Table of Contents
Citric acid is a versatile organic compound widely used in various industries and applications. Its chemical formula is C6H8O7, indicating that it contains six carbon (C) atoms, eight hydrogen (H) atoms, and seven oxygen (O) atoms. In this note, we will explore the formula and structure of citric acid, as well as its chemical and physical properties.
Formula and Structure of Citric Acid
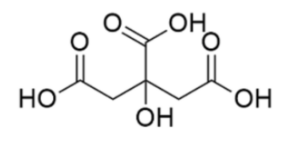
The formula C6H8O7 represents citric acid, a weak organic acid. It belongs to the carboxylic acid family. The structure of citric acid consists of a cyclic structure known as a tricarboxylic acid. It contains three carboxylic acid functional groups (COOH), which contribute to its acidity. The cyclic structure provides citric acid with its distinct properties and functionality.
Citric Acid Chemical Properties
- Acidity: Citric acid is a weak acid, meaning it partially dissociates in water to release hydrogen ions (H+). The presence of three carboxylic acid groups contributes to its acidity. Citric acid is commonly used as a flavoring and acidifying agent in food and beverages due to its sour taste.
- Chelating Agent: Citric acid acts as an effective chelating agent. It forms complexes with metal ions, such as calcium, magnesium, and iron. This property makes it useful in various applications, including food preservation, cleaning agents, and the pharmaceutical industry.
- Buffering Capacity: Citric acid has buffering capacity, which means it can resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. This property makes it valuable in pharmaceutical formulations and the preparation of certain food and beverage products.
- Redox Reactions: Citric acid can participate in redox reactions, acting as both an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent. It can donate or accept electrons, depending on the reaction conditions.
Citric Acid Physical Properties
- Appearance: Citric acid occurs as a white crystalline powder or granules. It has a tart taste and is soluble in water.
- Melting Point: The melting point of citric acid is approximately 153-154 degrees Celsius (307-309 degrees Fahrenheit). Upon heating, it can undergo thermal decomposition.
- Solubility: Citric acid is highly soluble in water. The solubility increases with temperature. It is also soluble in ethanol but less soluble in nonpolar solvents.
- Hygroscopicity: Citric acid exhibits hygroscopic properties, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the surrounding environment. This property can lead to clumping or caking of the powder in humid conditions.
- Stability: Citric acid is relatively stable under normal conditions. However, it may undergo degradation when exposed to high temperatures, light, or prolonged storage.
Solved Examples on Citric acid Formula
Example 1: Calculate the molar mass of citric acid (C6H8O7).
Solution: To calculate the molar mass of citric acid, we need to determine the atomic masses of each element present and multiply them by their respective subscripts in the formula.
Atomic mass of carbon (C) = 12.01 g/mol
Atomic mass of hydrogen (H) = 1.01 g/mol
Atomic mass of oxygen (O) = 16.00 g/mol
Molar mass of C6H8O7 = (6 * atomic mass of C) + (8 * atomic mass of H) + (7 * atomic mass of O)
= (6 * 12.01 g/mol) + (8 * 1.01 g/mol) + (7 * 16.00 g/mol)
= 72.06 g/mol + 8.08 g/mol + 112.00 g/mol
= 192.14 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of citric acid (C6H8O7) is 192.14 g/mol.
Example 2: How many moles of citric acid are present in 250 grams of C6H8O7?
Solution: To determine the number of moles of citric acid, we need to divide the given mass by the molar mass of C6H8O7.
Molar mass of C6H8O7= 192.14 g/mol (calculated in Example 1)
Number of moles = Mass (g) / Molar mass (g/mol)
= 250 g / 192.14 g/mol
≈ 1.30 mol (rounded to two decimal places)
Therefore, there are approximately 1.30 moles of citric acid in 250 grams of C6H8O7.
Frequently asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the chemical formula of citric acid?
The chemical formula of citric acid is C6H8O7. It indicates that each molecule of citric acid contains six carbon C atoms, eight hydrogen H atoms, and seven oxygen O atoms.
What is the systematic name of citric acid?
The systematic name of citric acid is 2 hydroxypropane 1,2,3 tricarboxylic acid. It is named based on its chemical structure, indicating the presence of hydroxy, carboxylic acid, and propane functional groups.
What is the molar mass of citric acid?
The molar mass of citric acid is approximately 192.14 grams per mole g/mol. It is calculated by adding up the atomic masses of the constituent elements according to their respective subscripts in the formula.
What is the structure of citric acid?
Citric acid has a cyclic structure known as a tricarboxylic acid. It contains three carboxylic acid functional groups COOH attached to a central carbon atom, along with hydroxyl OH groups. The cyclic structure plays a crucial role in its chemical properties and reactivity.
What are the uses of citric acid?
Citric acid has various applications in industries and daily life. It is commonly used as a food and beverage additive, acting as a flavoring agent, acidulant, and preservative. Citric acid is also employed in the pharmaceutical industry, cleaning products, cosmetics, and as a chelating agent in certain processes. Additionally, it serves as a pH buffer and plays a role in the citric acid cycle, a vital metabolic pathway in organisms.






