Table of Contents
Lead Nitrate Formula
Lead nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Pb(NO₃)₂. It is a white crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. Lead nitrate is composed of one lead ion (Pb²⁺) and two nitrate ions (NO₃⁻). It is commonly used in various applications, including pyrotechnics, matches, laboratory research, PVC stabilization, and the production of dyes, pigments, and catalysts.
Formula of Lead Nitrate : Pb(NO₃)₂
The formula of lead nitrate, Pb(NO₃)₂, provides information about the composition and arrangement of atoms in the compound. Here is an explanation of each component of the formula:
– Pb: This symbol represents the chemical element lead. It is an atomic symbol derived from the Latin word “plumbum” (Pb). Lead is a heavy metal with a grayish color and is commonly used in various industrial applications.
– (NO₃)₂: This indicates the presence of two nitrate ions in the compound. The nitrate ion (NO₃⁻) consists of one nitrogen atom (N) bonded to three oxygen atoms (O). The brackets and subscript “2” outside the parentheses indicate that there are two nitrate ions in the compound.
Formula of Lead Nitrate: Structure
In the structure, the lead ion (Pb²⁺) is surrounded by two nitrate ions (NO₃⁻). Each nitrate ion is composed of one nitrogen atom (N) bonded to three oxygen atoms (O) through covalent bonds. The nitrate ions are negatively charged, balancing the positive charge of the lead ion to form the electrically neutral compound lead nitrate (Pb(NO₃)₂).
The structure of lead nitrate can be represented as follows:
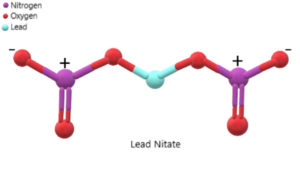
It is important to note that the structure shown represents the arrangement of atoms and bonds in lead nitrate, but it does not indicate the actual three-dimensional shape or orientation of the compound.
Formula of Lead Nitrate: Physical Properties
- Appearance: Lead nitrate is a white crystalline solid.
- Melting Point: It has a melting point of 470°C (878°F).
- Density: The density of lead nitrate is approximately 4.53 g/cm³.
- Solubility: It is highly soluble in water and slightly soluble in ethanol.
- Molecular Weight: 331.21 g/mol
Also Check: Zinc Nitrate Formula
Formula of Lead Nitrate: Chemical Properties
- Decomposition: Upon heating, lead nitrate decomposes to release nitrogen dioxide (NO₂), oxygen (O₂), and lead oxide (PbO).
- Oxidizing Agent: Lead nitrate is an oxidizing agent and can react with reducing agents to undergo redox reactions.
- Toxicity: Lead nitrate is toxic and poses health hazards if ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin. It is harmful to human health and the environment.
Uses of Lead Nitrate
- Pyrotechnics: Lead nitrate is commonly used in fireworks and pyrotechnic devices to produce a bright white light.
- Matches: It has been used historically in the production of matches, although this use has been significantly reduced due to safety concerns.
- Laboratory Applications: Lead nitrate finds applications in laboratories for analytical and research purposes.
- PVC Stabilizer: It is used as a heat stabilizer in the production of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) to prevent degradation of the polymer during processing and use.
- Other Uses: Lead nitrate is also utilized in the production of dyes, pigments, and certain catalysts.
Solved examples of Lead Nitrate Formula
Example 1: Calculate the molar mass of lead nitrate (Pb(NO₃)₂).
Solution:
– Molar mass of lead (Pb) = 207.2 g/mol
– Molar mass of nitrogen (N) = 14.0 g/mol
– Molar mass of oxygen (O) = 16.0 g/mol
– Number of nitrate ions in the formula = 2
– Molar mass of lead nitrate = (207.2 + 2 * (14.0 + 3 * 16.0)) g/mol
= 331.2 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of lead nitrate is 331.2 g/mol.
Example 2: How many moles of lead ions (Pb²⁺) are present in 5 grams of lead nitrate?
Solution:
– Molar mass of lead nitrate (Pb(NO₃)₂) = 331.2 g/mol
– Number of moles = Mass / Molar mass
= 5 g / 331.2 g/mol
≈ 0.0151 mol
Therefore, there are approximately 0.0151 moles of lead ions (Pb²⁺) in 5 grams of lead nitrate.
Example 3: What is the percent composition of nitrogen (N) in lead nitrate?
Solution:
– Molar mass of nitrogen (N) = 14.0 g/mol
– Molar mass of lead nitrate (Pb(NO₃)₂) = 331.2 g/mol
– Total molar mass of nitrogen in the formula = 2 * (14.0 g/mol)
– Percent composition = (Total molar mass of nitrogen / Molar mass of lead nitrate) * 100
= (2 * 14.0 g/mol / 331.2 g/mol) * 100
≈ 8.43%
Therefore, the percent composition of nitrogen (N) in lead nitrate is approximately 8.43%.
Related Links:
| Silver Chloride Formula |
| Nitrogen Dioxide Formula |
| Potassium Nitrate Formula |
| Ammonium nitrate formula |
| Magnesium Chloride Formula |
| Urea Formula |
FAQs on Lead Nitrate Formula
The chemical formula for lead nitrate, a type of inorganic compound, is Pb(NO3)2. This substance usually appears as colorless crystals or white powder and dissolves in water, unlike many other lead(II) salts.
Lead nitrate is a white or colorless solid with a sand-like texture. It is employed in the production of matches and specific types of explosives. Additionally, it finds use in the dye and photography sectors, and in process engraving.
Lead(II) nitrate is one of the rare lead salts that can dissolve in water. When dissolved, it typically has a pH ranging from 3 to 4.
When heated, lead nitrate undergoes a chemical breakdown to produce a yellow residue of lead oxide, brown nitrogen dioxide gas, and oxygen. The reaction is expressed as: 2Pb(NO3)2 (solid) —heat→ 2PbO (solid) + 4NO2 (gas) + O2 (gas) What is the formula for lead nitrate?
What are the uses of lead nitrate?
What is the pH level of lead nitrate?
Does lead nitrate burn?








