Table of Contents
SODIUM OXIDE FORMULA
Sodium oxide (Na2O) is a chemical compound composed of sodium (Na) and oxygen (O) atoms. The chemical formula of sodium oxide is Na2O, indicating that it contains two sodium ions (Na+) and one oxide ion (O2-). The subscript numbers in the formula indicate the ratio of the ions present in the compound.
Explanation: Sodium oxide is formed through the combination of sodium and oxygen atoms. The sodium atom donates one electron to the oxygen atom, resulting in the formation of two sodium ions (Na+) and one oxide ion (O2-). The ionic bonding between the oppositely charged ions holds the compound together.
Structural Formula: The structural formula of sodium oxide represents the arrangement of atoms within the compound. However, since sodium oxide is an ionic compound, it does not have a distinct structural formula like covalent compounds. Instead, it is represented by a formula unit that shows the ratio of sodium ions to oxide ions.
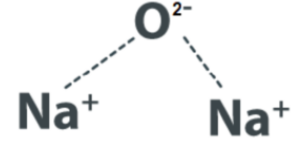
In the solid state, sodium oxide forms a crystal lattice structure where sodium ions and oxide ions are arranged in a repeating pattern. The arrangement of ions in the crystal lattice allows for the compound’s stability and characteristic properties.
Sodium oxide is an important compound used in various applications. It is commonly employed in the glass and ceramics industry as a flux, helping to lower the melting point of the materials being used. It is also used in the production of sodium hydroxide, an essential industrial chemical. Sodium oxide has other specialized uses, such as in the production of catalysts and as a desiccant to absorb moisture.
It’s important to note that sodium oxide is a highly reactive compound and should be handled with care. Direct contact with skin or eyes can cause irritation, and inhalation of its dust or fumes can be harmful. When using sodium oxide, appropriate safety precautions and protective equipment should be used to ensure safe handling.
Also read: SODIUM HYDROXIDE FORMULA
Physical Properties of Sodium Oxide:
- State: Sodium oxide is typically encountered as a solid substance at room temperature and pressure. It appears as a white or yellowish powder.
- Melting and Boiling Points: Sodium oxide has a high melting point of approximately 1,132°C (2,070°F). However, it does not have a well-defined boiling point since it decomposes before reaching the boiling point.
- Solubility: Sodium oxide is highly soluble in water, undergoing a vigorous exothermic reaction. It reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide (NaOH), releasing heat in the process.
- Crystal Structure: Sodium oxide adopts a crystal lattice structure in its solid state. The exact crystal structure depends on the conditions of formation, such as temperature and pressure. It typically forms a cubic crystal lattice.
- Conductivity: Sodium oxide is an ionic compound and, as a solid, does not conduct electricity. However, when dissolved in water, it dissociates into sodium ions (Na+) and oxide ions (O2-), allowing it to conduct electricity.
- Appearance: Sodium oxide appears as a white or yellowish powder. It does not have a distinct odour.
Chemical Properties of Sodium Oxide:
Sodium oxide (Na2O) exhibits various chemical properties due to the interaction of its sodium and oxide ions. Here are some important chemical properties of sodium oxide:
- Reactivity with Water: Sodium oxide reacts vigorously with water to form sodium hydroxide (NaOH). This reaction is highly exothermic, releasing heat. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
Na2O + H2O → 2NaOH - Basicity: Sodium oxide is a basic oxide because it reacts with water to form a strong alkali, sodium hydroxide. It readily accepts protons (H+) from water molecules, leading to the formation of hydroxide ions (OH–) and releasing hydroxide ions into the solution.
- Reactivity with Acids: Sodium oxide reacts with acids to form salts and water. The oxide ion in sodium oxide acts as a base, neutralizing the acidic properties of the acid. The general equation for this reaction is:
Na2O + 2HX → 2NaX + H2O (where X represents the anion of the acid) - Redox Reactions: Sodium oxide can undergo redox reactions, particularly when exposed to strong oxidizing or reducing agents. It can donate or accept electrons, depending on the reaction conditions.
- Stability: Sodium oxide is relatively stable under normal conditions. However, it can decompose at very high temperatures, releasing oxygen gas (O2). The decomposition reaction is:
2Na2O → 4Na + O2 - Reactivity with Carbon Dioxide: Sodium oxide reacts with carbon dioxide (CO2) to form sodium carbonate (Na2CO3). This reaction is often utilized in industrial processes for the removal of carbon dioxide from gases.
Na2O + CO2 → Na2CO3 - Interaction with Oxidizing Agents: Sodium oxide can act as a reducing agent when in the presence of strong oxidizing agents. It can donate electrons to oxidizing agents, reducing them in the process.
Solved Examples on Sodium oxide Formula:
Example 1: Calculation of Molar Mass
Calculate the molar mass of sodium oxide (Na2O).
The molar mass of sodium is 22.99 g/mol, and the molar mass of oxygen is 16.00 g/mol.
To calculate the molar mass of sodium oxide (Na2O), we add the molar masses of two sodium atoms and one oxygen atom.
Molar Mass = (Number of sodium atoms × Molar mass of sodium) + (Number of oxygen atoms × Molar mass of oxygen)
Molar Mass = (2 × 22.99 g/mol) + (1 × 16.00 g/mol)
Molar Mass = 45.98 g/mol + 16.00 g/mol
Molar Mass = 61.98 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of sodium oxide (Na2O) is 61.98 g/mol.
Example 2: Stoichiometry in a Reaction
Sodium oxide (Na2O) reacts with water (H2O) to form sodium hydroxide (NaOH). If you mix 10 grams of sodium oxide with excess water, what is the theoretical yield of sodium hydroxide?
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:
Na2O + H2O → 2NaOH
According to the stoichiometry of the balanced equation, 1 mole of sodium oxide reacts with 1 mole of water to produce 2 moles of sodium hydroxide.
First, we calculate the number of moles of sodium oxide using its molar mass:
Moles of Na2O = (Mass of Na2O ÷ Molar mass of Na2O)
= (10 g ÷ 61.98 g/mol) = 0.161 moles
Since the ratio of moles of sodium oxide to moles of sodium hydroxide is 1:2, the number of moles of sodium hydroxide produced is:
Moles of NaOH = (2 × Moles of Na2O) = (2 × 0.161 moles)
= 0.322 moles
Finally, we convert the moles of sodium hydroxide to grams using its molar mass:
Mass of NaOH = (Moles of NaOH × Molar mass of NaOH) = (0.322 moles × 40.00 g/mol)
= 12.88 grams
Therefore, the theoretical yield of sodium hydroxide in the reaction is 12.88 grams.
Also read: Sulfur Dioxide Formula
Frequently asked Questions (FAQs) on Sodium Oxide Formula
Sodium oxide is not corrosive on its own. However, when it reacts with water, it forms sodium hydroxide, which is a strong alkaline and caustic substance. Sodium hydroxide can be corrosive and can cause skin and eye irritation. Proper precautions should be taken when handling sodium oxide or its aqueous solutions.
Sodium oxide is commonly used in the production of glass. It acts as a flux, reducing the melting temperature of silica (silicon dioxide) and other components in the glass mixture. This helps to facilitate the melting and shaping of glass during the manufacturing process.
When handling sodium oxide, it is important to wear appropriate protective equipment, such as gloves and safety goggles, to avoid contact with the skin and eyes. Proper ventilation should be ensured to avoid inhalation of dust or fumes. In case of skin or eye contact, rinse thoroughly with water and seek medical attention if necessary.
Sodium oxide should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from moisture and incompatible substances. It should be kept in a tightly sealed container to prevent absorption of moisture from the air. Additionally, it should be stored away from sources of heat, flames, and oxidizing agents. Is sodium oxide corrosive?
What is the role of sodium oxide in glass production?
What safety precautions should be taken when handling sodium oxide?
How should sodium oxide be stored?






