Table of Contents
Separation of Substances Class 6 Extra Questions Science Chapter 5
Class 6 Science chapter 5 Separation of Substances, covers essential methods and techniques used to separate different components of mixtures. This chapter, included in the CBSE syllabus, provides students with a fundamental understanding of why separation is necessary and how it is achieved through various processes such as handpicking, winnowing, sieving, sedimentation, decantation, filtration, evaporation, and condensation. By mastering these concepts form NCERT textbook and taking help of extra questions, students gain practical knowledge that applies to everyday life and scientific studies.
The class 6 Science chapter 5 Separation of Substances extra question answer are designed to provide additional practice and reinforce students’ understanding of the chapter. These separation of substances class 6 extra questions help ensure thorough comprehension, better retention, and effective exam preparation, allowing students to grasp key concepts and processes involved in the separation of substances.
CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Extra Question Answer
Here are the topics wise NCERT extra questions for Class 6 Science chapter 5 Separation of Substances:
Methods of separation
Question 1: When is handpicking used?
Answer:
Handpicking is used to remove unwanted components when they are present in small amounts.
Question 2: What is threshing? How is it done?
Answer:
Threshing separates grain from stalks by beating the stalks to release the grains. This can be done manually or with machines.
Question 3: Which type of separation is used in cashew nut factories?
Answer:
Sieving.
Question 4: Give one example of sieving used in everyday life.
Answer:
Sieving is used to separate bran from flour.
Question 5: Name some materials that are used as filters.
Answer:
Cotton, ceramic, filter cloth, and filter paper.
Question 6: Name the process of separating two immiscible liquids.
Answer:
Using a separating funnel or decantation.
Question 7: Which substance is used for loading?
Answer:
Alum (phitkari).
Question 8: What is the use of alum in loading?
Answer:
Alum helps the sedimentation process by making clay particles settle faster.
Question 9: Which process is used to separate bacteria from water?
Answer:
Filtration, using bacteria-proof filters.
Question 10: What is decantation?
Answer:
Decantation separates insoluble solids from liquids. The mixture is allowed to stand, the solids settle, and the clear liquid is poured off.
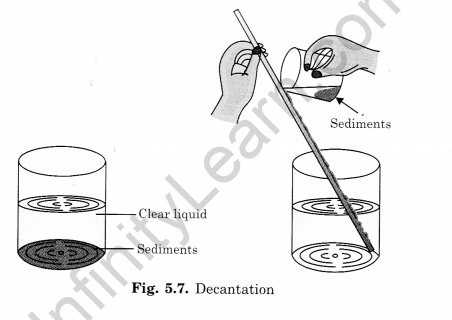
This is called sedimentation. The clean water is transferred into another beaker, without disturbing the settled particles. This type of separation is called decantation (Fig. 5.7).
Question 11: What is the use of decantation?
Answer:
Decantation is used to separate insoluble solids from liquids and to separate two immiscible liquids.
Question 12: What is filtration?
Answer:
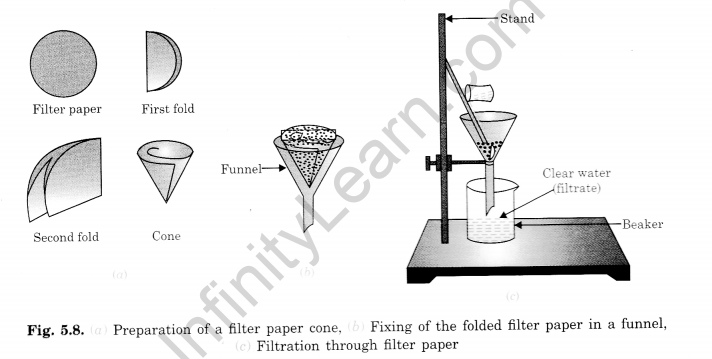
Filtration separates an insoluble substance from a liquid by passing the mixture through filter paper. The solid stays on the paper, and the liquid passes through.
Filtration is a process that separates an insoluble substance from a solution by passing the solution through a porous filter paper. During filtration, the solid insoluble substance stays on the filter paper as residue, while the liquid, free of any suspended particles, passes through and is collected as the filtrate. The filtrate can be heated to evaporate and retrieve any dissolved components. Figures 5.8 (a), (b), and (c) illustrate how to fold and use filter paper in filtration.
Question 13: What is the drawback of evaporation?
Answer:
The main drawback of evaporation is that the liquid component of the mixture is lost to the air and is not recovered. This process only allows the solid component to be collected, while the liquid evaporates and disperses into the atmosphere, making it unavailable for reuse.
Question 14: Name the process to obtain salt from seawater.
Answer:
Salt is obtained from seawater through the process of evaporation. Seawater is collected in shallow ponds and allowed to evaporate naturally under the sun. As the water evaporates, salt crystals are left behind and can be collected.
Question 15: Which types of mixtures are separated by evaporation?
Answer:
Evaporation is used to separate mixtures where a solid is dissolved in a liquid. The liquid component is evaporated, leaving the solid residue behind. This method is commonly used to obtain salt from saltwater or to concentrate solutions by removing the solvent.
Question 16: Describe the method to obtain pure salt from rock salt.
Answer:
To obtain pure salt from rock salt, follow these steps:
- Crush and grind the rock salt into smaller particles.
- Add water to dissolve the salt, creating a salt solution.
- Filter the solution to remove any insoluble impurities.
- Collect the clear salt solution (filtrate).
- Heat the filtrate to evaporate the water.
- As the water evaporates, pure salt crystals are left behind. This process involves dissolving, filtering, and evaporating to separate pure salt from the impurities.
Question 17: How will you separate pure water from a solution of salt in water?
Answer:
Pure water can be separated from a saltwater solution through the process of distillation. This involves two main steps:
- Evaporation: Heat the saltwater solution to convert the water into vapor, leaving the salt behind.
- Condensation: Cool the water vapor in a condenser to turn it back into liquid water, which is collected as pure water.
Question 18: Write the opposite process of condensation.
Answer:
The opposite process of condensation is evaporation. While condensation involves the transformation of a gas into a liquid, evaporation involves the transformation of a liquid into a gas.
Question 19: How is common salt obtained from seawater?
Answer:
Common salt is obtained from seawater through the following steps:
- Seawater is collected in shallow pits and allowed to evaporate naturally under the sun.
- As the water evaporates, it leaves behind impure solid salts.
- These solid salts are crushed into a fine powder.
- The powdered salt is dissolved in water to form a salt solution.
- The solution is filtered to remove insoluble impurities.
- The clear salt solution is heated to evaporate the water.
- As the water evaporates, a concentrated salt solution is left behind.
- The hot, concentrated solution is allowed to cool, leading to the formation of pure salt crystals through crystallization.
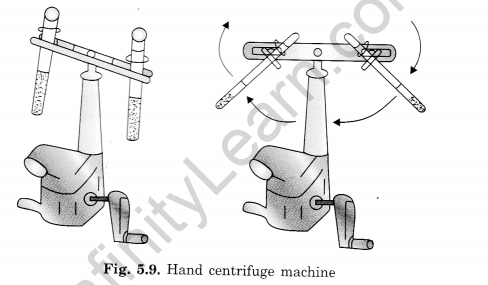
Question 20: What is the importance of centrifugation? How is it done?
Answer:
Centrifugation is important for separating suspended particles from a liquid by spinning the mixture at high speeds. Here’s how it is done:
- The mixture is placed in a centrifuge tube and inserted into a centrifuge machine.
- The machine spins the tube rapidly, causing the heavier particles to move outward and settle at the bottom due to centrifugal force.
- The lighter particles remain at the top.
- This process is useful for separating cream from milk, where the cream (being lighter) collects at the center and floats on top, while the heavier milk remains at the bottom.
Question 21: What do you mean by solubility?
Answer:
Solubility is the maximum amount of a solute that can dissolve in 100 grams of a solvent at a specific temperature. It indicates how much of a substance can be dissolved in a solvent to form a homogeneous solution under certain conditions.
Question 22: Why is water a universal solvent?
Answer:
Water is considered a universal solvent because it can dissolve a wide variety of substances. Its polar nature and ability to form hydrogen bonds with other molecules make it effective in dissolving salts, sugars, acids, bases, and many other compounds.
Question 23: What is the effect of temperature on solubility?
Answer:
The solubility of most substances increases with an increase in temperature. As the temperature rises, the kinetic energy of the molecules increases, allowing more solute particles to dissolve in the solvent.
Question 24: Differentiate between saturated and unsaturated solutions.
Answer:
- Saturated solution: A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at a given temperature. It has reached its maximum capacity for dissolving the solute.
- Unsaturated solution: A solution in which more solute can be dissolved at a given temperature. It has not yet reached its maximum capacity for dissolving the solute.
Question 25: During centrifugation, which particles settle down at the bottom?
Answer:
During centrifugation, the heavier particles settle down at the bottom of the centrifuge tube due to the centrifugal force, while the lighter particles remain at the top.

Question 26: Name the method by which you can separate butter from milk.
Answer:
Butter can be separated from milk using the method of centrifugation.
Question 27: Name the device by which cream can be separated from milk at home.
Answer:
A mixer-grinder can be used to separate cream from milk at home.
Question 28: Why does visibility increase after rains?
Answer:
Visibility increases after rains because rainwater causes fine dust particles in the air to settle down. This process, known as loading, clears the air, making distant objects more visible.
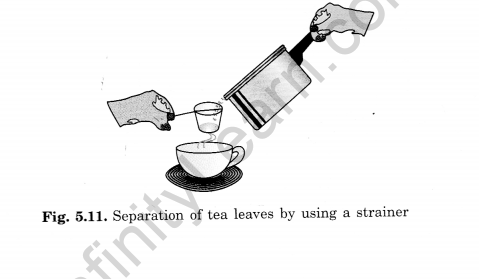
Question 29: What is a strainer?
Answer:
A strainer is a wire mesh used to separate larger particles from liquids. For example, when making tea, a strainer is used to separate the tea leaves from the liquid tea.
Question 30: Name the property of the components used for separating the following mixtures:
- Salt and camphor: Sublimation, because camphor sublimes (changes from solid to gas) when heated, leaving salt behind.
- Wheat and husk: Winnowing, which separates lighter husk from heavier wheat grains using wind or blowing air.
- Iron filings and sawdust: Magnetic separation, since iron filings are magnetic and can be separated using a magnet.
- Coconut oil and water: Decantation, where the two immiscible liquids are allowed to separate and the top layer (coconut oil) is poured off.
Question 31: Mention the methods that can be used for the separation of the following mixtures:
wheat, sugar, and husk
Answer:
- Wheat, sugar, and husk:
- Winnowing: This method can be used to separate husk from the mixture because husk is lighter than wheat and sugar.
- Sieving: Once the husk is removed, wheat and sugar can be separated by sieving due to their different particle sizes.
- Rice, gram, and iron fillings:
- Magnetic Separation: Use a magnet to separate the iron fillings from the mixture.
- Sieving or Handpicking: After removing the iron fillings, rice and gram can be separated either by sieving or handpicking.
- Sand, black gram (urad), and husk:
- Sieving: Sand can be separated from the mixture by sieving.
- Winnowing: The remaining mixture of black gram and husk can be separated by winnowing, as husk is lighter and will be blown away.
Question 32: Write various methods of separation of compounds from their mixture.
Answer:
- Handpicking
- Threshing
- Winnowing
- Sedimentation
- Decantation
- Filtration
- Evaporation
- Condensation
Question 33: How will you separate a mixture of common salt and chalk powder?
Answer:
Common salt and chalk powder can be separated based on their solubility in water:
- Dissolution and Filtration: Add water to the mixture and stir well. Chalk powder, being sparingly soluble, will remain as a residue, while the common salt will dissolve in the water. Filter the mixture using filter paper to separate the chalk powder.
- Evaporation: Heat the filtrate (salt solution) to evaporate the water, leaving behind dry common salt.
Activity 2:
Bring a packet of food grain purchased from a shop to the classroom. Spread the grains on a sheet of paper. You will notice that there are pieces of stone, husks, broken grains, and particles of other grains mixed in. These can be separated by various methods like handpicking, winnowing, and sieving.
Activity 3:
Make a mixture of dry sand and sawdust or powdered dry leaves. Place this mixture on a plate or newspaper. You will observe that the components have different particle sizes, making it difficult to separate them by handpicking. Take the mixture to an open area and tilt the plate or paper slightly. The lighter sawdust will be blown away by the wind, while the heavier sand will fall near the plate.
Activity 4:
Bring a sieve and some flour to the class. Sieve the flour to remove impurities. Next, mix powdered chalk with the flour. You will find that you cannot separate the flour and powdered chalk by sieving because their particles are similar in size.
Activity 5:
Collect some muddy water from a pond or river, or mix soil with water in a glass. Let it stand for half an hour. You will observe that the heavier soil particles settle at the bottom of the glass. This process is called sedimentation.
Activity 6:
Heat a beaker of water until it boils and eventually evaporates, turning into steam and disappearing completely. Next, dissolve two spoons of salt in another beaker of water. The water will turn slightly white, and the salt will dissolve completely. Boil this saltwater solution until all the water evaporates, leaving salt crystals behind in the beaker.

Some salt will be left in the beaker.
Activity 10.
Take two glasses and pour half a cup of water in each of them. Add a teaspoon of salt to one glass and stir till the salt dissolves. Go on adding salt, one teaspoon at a time, till the solution saturates. Record the number of spoons of salt that dissolved in the water, in Table 5.2. Now, repeat the same activity with sugar. Repeat this with some other substances that are soluble in water.
What do you notice from Table 5.2? Do you find that water dissolves different substances in different amounts?
Table 5.2
| Substance | Number of spoons of substance that dissolved in water |
| Salt | 1 spoon of salt in 100 gm water at 25°C |
| Sugar | 4 spoons of sugar in 100 gm water at 25°C |
| Copper sulphate | Nearly 4 spoon of copper sulphate in 100 gm of water at 25°C |
We notice from the table that different substances dissolve in water in different amounts.
- Chapter 1 Food: Where Does It Come From?
- Chapter 2 Components of Food
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups
- Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
- Chapter 6 Changes Around Us
- Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants
- Chapter 8 Body Movements
- Chapter 9 The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings
- Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
- Chapter 11 Light, Shadows, and Reflection
- Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
- Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
- Chapter 14 Water
- Chapter 15 Air Around Us
- Chapter 16 Garbage In, Garbage Out
Separation of Substances Class 6 Objective Type Extra Questions
Question 1. Match the following items given in Column A with that in Column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Handpicking | (i) Conversion of water vapours into liquids |
| (b) Threshing | (ii) Separating bran from flour |
| (c) Winnowing | (iii) Separating larger size impurities |
| (d) Sieving | (iv) Separating butter from milk |
| (e) Sedimentation | (v) Conversion of water into Us vapours |
| (f) Evaporation | (vi) Separating grains from its stalks |
| (g) Condensation | (vii) Settling of heavier components at bottom |
| (h) Churning | (viii) Separation by wind or by blowing air |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Handpicking | (iii) Separating larger size impurities |
| (b) Threshing | (iv) Separating grains from its stalks |
| (c) Winnowing | (viii) Separation by wind or by blowing air |
| (d) Sieving | (ii) Separating bran from flour |
| (e) Sedimentation | (vii) Settling of heavier components at bottom |
| (f) Evaporation | (v) Conversion of water into its vapours |
| (g) Condensation | (i) Conversion of water vapours into liquids |
| (h) Churning | (iv) Separating butter from milk |
Question 2: Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
- Peanuts are separated from a mixture of wheat and peanuts by ____________.
- ____________ is used to separate husk from wheat.
- Fine sand can be separated from larger particles by ____________.
- Glass is a ____________.
- Compounds have ____________ melting points.
- Milk has a ____________ boiling point.
- Boiling point of pure water is ____________ than that of impure water.
- Mixture may be solid, liquid, or ____________.
- Butter is a component of ____________.
- Sugarcane juice is a mixture of ____________, water, and many other substances.
- Separation of components is done to obtain a ____________ substance.
- Components retain their properties in a ____________.
Answer:
- handpicking
- Winnowing
- sieving
- mixture
- fixed
- variable
- lower
- gas
- buttermilk
- sugar
- pure
- mixture
Question 3: State whether the statements given below are True or False:
- Butter is separated from buttermilk by churning.
- Separation of components of a mixture is a useful process.
- Ink loses its properties when mixed in water.
- ‘Sharbat’ is a mixture of sugar and water.
- Rocks are pure substances.
- Milk is a mixture.
- Common salt is a pure substance.
- Mixture has properties different from its components.
- Tap water and pond water are alike.
- Elements are pure substances.
- A pure substance has fixed melting and boiling points.
- Condensation method is used for separating substances which on heating change directly into vapour.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True
- True
- False
Separation of Substances Class 6 Extra Questions MCQ
Choose the correct option in the following questions:
1. Butter is separated from milk by
(a) sedimentation
(b) filtration
(c) churning
(d) decantation
Answer: (c) Butter is separated by churning.
2. Filtration is a method to separate the components of a
(a) solution
(b) mixture of a liquid and an insoluble substance
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) pure substance
Answer: (b) Components of a solution cannot be separated by this method.
3. Threshing is done by
(a) beating
(b) bullocks
(c) machines
(d) all of these
Answer: (d) All three methods can be used for threshing.
4. Which method is used to separate pebbles and stones from sand?
(a) Handpicking
(b) Winnowing
(c) Sieving
(d) Any of these
Answer: (c) Handpicking will take more time, and winnowing is not suitable.
5. The components of a solution (e.g., sugar in water) can be separated by
(a) filtration
(b) evaporation
(c) sedimentation
(d) decantation
Answer: (b) By evaporation, the volatile component is evaporated and then condensed.
6. Sand from water is separated by
(a) sieving
(b) evaporation
(c) filtration
(d) sedimentation and decantation
Answer: (d) It can also be done by evaporation and filtration, but sedimentation and decantation are easier.
7. The process of conversion of water vapors into liquid is called
(a) condensation
(b) decantation
(c) sedimentation
(d) evaporation
Answer: (a) Water vapors changing into liquid is called condensation.
8. The process of conversion of water into its vapors is called
(a) evaporation
(b) condensation
(c) guttation
(d) transpiration
Answer: (a) The conversion of water into vapors is called evaporation.
9. A mixture of ammonium chloride and sand is separated by
(a) evaporation
(b) decantation
(c) sublimation
(d) filtration
Answer: (c) Ammonium chloride is separated by sublimation.
10. The property which forms the basis of sieving
(a) difference in weight
(b) difference in color
(c) difference in shape
(d) difference in size
Answer: (d) Sieving is used for separating solid constituents of a mixture based on their size differences.
| Other Resources for Class 6 | |
| Worksheet for Class 6 All subjects | CBSE Notes Class 6 |
| NCERT Books for Class 6 | Online Tuition for Class 6 |
FAQs on Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Extra Question
What are the Methods of Separation of Substances Class 6?
Methods include handpicking, winnowing, sieving, sedimentation, decantation, and filtration. These techniques help separate different components based on their properties.
Methods include handpicking, winnowing, sieving, sedimentation, decantation, and filtration. These techniques help separate different components based on their properties.
The principle involves utilizing the physical properties of substances like size, weight, and solubility to separate them effectively. Different methods leverage these principles for separation.
Is Separation Physical or Chemical?
Separation is primarily a physical process where substances are separated based on physical properties like size, shape, or state without changing their chemical composition.
How to Separate a Pure Substance?
A pure substance can be obtained by using methods like filtration, evaporation, or distillation to remove impurities and isolate the desired substance in its pure form.
Why is Separation Necessary Class 6?
Separation is necessary to remove harmful or unwanted components from mixtures, ensuring the purity and usability of substances. It helps in obtaining pure substances for various applications.
Separation is necessary to remove harmful or unwanted components from mixtures, ensuring the purity and usability of substances. It helps in obtaining pure substances for various applications.
The main reasons for separation include obtaining pure substances for analysis, research, industrial processes, waste management, resource recovery, food production, and medical applications. Separation ensures the quality and safety of materials.






