Table of Contents
Lactic acid is a naturally occurring organic compound that plays a significant role in various biological processes. Its chemical formula is C3H6O3, indicating that it contains three carbon (C) atoms, six hydrogen (H) atoms, and three oxygen (O) atoms. In this note, we will explore the formula and structure of lactic acid, as well as its chemical and physical properties.
Formula and Structure of Lactic Acid
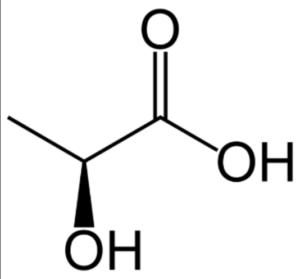
The formula C3H6O3 represents lactic acid, which belongs to the carboxylic acid family. It is a chiral molecule, meaning it has two possible enantiomeric forms: L-lactic acid and D-lactic acid. Lactic acid is often found in its L-form, denoted as (S)-lactic acid. The structure of lactic acid consists of three carbon atoms forming a chain, with a carboxylic acid group (COOH) attached to one end and a hydroxyl group (OH) attached to another carbon atom.
Lactic Acid Chemical Properties
- Acidity: Lactic acid is a weak acid and can partially dissociate in water, releasing hydrogen ions (H+). It has a sour taste and contributes to the tangy flavor of fermented products such as yogurt and sourdough bread.
- Optical Isomerism: Due to its chiral nature, lactic acid exists in two enantiomeric forms: L-lactic acid and D-lactic acid. These isomers have the same chemical formula but differ in their three-dimensional arrangement of atoms. They exhibit different optical activities and can rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions.
- Hydroxy Acid: Lactic acid is classified as a hydroxy acid because it contains both a carboxylic acid group and a hydroxyl group in its structure. This property allows lactic acid to participate in various reactions, including esterification, oxidation, and condensation reactions.
- Biodegradability: Lactic acid is biodegradable and can be readily metabolized by many microorganisms. This property makes it environmentally friendly and suitable for use in biodegradable plastics and other sustainable materials.
Lactic Acid Physical Properties
- Appearance: Lactic acid is a clear, colorless to pale yellow liquid or solid depending on its concentration and temperature. In its solid form, it exists as crystals.
- Melting and Boiling Points: The melting point of lactic acid is approximately 18 degrees Celsius (64 degrees Fahrenheit), while the boiling point is around 122-135 degrees Celsius (252-275 degrees Fahrenheit). These values may vary depending on the specific isomer and concentration.
- Solubility: Lactic acid is highly soluble in water. It readily dissolves and forms a clear solution. It is also soluble in alcohol and other polar solvents.
- Density: The density of lactic acid varies depending on its concentration. For a typical solution of lactic acid, the density is around 1.21-1.23 g/cm³.
- Odor: Lactic acid has a slightly sour or acidic odor, resembling the smell of fermented dairy products.
| Also Check | |
| Methane formula | Sodium carbonate formula |
| Aluminium chloride formula | Citric acid formula |
Solved Examples on Lactic acid formula
Example 1: Calculate the molar mass of lactic acid (C3H6O3).
Solution: To calculate the molar mass of lactic acid, we need to determine the atomic masses of each element present and multiply them by their respective subscripts in the formula.
Atomic mass of carbon (C) = 12.01 g/mol
Atomic mass of hydrogen (H) = 1.01 g/mol
Atomic mass of oxygen (O) = 16.00 g/mol
Molar mass of C3H6O3 = (3 * atomic mass of C) + (6 * atomic mass of H) + (3 * atomic mass of O)
= (3 * 12.01 g/mol) + (6 * 1.01 g/mol) + (3 * 16.00 g/mol)
= 36.03 g/mol + 6.06 g/mol + 48.00 g/mol
= 90.09 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of lactic acid (C3H6O3) is 90.09 g/mol.
Example 2: How many moles of lactic acid are present in 200 grams of C3H6O3?
Solution: To determine the number of moles of lactic acid, we need to divide the given mass by the molar mass of C3H6O3.
Molar mass of C3H6O3 = 90.09 g/mol (calculated in Example 1)
Number of moles = Mass (g) / Molar mass (g/mol)
= 200 g / 90.09 g/mol
≈ 2.22 mol (rounded to two decimal places)
Therefore, there are approximately 2.22 moles of lactic acid in 200 grams of C3H6O3.
Example 3: What is the mass percentage of carbon in lactic acid (C3H6O3)?
Solution: To determine the mass percentage of carbon, we need to calculate the mass of carbon in one mole of lactic acid and divide it by the molar mass of lactic acid, then multiply by 100.
The molar mass of carbon = 12.01 g/mol (atomic mass of C)
Mass of carbon in one mole of lactic acid = (3 * molar mass of carbon)
= 3 * 12.01 g
= 36.03 g
Mass percentage of carbon = (Mass of carbon / Molar mass of lactic acid) * 100
= (36.03 g / 90.09 g) * 100
≈ 39.96%
Therefore, the mass percentage of carbon in lactic acid (C3H6O3) is approximately 39.96%.
Frequently asked Questions (FAQs)
The chemical formula of lactic acid is C3H6O3. It indicates that each molecule of lactic acid contains three carbon C atoms, six hydrogen H atoms, and three oxygen O atoms.
Lactic acid is an organic compound. It belongs to the carboxylic acid family, which is a class of organic compounds containing a carboxyl group COOH .
Lactic acid has two isomers: Llactic acid and Dlactic acid. The L and D prefixes represent the orientation of the molecule's chiral center. L lactic acid is the more common form found in nature, while Dlactic acid is less common.
Lactic acid is naturally produced in the body during various metabolic processes, such as exercise. It is also present in certain foods and beverages, including fermented dairy products like yogurt, sauerkraut, and sourdough bread. In addition, lactic acid can be produced through microbial fermentation, which is utilized in the production of commercial lactic acid for various applications. What is the chemical formula of lactic acid?
Is lactic acid an organic or inorganic compound?
What is the common name of lactic acid's isomers?
What are the sources of lactic acid?






