Table of Contents
Oxygen Formula
Oxygen, a colorless and odorless gas, is the very essence that sustains life on Earth. It plays a pivotal role in the respiration of living organisms, from tiny microbes to towering trees and every creature in between. In this blog, we will delve into the significance of oxygen, oxygen formula, exploring its properties, sources, and essential role in the natural world.
Formula and Structure of Oxygen:
The formula for oxygen is O2, indicating that it exists as a diatomic molecule. Each oxygen molecule consists of two oxygen (O) atoms that are covalently bonded together.
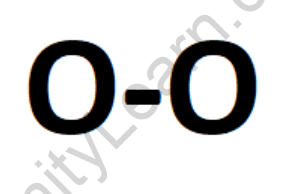
oxygen (O2)
Chemical Properties of Oxygen:
- Reactivity: Oxygen is a highly reactive element. It readily reacts with other elements to form oxides. For example, when oxygen reacts with iron, it forms iron oxide (rust). It also supports combustion, allowing substances to burn in the presence of oxygen.
- Oxidizing Agent: Oxygen acts as a powerful oxidizing agent. It can accept electrons from other substances, causing them to undergo oxidation. This property is essential for many biological and chemical processes.
- Combustion: Oxygen supports combustion, making it necessary for various combustion processes, such as burning fuels. In the presence of oxygen, substances can undergo rapid oxidation, releasing heat and light energy.
Physical Properties of Oxygen:
- State: Oxygen is a gas at standard temperature and pressure. It exists as a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas.
- Density: The density of oxygen gas is approximately 1.43 kg/m³. It is slightly denser than air, which makes it capable of displacing air in closed spaces.
- Boiling and Melting Points: Oxygen has a boiling point of -183°C (-297.4°F) and a melting point of -218.79°C (-361.82°F). These temperatures indicate the phase changes of oxygen from gas to liquid and from liquid to solid, respectively.
- Solubility: Oxygen is sparingly soluble in water. Its solubility increases with decreasing temperature and increasing pressure. This property is essential for the process of oxygen diffusion in aquatic environments.
- Molecular Weight: The molecular weight of oxygen is approximately 32 g/mol. This value represents the average mass of one oxygen molecule, which consists of two oxygen atoms.
Solved Examples on Oxygen Formula:
Example 1: Calculate the total number of electrons in one molecule of oxygen.
Solution:
The formula for oxygen is O2, which means that one molecule of oxygen consists of two oxygen (O) atoms. To calculate the total number of electrons, we need to determine the number of electrons in each oxygen atom and multiply it by 2.
Each oxygen atom has 8 electrons, as it is located in Group 16 of the periodic table. Therefore, the total number of electrons in one molecule of oxygen is:
Number of electrons in one oxygen atom = 8
Total number of electrons in one molecule of oxygen = Number of electrons in one oxygen atom * Number of oxygen atoms
= 8 * 2
= 16
Therefore, there are 16 electrons in one molecule of oxygen.
Example 2: Write the electron configuration of an oxygen atom.
Solution:
The electron configuration of an oxygen atom (O) can be determined by following the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons fill atomic orbitals in order of increasing energy. The electron configuration of oxygen is:
1s2 2s2 2p4
This indicates that oxygen has two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and four electrons in the 2p orbital. The presence of six valence electrons in the outermost energy level gives oxygen its reactivity and bonding behavior.
Note: The electron configuration of an oxygen molecule (O2) is the same as that of an oxygen atom, as both consist of two oxygen atoms with the same electronic structure.
Frequently asked Questions on Oxygen Formula
The chemical formula of oxygen is O2. This indicates that each molecule of oxygen consists of two oxygen (O) atoms bonded together.
Oxygen is a gas at room temperature. It exists as a colorless and odorless gas in its standard state. However, under extremely low temperatures and high pressures, oxygen can condense into a pale blue liquid or solid.
Oxygen supports combustion by acting as an oxidizing agent. It readily reacts with other substances, such as fuels, enabling them to burn. In a combustion reaction, oxygen combines with the fuel, releasing energy in the form of heat and light.
Yes, oxygen is commonly used for medical purposes. It is often administered to patients who have difficulty breathing or require respiratory support. Oxygen therapy provides supplemental oxygen to increase the oxygen levels in the body, aiding in respiration.
Oxygen plays a vital role in the process of respiration. In aerobic respiration, oxygen is used by living organisms to break down glucose and release energy. Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, facilitating the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of cells. What is the chemical formula of oxygen?
Is oxygen a gas, liquid, or solid at room temperature?
How does oxygen support combustion?
Can oxygen be used for medical purposes?
What is the role of oxygen in the process of respiration?






