions, leading to precipitation reactions. For example, when sodium phosphate is added to a solution containing calcium ions (Ca2+), it forms insoluble calcium phosphate (Ca3(PO4)2) precipitate.
- Buffering Capacity: Sodium phosphate has buffering properties, meaning it can resist changes in pH when an acid or a base is added. It can maintain a relatively stable pH in solutions and is commonly used in biological and chemical applications that require pH control.
- Complex Formation: Sodium phosphate can form complexes with certain metal ions, particularly in the presence of ligands. These complexes can exhibit different chemical and physical properties compared to the individual components.
- Reaction with Other Compounds: Sodium phosphate can react with other compounds to form various products depending on the reaction conditions. For example, it can react with certain acids to form salts and water, or it can react with metal oxides to form different types of phosphates.
Conclusion
In conclusion, zinc carbonate (ZnCO3) is a compound that finds various applications across different industries. It is primarily used as a raw material in the production of zinc oxide, which is widely used in the rubber, ceramics, and paint industries. Zinc carbonate is also utilized as an ingredient in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and personal care products. Its properties, such as its ability to act as an absorbent and its pH-regulating characteristics, make it suitable for use in antacids and skincare formulations. Additionally, zinc carbonate has applications in agriculture, where it is used as a zinc fertilizer to address zinc deficiency in soils. Overall, zinc carbonate serves multiple purposes across different sectors due to its diverse range of properties and applications.
Solved Examples on Zinc Carbonate Formula
Example 1: Calculate the mass of zinc carbonate required to obtain 25 grams of zinc oxide (ZnO) through the decomposition reaction of zinc carbonate.
Solution:
Write the balanced chemical equation for the decomposition of zinc carbonate:
ZnCO3 (s) -> ZnO(s) + CO2(g)
Determine the molar mass of zinc carbonate (ZnCO3):
Molar mass of Zn = 65.38 g/mol
Molar mass of C = 12.01 g/mol
Molar mass of O = 16.00 g/mol
Molar mass of ZnCO3 = (65.38 + 12.01 + 3 * 16.00) g/mol = 125.39 g/mol
Use the molar mass to convert grams of ZnO to moles of ZnCO3:
Moles of ZnCO3 = 25 g ZnO * (1 mol ZnCO3 / 81.38 g ZnO)
= 0.308 moles ZnCO3
Convert moles of ZnCO3 to grams:
Mass of ZnCO3 = 0.308 moles ZnCO3 * (125.39 g ZnCO3 / 1 mol ZnCO3)
= 38.5 grams ZnCO3
Therefore, 38.5 grams of zinc carbonate are required to obtain 25 grams of zinc oxide through the given reaction.
Example 2: A 250 mL solution contains zinc carbonate (ZnCO3) at a concentration of 0.5 M. Calculate the number of moles and grams of zinc carbonate present in the solution.
Solution:
Determine the volume of the solution in liters:
Volume of solution = 250 mL = 250/1000 L = 0.25 L
Calculate the number of moles of zinc carbonate:
Molarity (M) = moles of solute / volume of solution in liters
moles of solute = Molarity * volume of solution in liters
= 0.5 M * 0.25 L = 0.125 moles
Therefore, there are 0.125 moles of zinc carbonate present in the solution.
Convert moles of zinc carbonate to grams:
Molar mass of ZnCO3 = (65.38 g/mol + 12.01 g/mol + 3 * 16.00 g/mol)
= 125.39 g/mol
Mass of zinc carbonate = moles of zinc carbonate * molar mass of ZnCO3
= 0.125 moles * 125.39 g/mol = 15.674 g
Therefore, there are 0.125 moles (15.674 grams) of zinc carbonate present in the 250 mL solution.
Frequently Asked Questions on Zinc Carbonate Formula
What is the Colour of zinc?
Zinc is often characterized by its bluish-white hue. When freshly exposed, it shines brightly but can develop a slight tarnish over time. Its distinct color helps distinguish it from other metals like aluminum and tin.
What is zinc rust called?
The corrosion of zinc is commonly referred to as white rust. Unlike the familiar red rust of iron, white rust is a soft, powdery, white substance that forms on zinc surfaces when exposed to moisture and air.
What is zinc also known as?
Zinc is primarily known by its chemical name. On the periodic table, it is denoted by the symbol Zn. While it doesn't have popular alternate names, its various compounds and alloys may have different names, such as brass for the alloy of copper and zinc.
What is zinc powder called?
Zinc in its powdered form is directly called zinc powder. This form of zinc is often used in various applications like paint, cosmetics, and chemical reactions due to its small particle size, which enhances reactivity and coverage.
What is another name for zinc carbonate?
Another common name for zinc carbonate is smithsonite. Historically, it was also referred to as calamine before the distinction between zinc carbonate and zinc silicate became clear.
Zinc Carbonate Formula
The chemical formula for zinc carbonate is ZnCO₃. Representing the compound, this formula indicates that one atom of zinc is combined with one molecule of carbonate. This compound occurs naturally and is used in various applications.
Is zinc carbonate soluble or insoluble?
Zinc carbonate is insoluble in water, which means it does not dissolve when mixed with water. Instead, it remains as a solid or settles to the bottom if suspended in a liquid.
What is the formula reaction of zinc carbonate?
When zinc carbonate is subjected to heat, it decomposes to form zinc oxide and carbon dioxide. The chemical reaction can be represented as: ZnCO₃ → ZnO + CO₂. This decomposition reaction is a type of thermal decomposition.
What is zinc carbonate also known as?
Besides its chemical name, zinc carbonate is also commonly known as smithsonite. In the past, the term calamine was used interchangeably for zinc carbonate and zinc silicate, but today it is more specifically associated with smithsonite.








