Table of Contents
Indian Railways, often referred to as the lifeline of the nation, is an extensive network connecting the length and breadth of India. Spanning over 67,000 kilometers, it is one of the largest rail systems in the world, serving millions of passengers every day. It serves millions daily, connecting cities to remote villages, ensuring accessible travel for all. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the Indian Railway Map, exploring its various zones and routes to help you navigate through this intricate web of tracks and stations.
Railways Network in India
Indian Railways is not just a transportation system; it’s a lifeline connecting people, cultures, and economies across the vast Indian subcontinent. As a symbol of unity and connectivity, Indian Railways remains a lifeline of India’s transportation system. The Government of India runs Indian Railways, one of the biggest railway networks in the world. It began when the first train chugged across Indian territory in 1853. Today, this vast network spans 29 states, 7 union territories, and even extends its services to neighboring countries like Nepal, Bangladesh, and Pakistan. Indian Railways employs millions of people worldwide and is the largest employer in the world, with about 18 million passengers depending on it every day.
Indian Railway Map
The Indian Railway Network Map, also known as the Indian Railway Route Map or Indian Railway Line Map, showcases the vast and intricate web of tracks that crisscross the nation. This extensive network connects diverse regions and communities across the country. Explore the central, eastern, northern, northeastern, southern, southeastern, and western railways of India by viewing the rail map. Download the Indian Railway route map PDF to get a comprehensive overview of the extensive railway network spanning across the country.
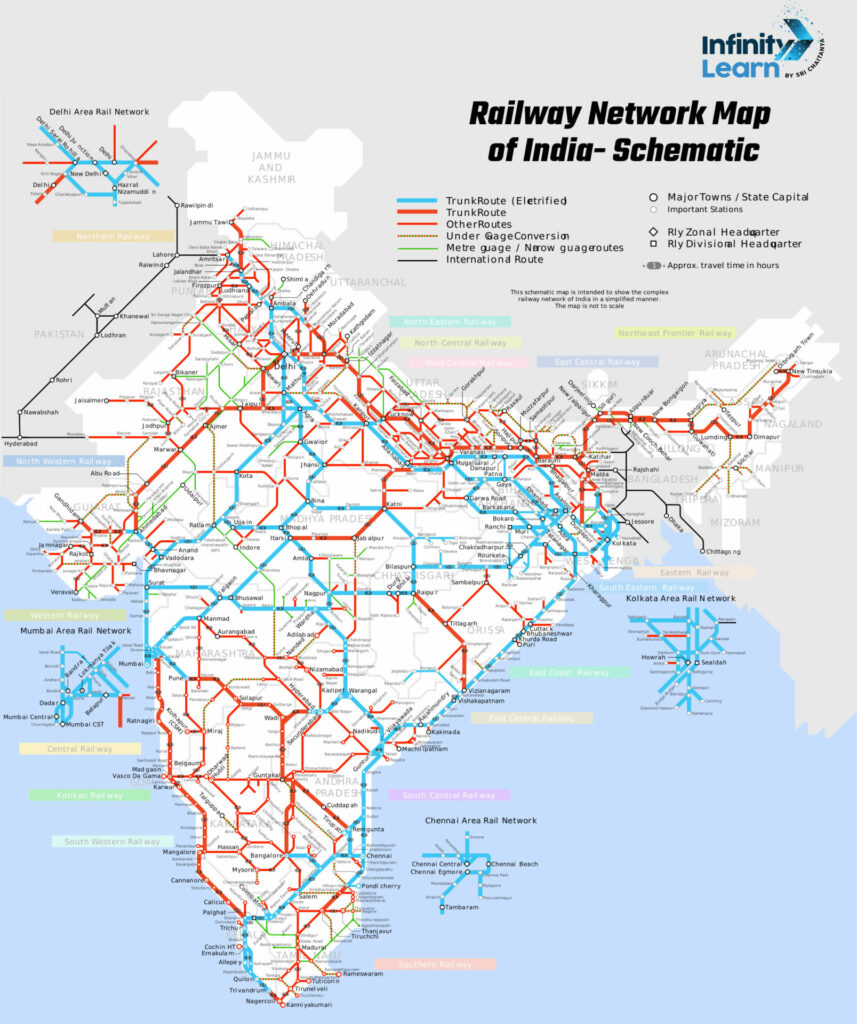
Understanding the Different Zones of Indian Railway Map
The Indian Railways is divided into zones, each responsible for managing the railway operations within its designated territory. Currently, there are a total of 18 railway zones in India, each with its distinct identity and network.
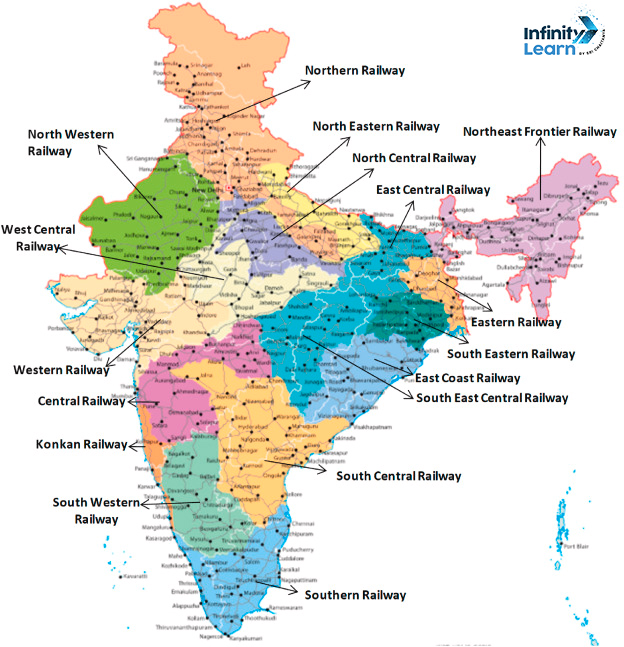
- Northern Railway Zone: The Northern Railway Zone covers Delhi, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, and Uttarakhand.
- Southern Railway Zone: The Southern Railway Zone covers Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, and parts of Karnataka.
- Eastern Railway Zone: Serving the eastern states of West Bengal, Bihar, and Jharkhand.
- Western Railway Zone: The Western Railway Zone, covering Maharashtra, Gujarat, Rajasthan, and parts of Madhya Pradesh.
- Central Railway Zone: Covering Maharashtra and parts of Madhya Pradesh and Karnataka.
- North Eastern Railway Zone: The North Eastern Railway Zone, reaching Assam, Manipur, and Nagaland.
- North Western Railway Zone: Operating in Rajasthan, Gujarat, and parts of Punjab.
- South Eastern Railway Zone: Serving the states of West Bengal, Jharkhand, and Odisha.
- South Western Railway Zone: The South Western Railway Zone connects Karnataka with parts of Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu.
- East Central Railway Zone: The East Central Railway Zone serves Bihar, Jharkhand, and parts of Uttar Pradesh.






