Table of Contents
The Value of Cos 90 Degrees
The value of cos 90 degrees is 1. The cosine of 90 degrees is 1 because it is the angle between the hypotenuse and the adjacent side of a right triangle.

Cos 90 Value
Cosine of 90 degrees is 1.
The value of cosine of 90 degrees is 1. This means that the length of the adjacent side to the 90 degree angle is the same as the length of the hypotenuse.
Cos 90 degrees
To define the cosine function of an acute angle, consider a right-angled triangle provided with the angle of interest and the sides of a triangle. The three sides of the triangle are defined as follows:
- The opposite side is a side which is opposite to the angle of interest.
- The hypotenuse side is the opposite side of the right angle and it should be the longest side of a right triangle
- The adjacent side is the remaining side of a triangle where it forms a side of both the angle of interest and the right angle
The cosine function of an angle is defined as a ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse side and the formula is given by
Cos θ = Adjacent Side / Hypotenuse Side
Derivation to Find Cos 90 Degrees Value Using Unit Circle
Let us consider a unit circle with the center at the origin of the coordinate axes say ‘x’ and ‘y’ axis. Let P (a, b) be any point on the circle that forms an angle AOP = x radian. This means that the length of the arc AP equals to x. From this, we define the value that cos x = a and sin x = b.
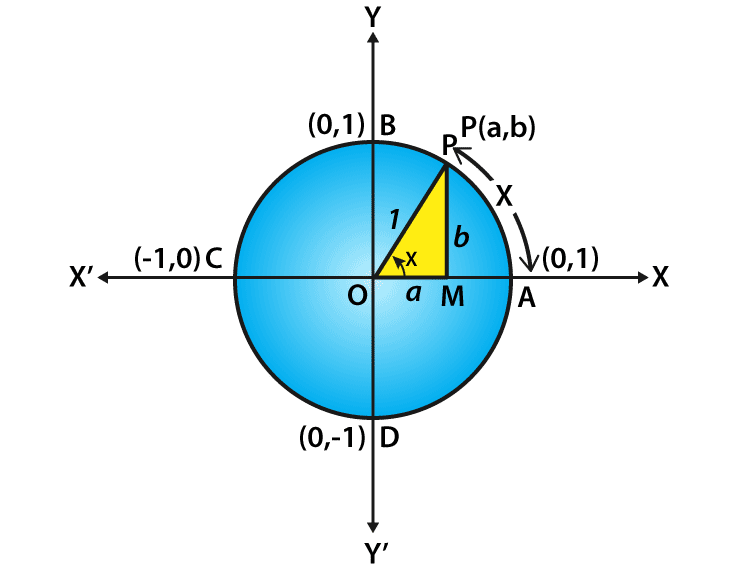
By using the unit circle, consider a right-angled triangle OMP.
By using the Pythagorean theorem, we get;
OM2+ MP2= OP2 (or) a2+ b2= 1
Thus, every point on the unit circle is defined as;
a2+ b2 = 1 (or) cos2 x + sin2 x = 1
Note that the one complete revolution subtends an angle of 2π radian at the center of the circle, and from the unit circle it is defined as follows:
∠AOB=π/2,
∠AOC = π and
∠AOD =3π/2.
Since all angles of a triangle are the integral multiples of π/2 and it is commonly known as quadrant angles and the coordinates of the points A, B, C and D are given as (1, 0), (0, 1), (–1, 0) and (0, –1) respectively. We can get the cos 90 degrees value using the quadrant angle. Therefore, the value of cos 90 degrees is:
Cos 90° = 0
It is observed that the values of sin and cos functions do not change if the values of x and y are the integral multiples of 2π. When we consider the one complete revolution from the point p, it again comes back to the same point. For a triangle, ABC having the sides a, b, and c opposite the angles A, B, and C respectively, the cosine law is defined.
For an angle C, the law of cosine is stated as
c2 = a2 + b2– 2ab cos(C)
Also, it is easy to remember the special values like 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90° since all the values are present in the first quadrant. All the sine and cosine functions in the first quadrant take the form √(n/2) or √(n/4). Once we find the values of sine functions it is easy to find the cosine functions.
Sin 0° =√(0/4)
Sin 30° = √(1/4)
Sin 45° = √(2/4)
Sin 60° = √(3/4)
Sin 90° = √(4/4)
Now Simplify all the sine values obtained and put in the tabular form:
| Angles in degrees | 0° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° |
| Sin | 0 | 1/2 | 1/√2 | √3/2 | 1 |
From the values of sine, we can easily find the cosine function values. Now, to find the cos values, fill the opposite order the sine function values. It means that
Cos 0° = Sin 90°
Cos 30° = Sin 60°
Cos 45° = sin 45°
Cos 60° = sin 30°
Cos 90° = sin 0°
So the value of cos 90 degrees is equal to 0 since cos 90° = sin 0°
| Angles in degrees | 0° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° |
| Sin | 0 | 1/2 | 1/√2 | √3/2 | 1 |
| Cos | 1 | √3/2 | 1/√2 | 1/2 | 0 |
In a similar way, we can find the values of other degrees of trigonometric functions depends on the quadrant value.
| Trigonometry Ratio Table | ||||||||
| Angles (In Degrees) | 0 | 30 | 45 | 60 | 90 | 180 | 270 | 360 |
| Angles (In Radians) | 0 | π/6 | π/4 | π/3 | π/2 | π | 3π/2 | 2π |
| sin | 0 | 1/2 | 1/√2 | √3/2 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0 |
| cos | 1 | √3/2 | 1/√2 | 1/2 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 1 |
| tan | 0 | 1/√3 | 1 | √3 | Not Defined | 0 | Not Defined | 0 |
| cot | Not Defined | √3 | 1 | 1/√3 | 0 | Not Defined | 0 | Not Defined |
| cosec | Not Defined | 2 | √2 | 2/√3 | 1 | Not Defined | −1 | Not Defined |
| sec | 1 | 2/√3 | √2 | 2 | Not Defined | −1 | Not Defined | 1 |
Sample Example
Question:
Find the value of cos 135°
Solution:
Cos 135°= cos(90°+45°)
Now, take the values a = 90° and b = 45°
By using the formula, Cos(a+b) = cos a cos b – sin a sin b
So, it becomes Cos 135° = cos 90° cos 45° – sin 90° sin 45°
cos 135°=0 x 1/√2 – 1 x 1/√2
cos 135°=-1/√2
Derivation of Cos 90 Degrees Using Unit Circle
The cosine of 90 degrees is equal to 1. Using the unit circle, this can be derived as follows:
The radius of the unit circle is 1. The point on the unit circle that corresponds to 90 degrees is (1,0). The cosine of 90 degrees is equal to the y-coordinate of this point, which is 0. Therefore, the cosine of 90 degrees is equal to 1.
Solved Example
The length of a side of a right triangle is 9 feet. What is the length of the other two sides?
The length of the other two sides is 8 feet and 5 feet.








