Table of Contents
What is Acetic Acid?
Acetic Acid is an organic compound with the formula CH₃COOH, also called ethanoic acid, the most important of the carboxylic acids. It is a carboxylic acid consisting of a methyl group attached to a carboxyl functional group. The systematic IUPAC name of acetic acid is ethanoic acid, and its chemical formula can also be written as C₂H₄O₂. Vinegar is a solution of acetic acid in water and contains between 5% to 20% ethanoic acid by volume. The pungent smell and the sour taste are characteristic of the acetic acid present in it.
An undiluted solution of acetic acid is commonly referred to as glacial acetic acid. It forms crystals which appear like ice at temperatures below 16.6°C. It has a wide range of applications as a polar, protic solvent. In the field of analytical chemistry, glacial acetic acid is widely used in order to estimate substances that are weakly alkaline.
The chemical name of CH₃COOH is Acetic Acid. It is commonly known as the main component of vinegar, contributing to its sour taste and strong smell.
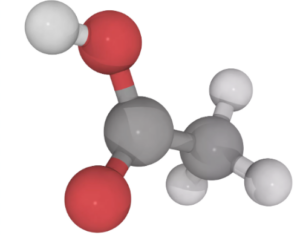
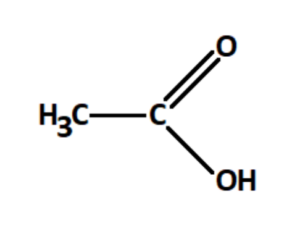
Properties of Acetic Acid Formula
- Acetic Acid has a pungent and vinegar-like odour
- Acetic Acid has the appearance of a Colourless liquid.
- It is miscible in water.
- Acetic Acid has a melting point of 16 to 17 degrees Celsius
- Acetic Acid has a boiling point of 118 to 119 degrees Celsius
- Acetic Acid molar mass is 60.052g/mol-1
Formula and Structure of Acetic Acid
The chemical formula for acetic acid is C2H4O2.
Structurally, ethanoic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (the simplest being formic acid, HCOOH), and is essentially a methyl group with a carboxyl functional group attached to it.
Physical Properties of Acetic Acid
Even though ethanoic acid is considered to be a weak acid, in its concentrated form, it possesses strong corrosive powers and can even attack the human skin if exposed to it. Some general properties of acetic acid are listed below.
- Ethanoic acid appears to be a colourless liquid and has a pungent smell.
- At STP, the melting and boiling points of ethanoic acid are 289K and 391K respectively.
- The molar mass of acetic acid is 60.052 g/mol and its density in the liquid form is 1.049 g.cm-3.
- The carboxyl functional group in ethanoic acid can cause ionization of the compound, given by the reaction: CH3COOH ⇌ CH3COO– + H+
- The release of the proton, described by the equilibrium reaction above, is the root cause of the acidic quality of acetic acid.
- The acid dissociation constant (pKa) of ethanoic acid in a solution of water is 4.76.
- The conjugate base of acetic acid is acetate, given by CH3COO–.
- The pH of an ethanoic acid solution of 1.0M concentration is 2.4, which implies that it does not dissociate completely.
- In its liquid form, acetic acid is a polar, protic solvent, with a dielectric constant of 6.2.
Chemical Properties of Acetic Acid
The chemical reactions undergone by acetic acid are similar to those of other carboxylic acids. When heated to temperatures above 440oC, this compound undergoes decomposition to yield either methane and carbon dioxide or water and ethenone, as described by the following chemical equations.
CH3COOH + Heat → CO2 + CH4
CH3COOH + Heat → H2C=C=O + H2O
Some metals such as magnesium, zinc, and iron undergo corrosion when exposed to acetic acid. These reactions result in the formation of acetate salts.
2CH3COOH + Mg → Mg(CH3COO)2 (magnesium acetate) + H2
The reaction between ethanoic acid and magnesium results in the formation of magnesium acetate and hydrogen gas, as described by the chemical equation provided above.
Production of Acetic Acid
Acetic acid has been prepared on an industrial scale by air oxidation of acetaldehyde, by oxidation of ethanol (ethyl alcohol), and by oxidation of butane and butene. Today acetic acid is manufactured by a process developed by the chemical company Monsanto in the 1960s; it involves a rhodium-iodine catalyzed carbonylation of methanol (methyl alcohol).
Pure acetic acid, often called glacial acetic acid, is a corrosive, colourless liquid (boiling point 117.9 °C [244.2 °F]; melting point 16.6 °C [61.9 °F]) that is completely miscible with water.
Solved Examples on Acetic Acid Formula
Example 1: Calculate the molar mass of acetic acid (CH3COOH).
Solution: To calculate the molar mass of acetic acid, we need to sum up the atomic masses of all the atoms in its formula.
Molar mass of carbon (C) = 12.01 g/mol
Molar mass of hydrogen (H) = 1.01 g/mol
Molar mass of oxygen (O) = 16.00 g/mol
Now, let’s calculate the molar mass of acetic acid:
(2 × molar mass of carbon) + (4 × molar mass of hydrogen) + (2 × molar mass of oxygen) + molar mass of hydrogen + molar mass of oxygen
= (2 × 12.01) + (4 × 1.01) + (2 × 16.00) + 1.01 + 16.00
= 24.02 + 4.04 + 32.00 + 1.01 + 16.00
= 77.07 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of acetic acid (CH3COOH) is 77.07 g/mol.
Example 2: How many moles of acetic acid are present in 25 grams of acetic acid?
Solution: To calculate the number of moles of acetic acid, we need to use the molar mass and the given mass.
Molar mass of acetic acid (CH3COOH) = 77.07 g/mol
Mass of acetic acid = 25 grams
Number of moles = Mass / Molar mass
Number of moles = 25 g / 77.07 g/mol
Number of moles ≈ 0.3246 mol
Therefore, there are approximately 0.3246 moles of acetic acid in 25 grams of acetic acid.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Acetic acid Formula (Ethanoic Acid)
What is the chemical formula of acetic acid?
The chemical formula of acetic acid is CH3COOH.
What are the elements present in acetic acid?
Acetic acid is composed of carbon C, hydrogen H, and oxygen O elements.
How many carbon atoms are in the formula of acetic acid?
The acetic acid formula CH3COOH contains two carbon atoms.
How many hydrogen atoms are in the formula of acetic acid?
The acetic acid formula CH3COOH contains four hydrogen atoms.
How many oxygen atoms are in the formula of acetic acid?
The acetic acid formula CH3COOH contains two oxygen atoms.
What is the structural formula of acetic acid?
The structural formula of acetic acid is CH3COOH, where the carbon atoms are arranged in a chain, with three hydrogen atoms attached to one carbon atom and one oxygen atom double bonded to another carbon atom, along with a singlebonded oxygen and hydrogen atom.
What is the molar mass of acetic acid?
The molar mass of acetic acid is approximately 60.05 g/mol.
What is the common name of acetic acid?
Acetic acid is commonly known as vinegar.
Is acetic acid an organic or inorganic compound?
Acetic acid is an organic compound as it contains carbon atoms bonded to other elements.
What is the acidity of acetic acid?
Acetic acid is a weak acid, meaning it does not completely dissociate in water and has a relatively low acidity compared to strong acids.








