Table of Contents
Calcium phosphate Formula
Calcium phosphate is a calcium salt of phosphoric acid with a chemical formula Ca3(PO4)2. It is also known as Calcium phosphate tribasic or Tricalcium Phosphate.
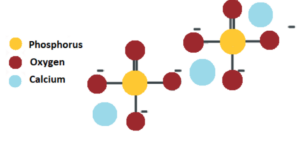
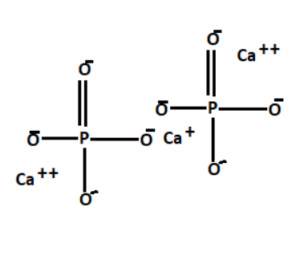
Calcium phosphate
Calcium phosphate appears as a white amorphous or crystalline powder that is odourless and tasteless. It is insoluble in ethanol, and acetic acid but soluble in dilute nitric acid and hydrochloric acid. It slightly dissolves in water. It is found in bones, milk, teeth, and ground.
Formula and Structure of Calcium Phosphate
The formula for hydroxyapatite, the most abundant form of calcium phosphate in the human body, is Ca5(PO4)3(OH). This formula indicates that each unit of hydroxyapatite consists of five calcium ions (Ca2+), three phosphate ions (PO43-), and one hydroxyl group (OH-). The calcium ions are surrounded by phosphate groups in a specific arrangement that gives hydroxyapatite its unique structure.
Chemical Properties of Calcium Phosphate
- Biocompatibility: Calcium phosphate compounds, including hydroxyapatite, are biocompatible, meaning they are compatible with living tissues. This property makes calcium phosphate suitable for applications in biomedicine, such as bone grafts, dental implants, and drug delivery systems.
- Mineralization: Calcium phosphate plays a crucial role in the mineralization of bones and teeth. It serves as a source of calcium and phosphate ions, which are essential for the formation and maintenance of skeletal structures.
- pH Buffering: Calcium phosphate acts as a pH buffer, helping to maintain the pH balance in biological systems. It can absorb and release hydrogen ions, helping to stabilize the acidity or alkalinity of solutions.
Physical Properties of Calcium Phosphate
- Appearance: Calcium phosphate compounds can vary in appearance depending on their specific forms. Hydroxyapatite, for example, is a white, crystalline solid.
- Solubility: The solubility of calcium phosphate compounds depends on their specific composition and conditions. Hydroxyapatite is sparingly soluble in water and insoluble in organic solvents.
- Density: The density of calcium phosphate compounds varies depending on their specific forms and crystalline structures. For hydroxyapatite, the density is typically around 3.16 g/cm³.
- Melting Point: The melting point of calcium phosphate compounds also depends on their specific forms. For hydroxyapatite, the melting point is approximately 1,250°C (2,282°F).
- Crystal Structure: Hydroxyapatite has a complex crystal structure. The calcium ions are arranged in layers, with phosphate groups occupying the space between these layers. This arrangement provides strength and stability to the structure.
Solved Examples on Calcium phosphate Formula
Example 1: Calculate the number of calcium ions (Ca2+) present in 2 moles of hydroxyapatite Ca5(PO4)3(OH).
Solution:
In the formula of hydroxyapatite, the ratio of calcium ions to the entire compound is 5:1. This means that for every 5 calcium ions, there is 1 hydroxyapatite molecule.
Number of moles of hydroxyapatite = 2 moles
Number of moles of calcium ions = (Number of moles of hydroxyapatite) * (Ratio of calcium ions to hydroxyapatite)
= 2 moles * (5/1)
= 10 moles
Therefore, there are 10 moles of calcium ions in 2 moles of hydroxyapatite.
Example 2: What is the mass percentage of phosphate (PO43-) in hydroxyapatite Ca5(PO4)3(OH)?
Solution:
To determine the mass percentage of phosphate, we need to calculate the mass of phosphate in one mole of hydroxyapatite and divide it by the molar mass of hydroxyapatite, then multiply by 100.
The molar mass of phosphate (PO43-) = (1 * atomic mass of phosphorus) + (4 * atomic mass of oxygen)
= (1 * 31.00 g/mol) + (4 * 16.00 g/mol)
= 31.00 g/mol + 64.00 g/mol
= 95.00 g/mol
Mass of phosphate in one mole of hydroxyapatite = (3 * molar mass of phosphate)
= 3 * 95.00 g
= 285.00 g
Molar mass of hydroxyapatite = (5 * atomic mass of calcium) + (3 * molar mass of phosphate) + (atomic mass of oxygen) + (atomic mass of hydrogen)
= (5 * 40.08 g/mol) + (3 * 95.00 g/mol) + 16.00 g/mol + 1.01 g/mol
= 200.40 g/mol + 285.00 g/mol + 16.00 g/mol + 1.01 g/mol
= 502.41 g/mol
Mass percentage of phosphate = (Mass of phosphate / Molar mass of hydroxyapatite) * 100
= (285.00 g / 502.41 g) * 100
≈ 56.70%
Therefore, the mass percentage of phosphate in hydroxyapatite Ca5(PO4)3(OH) is approximately 56.70%.
Frequently Asked Questions on Calcium Phosphate Formula
What is the chemical formula for calcium phosphate?
The chemical formula for calcium phosphate is Ca3(PO4)2, indicating the presence of three calcium atoms, two phosphate groups per unit.
What is the common name for calcium phosphate?
Calcium phosphate is often referred to as bone ash, given its common occurrence in bones and teeth of vertebrate animals.
What is the role of calcium phosphate in the body?
Calcium phosphate is crucial for bone and teeth formation, providing strength and structure. It also plays roles in cell signaling and muscle function.
Is calcium phosphate soluble in water?
Calcium phosphate has very low solubility in water, which is why it precipitates out to form the structural basis of bones and teeth.
What are the applications of calcium phosphate?
Applications of calcium phosphate include its use in fertilizers, food additives, dental products, and as a nutritional supplement for bone health.
What is the formula for calcium phosphate?
The formula for calcium phosphate is Ca3(PO4)2, representing the combination of calcium ions and phosphate ions in the compound.
How is calcium phosphate used?
Calcium phosphate is used in the agricultural, food, and health sectors. It's utilized as a fertilizer, food additive, and in dental and orthopedic applications.
What is calcium phosphate also known as?
Besides being called bone ash, calcium phosphate is also known as tricalcium phosphate, particularly in its use as a food additive or supplement.




