Table of Contents
Climate Map of India: India’s climate is diverse due to its vast size and geographical variations. The country experiences a range of climates, from tropical in the south to temperate and alpine in the Himalayan north. The presence of the Himalayas and the Thar Desert significantly influences the overall climate. The Himalayas act as a barrier against cold katabatic winds from Central Asia, while the Thar Desert creates arid conditions. The map of India serves as a visual guide, outlining the diverse climatic zones across the country through the informative lens of the Climate Map.
Climate Map of India
Discover India’s diverse climates with our interactive Climate Map. From the lush Tropical Rainforests of Assam to the arid Thar Desert in Rajasthan, each region offers unique landscapes. Explore the Tropical Savannah in Maharashtra or the Mountain Climate in Jammu and Kashmir. Planning a wildlife trip or trekking adventure? Use our Climate Map to tailor your plans based on weather conditions. Experience India’s climate diversity easily with our user-friendly map.
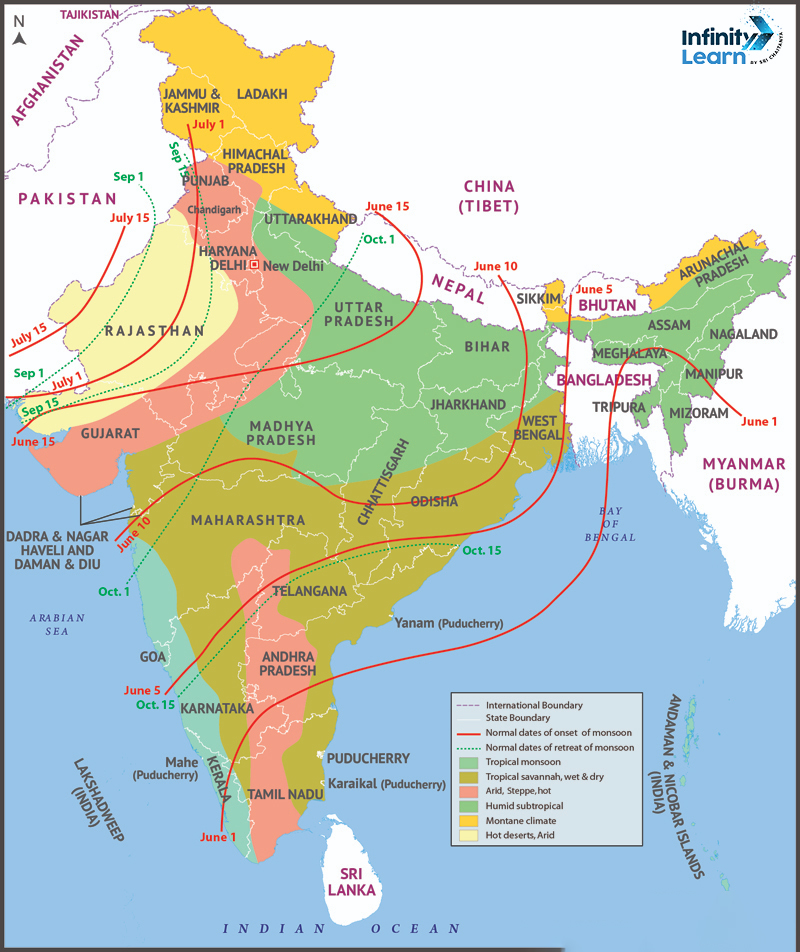
Types of Indian Climatic Regions
The Tropic of Cancer passing through the middle of India adds a tropical dimension to its climate. The classification of Indian Climatic Regions is based on the Koppen climate classification system, resulting in four main groups:
- Tropical Wet (Humid) Climate: It is subdivided into tropical monsoon climate and tropical wet and dry climate. The regions like the Western Ghats, Malabar Coast, and the Andaman Islands experience tropical monsoon climate, characterised by moderate to high temperatures and seasonal heavy rainfall from May to November.
- Tropical Dry Climate: It is further divided into tropical semi-arid (steppe) climate, sub-tropical arid (desert) climate, and sub-tropical semi-arid (steppe) climate. The areas like Karnataka, central Maharashtra, and parts of Tamil Nadu experience the tropical semi-arid (steppe) climate, marked by unreliable rainfall and hot, dry summers.
- Sub-Tropical Humid Climate: It is mainly observed in North and Northeast India. Summers are scorching, and winters can witness temperatures as low as 0°C. The rainfall mainly occurs in the summer, but some areas experience snowfall or occasional rain in winter.
- Mountain Climate: The Himalayas show various climates, ranging from tropical to tundra. The northern side of the western Himalayas, known as the trans-Himalayan belt, is cold, arid, and windswept, receiving less rain on the leeward side and heavy rainfall on well-exposed slopes.
Seasons of India
India typically has four seasons. During these seasons, there are significant temperature fluctuations around the country. The many seasons experienced in India. Their list is as follows:
- Winter (January-February): It begins in different months, with the northwest being cooler than the southeast. Some areas also experience rain.
- Summer/Pre-monsoon (March-June): There are hot conditions, especially in central India, with occasional storms and rain in some regions.
- Rainy/southwest monsoon (July-September): It is vital for agriculture, bringing about 75% of total rainfall. The onset and withdrawal times vary by region.
- Autumn/Post Monsoon (October-December): A transitional season marked by cooler, dry air in central and northern India.
Factors Affecting Indian Climate
Climate change facts underscore the alarming reality of rising global temperatures, melting ice caps, and increasing frequency of extreme weather events. India’s climate is affected by several factors. The factors affecting Indian climate are explained below.
Latitude: India’s climate is significantly impacted by its geographical location. The Tropic of Cancer, cutting through the middle from Mizoram in the east to the Rann of Kutch in the west, plays an essential role. The southern part, situated below the Tropic of Cancer, experiences a tropical climate, while the northern half belongs to the sub-tropical zone. This results in India having a mix of both sub-tropical and tropical climates.
Altitude: The northern region is flanked by mountains with an average height of 6,000 meters. At the same time, the southern part boasts an expansive coastline with a maximum height of approximately 30 meters. The Himalayas act as a natural barrier against cold winds from Central Asia. Therefore, the altitude of these mountains contributes to milder winters in the Indian subcontinent compared to Central Asia.
Monsoon Winds: The dominating influence on India’s climate is the monsoon winds, often referred to as the monsoon climate. The reversal of these winds marks a shift in seasons. It transforms the intense summer into the rainy or monsoon season. The entire country receives rainfall primarily from the southwest summer monsoons originating from the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea.
Western Disturbances and Tropical Cyclones: Large sections of peninsular India are affected by tropical cyclones originating in the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal. While most cyclones emerge from the Bay of Bengal, their impact is felt during the southwest monsoon season.
Additionally, western disturbances originating over the Mediterranean Sea influence weather conditions in the Western Himalayan region. These climatic phenomena play an essential role in shaping India’s weather patterns and seasonal variations.
Climate-Related Calamities
Climate-related disasters are a significant source of loss of life and property. Natural disasters that have occurred in the country include the following:
- Floods: It is common, especially in regions near rivers, with central India experiencing frequent torrential rains and flash floods.
- Droughts: These affect agriculture-dependent regions like Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan, and others due to water scarcity.
- Cyclones: The coastal areas, particularly Odisha, West Bengal, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh, face significant challenges during cyclones. The 1999 Cyclone 05B in Odisha was particularly devastating.
Where to go in India during different seasons?
The climate map of India has various climatic seasons. The climate change depends on the region, and many people want to spend their vacation in different places. The best destinations in India during different seasons are given below in the table.
| Best destinations in India during different seasons | ||
| Season | Ideal Destinations | Additional Information |
| Summer | Hill stations and mountains like Nainital and Manali. National parks for wildlife enthusiasts. | While the majority of the country experiences harsh summer conditions, hill stations and mountainous regions offer a pleasant escape. As the heat intensifies, animals actively seek water, enhancing wildlife sightings. |
| Monsoon | Ladakh and Jammu & Kashmir | The monsoon season can disrupt travel, but it’s an excellent time to explore Ladakh and Jammu & Kashmir in northern India. These regions showcase their beauty during the rainy season. |
| Winter | Seashores in Goa, beaches in Kerala, South India, and Rajasthan for desert landscapes. | Pristine beaches in Goa are famous in winter. Southern parts of India, including the beaches in Kerala, attract more visitors. Rajasthan’s deserts are best experienced in the winter months of December to February. |
Climate Map of India – Climatic Regions of India
India is characterized by several climatic zones of India, as outlined below:
| Climatic zones of India |
||
| Climatic Region | States or Territories | |
| Tropical Rainforest | Assam and parts of the Sahyadri Mountain Range | |
| Tropical Savannah | Sahyadri Mountain Range and parts of Maharashtra | |
| Tropical and subtropical steppe | Parts of Punjab and Gujarat | |
| Tropical Desert | Most parts of Rajasthan | |
| Moist subtropical with winter | Parts of Punjab, Assam, and Rajasthan | |
| Mountain Climate | Parts of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttaranchal | |
| Drought | Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Haryana | |
| Tropical Semi-arid Steppe | Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, and other parts of South India | |
| Discover More About India: Explore Related Articles | |
| Forest Map of India | Soil map of India |
| Map of Bihar | Earthquake Zoning Map of India |
| National River of India | Union Territories of India Map |
| National Bird of India | National Aquatic Animal of India |
| State Animals in India | National Flower of India |
| National Calendar of India | State birds of India |
| National Emblem of India | National Animal of India |
| State Flower Names | National Language of India |
| Lakes in India | Universities in India |
| Map of Himachal Pradesh | Map of Haryana |
Climate Map of India FAQs
What is the climate system of India?
India experiences the Tropical monsoon climate due to its unique position in the Asian continent and the Indian Ocean
How many zones are there in India?
India has six zones, with each state grouped into these zones, and an Advisory Council is established to encourage cooperative working among the states.
How many seasons are there in India?
India has three main seasons: summer, winter, and the rainy season. Additionally, the year is divided into six seasons: Vasant, Krishna, Varsha, Sharad, Hemant, and Shishir








