Table of Contents
Tartaric acid is a dicarboxylic acid with the chemical formula C4H6O6. Here are some notes on tartaric acid, including its formula, structure, and chemical and physical properties:
Formula and Structure of Tartaric acid:
The formula for tartaric acid is C4H6O6. It contains four carbon atoms (C), six hydrogen atoms (H), and six oxygen atoms (O). Tartaric acid is a dicarboxylic acid, which means it has two carboxylic acid functional groups (–COOH).
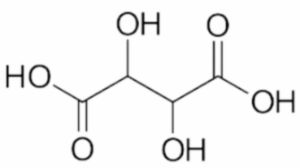
Chemical Properties of Tartaric acid:
- Acidic Nature: Tartaric acid is a weak organic acid. It can donate two hydrogen ions (H+) from its carboxylic acid groups in aqueous solutions, making it a diprotic acid.
- Chirality: Tartaric acid is a chiral compound, meaning it has stereoisomers. It has two chiral centers and can exist as four different stereoisomers: D-tartaric acid, L-tartaric acid, meso-tartaric acid, and DL-tartaric acid.
- Reactivity: Tartaric acid can participate in various chemical reactions due to the presence of carboxylic acid groups. It can undergo esterification, oxidation, and reduction reactions. It can also form salts, such as potassium bitartrate, commonly known as cream of tartar.
Physical Properties of Tartaric acid:
- Appearance: Tartaric acid is a white crystalline solid. It can occur as either colorless crystals or a fine powder.
- Solubility: Tartaric acid is highly soluble in water. It forms clear solutions when dissolved in water, and its solubility increases with temperature.
- Melting and Boiling Points: The melting point of tartaric acid is approximately 170-172°C (338-342°F). It decomposes upon further heating without boiling.
- Taste: Tartaric acid has a sour taste. It is often used as a flavoring agent in food and beverages due to its acidulant properties.
- Optical Activity: D-tartaric acid and L-tartaric acid are optically active isomers and can rotate the plane of polarized light in opposite directions. Meso-tartaric acid, which has an internal plane of symmetry, does not exhibit optical activity.
Applications of Tartaric acid:
Tartaric acid has several applications in various industries, including:
– Food and Beverage Industry: It is used as an acidulant, flavoring agent, and pH regulator in food and beverages, such as soft drinks, candies, and wines.
– Pharmaceutical Industry: Tartaric acid is used in the production of medicines, particularly in the formulation of effervescent tablets and as a chelating agent.
– Chemical Industry: It is utilized in the synthesis of other chemicals, such as tartarates, which are used as additives in various industries.
Solved Examples on Tartaric acid Formula
Example 1: Calculate the molar mass of tartaric acid.
Solution:
To calculate the molar mass of tartaric acid, we need to find the atomic masses of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) from the periodic table and multiply them by the respective number of atoms present in the formula.
Atomic mass of carbon (C) = 12.01 g/mol
Atomic mass of hydrogen (H) = 1.008 g/mol
Atomic mass of oxygen (O) = 16.00 g/mol
Molar mass of tartaric acid = (4 × atomic mass of carbon) + (6 × atomic mass of hydrogen) + (6 × atomic mass of oxygen)
= (4 × 12.01 g/mol) + (6 × 1.008 g/mol) + (6 × 16.00 g/mol)
= 88.08 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of tartaric acid is 88.08 g/mol.
Example 2: Determine the number of moles of tartaric acid in a 25 g sample.
Solution:
To calculate the number of moles, we need to divide the mass of the sample by the molar mass of tartaric acid.
Mass of the sample = 25 g
Molar mass of tartaric acid = 88.08 g/mol
Number of moles = Mass of the sample / Molar mass of tartaric acid
= 25 g / 88.08 g/mol
≈ 0.284 mol
Therefore, there are approximately 0.284 moles of tartaric acid in a 25 g sample.
Frequently asked questions on Tartaric acid Formula:
1: Is tartaric acid an organic or inorganic compound?
Answer: Tartaric acid is an organic compound. It belongs to the class of compounds known as dicarboxylic acids, which are organic acids containing two carboxylic acid groups.
2: What is the structure of tartaric acid?
Answer: Tartaric acid has a unique structure due to the presence of chiral centers. It exists as four stereoisomers: D-tartaric acid, L-tartaric acid, meso-tartaric acid, and DL-tartaric acid. These isomers have different spatial arrangements of the atoms, resulting in different physical and chemical properties.
3: How is tartaric acid synthesized?
Answer: Tartaric acid can be synthesized through various methods, including the isolation from natural sources like grapes or other fruits, or through chemical synthesis from other starting materials. One common method involves the oxidation of natural tartaric acid salts, such as potassium bitartrate, with a strong oxidizing agent.
4: What are the uses of tartaric acid?
Answer: Tartaric acid has several applications in different industries. It is commonly used as an acidulant and flavoring agent in the food and beverage industry. It is also used in the pharmaceutical industry for the formulation of medicines and in the chemical industry for the synthesis of various compounds.
5: Is tartaric acid safe for consumption?
Answer: Tartaric acid is generally recognized as safe for consumption when used in appropriate amounts. It is a naturally occurring acid found in many fruits and is commonly used in food and beverage products. However, excessive intake may cause digestive discomfort in some individuals. It is always advisable to follow recommended dosage guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional if any concerns arise.






