Table of Contents
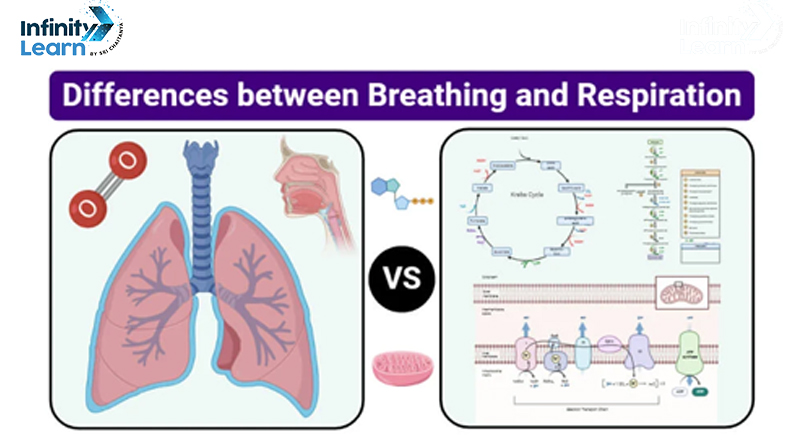
Breathing and respiration are distinct yet closely connected bodily functions that help our organs work correctly. Breathing involves the physical exchange of gases, while respiration is a chemical process occurring within cells, generating energy.
What is Breathing?
Breathing is an essential life process, but what exactly is it? Simply put, it is the physical act of inhaling and exhaling air through the lungs. When we breathe, oxygen from the air is drawn into the lungs, and carbon dioxide, a waste product, is expelled.
This might sound straightforward, but there’s more to it than meets the eye. While discussing breathing, it’s interesting to note that it’s often confused with respiration, another vital process.
However, unlike respiration, breathing doesn’t involve the chemical breakdown of oxygen. This distinction is similar to understanding what is the difference between renewable and nonrenewable resources – both are sources of energy, yet fundamentally different in nature and usage.
How Do We Breathe?
Breathing is how we get air into and out of our bodies. It starts when you breathe in air through your nose or mouth. This air goes down your throat and into a big tube called the windpipe. From there, it goes into smaller tubes in your lungs called bronchial tubes. Let’s look at the parts that help us breathe:
- Nose and the inside part of the nose (nasal cavity)
- Sinuses
- Mouth
- Throat and voice box
- Windpipe
- Diaphragm (a muscle under your lungs)
- Lungs
- Small tubes in the lungs (bronchial tubes and bronchioles)
- Tiny air pockets (alveoli)
- Small blood vessels (capillaries)
The small tubes in your lungs split into even tinier tubes called bronchioles. At the end of these tubes are small air pockets called alveoli. These air pockets are wrapped in tiny blood vessels. When you breathe in, oxygen from the air goes into these blood vessels. Then, the oxygen-rich blood goes to your heart, and your heart sends it to all parts of your body. Your body uses the oxygen, and then you breathe out carbon dioxide, a waste gas.
When you breathe in (inhale), your chest gets bigger because a muscle called the diaphragm moves down. This makes more space in your chest and pulls air into your lungs. Your lungs are stretchy, and when they fill with air, they push back in.
When you breathe out (exhale), the diaphragm goes back up, your chest gets smaller, and the air goes out of your lungs. Exhaling doesn’t need your muscles to work hard; it happens mostly by itself.
What is Respiration?
Respiration is a chemical process that happens within cells where oxygen is used to produce energy, and carbon dioxide is released as a byproduct. This process is crucial for all living organisms as it provides the energy required for all bodily functions.
Understanding respiration is key to comprehending how our body utilizes the air we breathe. Just like breathing, respiration is often mistakenly thought to be the same as breathing. However, the difference between breathing and respiration lies in their respective roles – one is a mechanical process, while the other is chemical.
Respiration is a vital biological process that allows organisms to extract energy from nutrients. It’s mainly of two types: aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
- Aerobic Respiration: This is the more common form of respiration and occurs when oxygen is abundant. It happens in the mitochondria, often referred to as the “powerhouse of the cell.” The process involves the breakdown of glucose (a simple sugar) in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy. The energy released is stored in molecules called ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which cells use to perform various functions. Aerobic respiration is more efficient and produces more energy compared to anaerobic respiration.
- Anaerobic Respiration: This type of respiration occurs when there is not enough oxygen available, such as during intense physical activity or in certain microorganisms. Instead of oxygen, other molecules are used as electron acceptors in the process. In humans, anaerobic respiration results in the production of lactic acid in muscles. This can lead to muscle fatigue and cramps. Anaerobic respiration is less efficient than aerobic respiration in terms of energy production.
Both these processes are crucial for the survival of organisms. Aerobic respiration is the primary method for energy production under normal conditions. While anaerobic respiration serves as a backup during oxygen-deficient situations.
List the Differences Between Breathing and Respiration
When discussing the difference between breathing and respiration, it’s helpful to lay out the distinctions. Here’s a table to simplify the comparison:
| Aspect | Breathing | Respiration |
| Definition | Physical process of inhaling and exhaling air. | Chemical process of energy production in cells. |
| Involvement | Involves lungs and respiratory organs. | Occurs in cells, involving enzymes. |
| Products | Does not produce energy directly. | Produces energy, carbon dioxide, and water. |
| Oxygen Use | Involves intake of oxygen. | Oxygen is used to break down glucose. |
| Carbon Dioxide | Expels carbon dioxide. | Produces carbon dioxide as a byproduct. |
Understanding the breathing and respiration difference and breathing and respiration as separate yet interconnected processes clarifies many misconceptions.
What is the difference between respiration, ventilation and breathing?
Breathing is the process of moving air in and out of the lungs. In medicine, this process is called ventilation.
Ventilation is the physical process of moving air into and out of the lungs. It’s caused by pressure gradients created by the contraction of the diaphragm and thoracic muscles.
Respiration is the process of exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs and cells. It’s controlled by hormonal and neural signaling that detects oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations.
Mnemonics for Remembering the Difference between Breathing and Respiration
Here are two mnemonics to help you remember the key differences between breathing and respiration:
Mnemonic 1: B.R.E.A.T.H.E.
- B: Breathing is mechanical, while respiration is chemical.
- R: Breathing involves movement of air, while respiration involves chemical reactions.
- E: Breathing happens in the lungs, while respiration happens in the mitochondria of cells.
- A: Breathing supplies oxygen to the bloodstream, while respiration uses oxygen to produce energy.
- T: Breathing is the physical process, while respiration is the cellular process.
- H: Breathing is conscious, while respiration is unconscious.
Mnemonic 2: O.R.G.A.N.
- O: Oxygen enters the body through breathing.
- R: Respiration uses oxygen to convert glucose into energy.
- G: Glucose is the fuel used in respiration.
- A: ATP is the energy molecule produced by respiration.
- N: Respiration takes place in the mitochondria of cells.
| Check all the Biology Difference Between Articles | |
| Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell | Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell |
| Difference Between DNA and RNA | Difference Between Cold Blooded and Warm Blooded |
| Difference Between Flora and Fauna | Difference between mitosis and meiosis |
| Difference Between Weather and Climate | Difference Between Arteries and Veins |
| Difference Between Xylem and Phloem | Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration |
| Difference Between Diffusion and Osmosis | Difference Between Turtle and Tortoise |
| Difference Between Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria | Difference Between Renewable and Non Renewable Resources |
FAQs on the Difference Between Breathing and Respiration
What happens if I hold my breath?
Holding your breath temporarily stops the exchange of gases in the lungs. This can lead to a decrease in oxygen levels and an increase in carbon dioxide levels in the blood, causing dizziness, lightheadedness, and even fainting
Can I breathe without respiring?
No, respiration depends on breathing to provide the oxygen needed for the process. Without breathing, there would be no oxygen in the bloodstream to reach the cells, and respiration would cease.
What are the signs of poor breathing?
Shortness of breath, wheezing, chest pain, and rapid breathing are all signs of improper breathing and may indicate an underlying medical condition.
What are the environmental factors that can affect breathing?
Air pollution, high altitudes, and extreme temperatures can all negatively impact breathing and respiratory health.
What is the main function of breathing?
The primary function of breathing is to exchange gases, taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide
How is respiration different from breathing?
Respiration involves complex chemical processes within cells to produce energy, whereas breathing is the physical act of inhaling and exhaling
Can we control respiration voluntarily?
No, respiration is mostly involuntary and regulated by the autonomic nervous system.
Is respiration only related to humans?
No, respiration is a vital process occurring in all living organisms, not just humans.
Are there any environmental connections to the concept of breathing and respiration?
Yes, just as breathing sustains life, understanding resource types is vital for environmental sustainability.
Can you provide a simple analogy to explain the difference?
If breathing is like inhaling and exhaling air, then respiration is akin to the body's internal 'energy factory.'








