Table of Contents
Acetone Formula: Acetone, with the chemical formula C3H6O, is a colourless, volatile liquid that belongs to the ketone functional group. It is one of the most widely used solvents in various industries and has a range of applications. Let’s explore acetone structure, formula, physical properties, and chemical properties in detail.
Acetone Structure and Formula
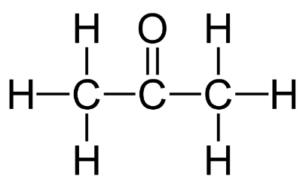
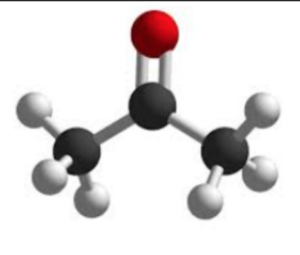
The chemical formula of acetone is C3H6O. It consists of three carbon (C) atoms, six hydrogen (H) atoms, and one oxygen (O) atom. The acetone structure can be represented as follows:
In the structure, the three carbon atoms are bonded to each other in a linear chain. One of the carbon atoms is also bonded to an oxygen atom through a double bond, forming a carbonyl group. The remaining two carbon atoms are bonded to hydrogen atoms.
Physical Properties of Acetone
- State: Acetone is a colourless liquid at room temperature.
- Odour: It has a characteristic sweet, fruity odour.
- Boiling Point: The boiling point of acetone is approximately 56.5 degrees Celsius (133.7 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Melting Point: Acetone has a melting point of around -95 degrees Celsius (-139 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Density: The density of acetone is about 0.79 (g/cm³).
- Solubility: Acetone is highly soluble in water and many organic solvents.
Chemical Properties of Acetone
- Flammability: Acetone is highly flammable and can easily ignite. It has a low flash point and can form explosive mixtures with air.
- Volatility: Acetone is a volatile compound, evaporating rapidly at room temperature.
- Solvent Properties: Acetone is an excellent solvent for many organic compounds, including resins, oils, fats, and waxes. It is widely used as a solvent in various industries, including paints, coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals.
- Reactivity: Acetone can undergo a variety of chemical reactions. It can act as both a nucleophile and an electrophile, participating in addition, condensation, and substitution reactions. It can also undergo oxidation reactions.
- Stability: Acetone is relatively stable under normal conditions. It is not easily oxidized or reduced. However, it is sensitive to prolonged exposure to air and light, which can lead to the formation of peroxides.
Applications of Acetone
- Solvent: Acetone is extensively used as a solvent in numerous industries, including paints, coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals. It effectively dissolves a wide range of substances.
- Nail Polish Remover: Acetone is commonly used as a nail polish remover due to its ability to dissolve and remove nail polish quickly.
- Chemical Intermediary: Acetone serves as an important intermediate compound in the synthesis of various chemicals, including pharmaceuticals, plastics, and fibers.
- Cleaning Agent: Acetone is employed as a cleaning agent for removing grease, oil, and other contaminants from surfaces.
- Extraction Agent: It is used in certain extraction processes to separate and purify compounds.
Solved Examples on Acetone Structure and Formula
Example 1. What is the molecular weight of acetone (C3H6O)?
Solution: To determine the molecular weight of acetone, we need to calculate the sum of the atomic weights of its constituent elements.
The atomic weights are as follows:
C (carbon) = 12.01 g/mol
H (hydrogen) = 1.008 g/mol
O (oxygen) = 16.00 g/mol
Now, let’s calculate the molecular weight:
Molecular weight of acetone = (3 * C) + (6 * H) + O
= (3 * 12.01) + (6 * 1.008) + 16.00
= 58.08 g/mol
Therefore, the molecular weight of acetone (C3H6O) is 58.08 g/mol.
Example 2. How many moles of acetone are present in 250 grams of acetone (C3H6O)?
Solution: To determine the number of moles of acetone, we need to use the molar mass of acetone.
The molar mass of acetone (C3H6O) can be calculated by adding up the atomic masses of its constituent elements:
C (carbon) = 12.01 g/mol
H (hydrogen) = 1.008 g/mol
O (oxygen) = 16.00 g/mol
Molar mass of acetone (C3H6O) = (3 * C) + (6 * H) + O
= (3 * 12.01) + (6 * 1.008) + 16.00
= 58.08 g/mol
Given that the mass of acetone is 250 grams, we can use the molar mass to calculate the number of moles:
Number of moles = Mass / Molar mass
= 250 g / 58.08 g/mol
≈ 4.31 moles
Therefore, there are approximately 4.31 moles of acetone in 250 grams of acetone.
Frequently asked Question on Acetone Formula and Structure
What is the chemical formula of acetone?
The chemical formula of acetone is C3H6O.
How many carbon atoms are present in the formula of acetone?
Acetone contains three carbon C atoms.
What is the molecular weight of acetone?
The molecular weight of acetone is approximately 58.08 grams per mole g/mol.
What are the elements present in the formula of acetone?
The formula of acetone consists of carbon C, hydrogen H, and oxygen O atoms.
Is acetone a flammable substance?
Yes, acetone is highly flammable. It has a low flash point and can form explosive mixtures with air.








